Jonathan Zhang
DYCP: Dynamic Context Pruning for Long-Form Dialogue with LLMs
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often exhibit increased response latency and degraded answer quality as dialogue length grows, making effective context management essential. However, existing methods rely on extra LLM calls to build memory or perform offline memory construction without considering the current user utterance, which can introduce inefficiencies or disrupt conversational continuity. We introduce DyCP, a lightweight context management method that dynamically segment and retrieve relevant memory at query time. It preserves the sequential structure of dialogue without predefined topic boundaries and supports efficient, adaptive context retrieval. Across three long-form dialogue benchmarks, LoCoMo, MT-Bench+, and SCM4LLMs, and multiple LLMs, DyCP consistently improves answer quality while reducing response latency. We also examine the gap between modern LLMs' expanded context windows and their actual long-context processing capacity, highlighting the continued importance of effective context management.
Reasoning Relay: Evaluating Stability and Interchangeability of Large Language Models in Mathematical Reasoning
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has significantly advanced the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). While prior work focuses on improving model performance through internal reasoning strategies, little is known about the interchangeability of reasoning across different models. In this work, we explore whether a partially completed reasoning chain from one model can be reliably continued by another model, either within the same model family or across families. We achieve this by assessing the sufficiency of intermediate reasoning traces as transferable scaffolds for logical coherence and final answer accuracy. We interpret this interchangeability as a means of examining inference-time trustworthiness, probing whether reasoning remains both coherent and reliable under model substitution. Using token-level log-probability thresholds to truncate reasoning at early, mid, and late stages from our baseline models, Gemma-3-4B-IT and LLaMA-3.1-70B-Instruct, we conduct continuation experiments with Gemma-3-1B-IT and LLaMA-3.1-8B-Instruct to test intra-family and cross-family behaviors. Our evaluation pipeline leverages truncation thresholds with a Process Reward Model (PRM), providing a reproducible framework for assessing reasoning stability via model interchange. Evaluations with a PRM reveal that hybrid reasoning chains often preserve, and in some cases even improve, final accuracy and logical structure. Our findings point towards interchangeability as an emerging behavioral property of reasoning models, offering insights into new paradigms for reliable modular reasoning in collaborative AI systems.
PLANET: A Collection of Benchmarks for Evaluating LLMs' Planning Capabilities
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Planning is central to agents and agentic AI. The ability to plan, e.g., creating travel itineraries within a budget, holds immense potential in both scientific and commercial contexts. Moreover, optimal plans tend to require fewer resources compared to ad-hoc methods. To date, a comprehensive understanding of existing planning benchmarks appears to be lacking. Without it, comparing planning algorithms' performance across domains or selecting suitable algorithms for new scenarios remains challenging. In this paper, we examine a range of planning benchmarks to identify commonly used testbeds for algorithm development and highlight potential gaps. These benchmarks are categorized into embodied environments, web navigation, scheduling, games and puzzles, and everyday task automation. Our study recommends the most appropriate benchmarks for various algorithms and offers insights to guide future benchmark development.
LASP: Surveying the State-of-the-Art in Large Language Model-Assisted AI Planning
Sep 03, 2024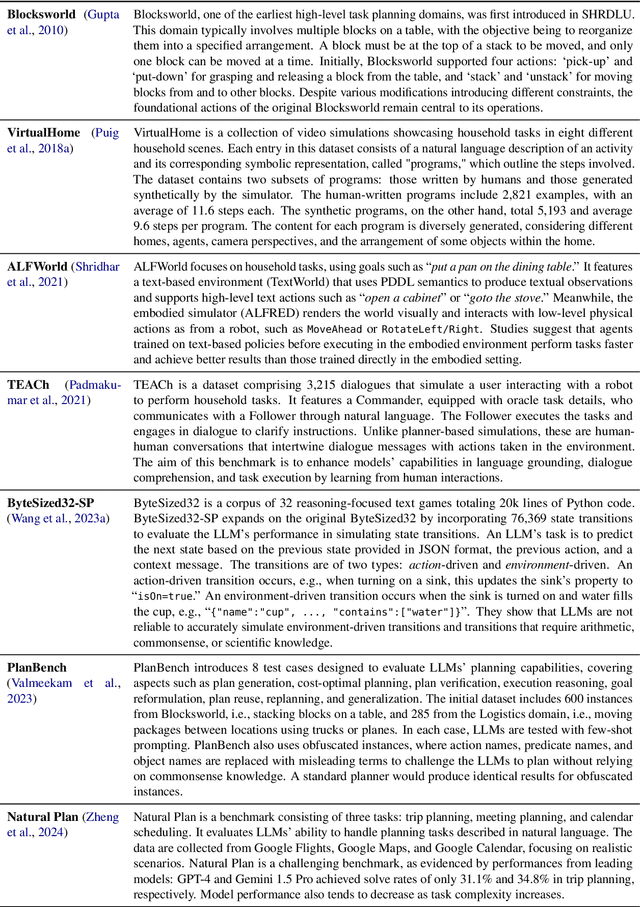
Abstract:Effective planning is essential for the success of any task, from organizing a vacation to routing autonomous vehicles and developing corporate strategies. It involves setting goals, formulating plans, and allocating resources to achieve them. LLMs are particularly well-suited for automated planning due to their strong capabilities in commonsense reasoning. They can deduce a sequence of actions needed to achieve a goal from a given state and identify an effective course of action. However, it is frequently observed that plans generated through direct prompting often fail upon execution. Our survey aims to highlight the existing challenges in planning with language models, focusing on key areas such as embodied environments, optimal scheduling, competitive and cooperative games, task decomposition, reasoning, and planning. Through this study, we explore how LLMs transform AI planning and provide unique insights into the future of LM-assisted planning.
Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Severity in Fundus Images with DenseNet121 and ResNet50
Aug 19, 2021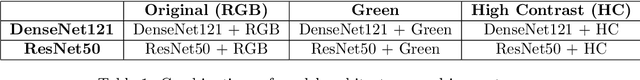
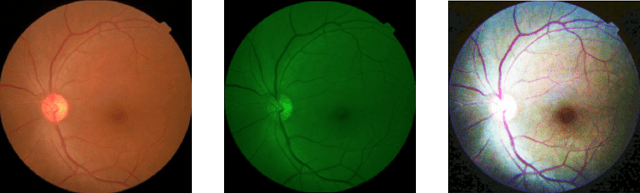
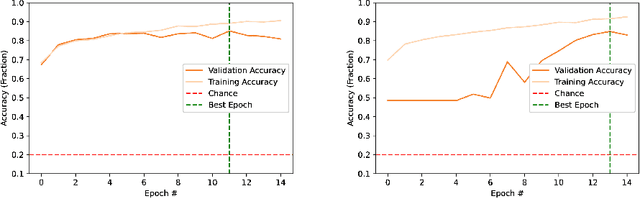

Abstract:In this work, deep learning algorithms are used to classify fundus images in terms of diabetic retinopathy severity. Six different combinations of two model architectures, the Dense Convolutional Network-121 and the Residual Neural Network-50 and three image types, RGB, Green, and High Contrast, were tested to find the highest performing combination. We achieved an average validation loss of 0.17 and a max validation accuracy of 85 percent. By testing out multiple combinations, certain combinations of parameters performed better than others, though minimal variance was found overall. Green filtration was shown to perform the poorest, while amplified contrast appeared to have a negligible effect in comparison to RGB analysis. ResNet50 proved to be less of a robust model as opposed to DenseNet121.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge