John Hood
Near-Universal Multiplicative Updates for Nonnegative Einsum Factorization
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Despite the ubiquity of multiway data across scientific domains, there are few user-friendly tools that fit tailored nonnegative tensor factorizations. Researchers may use gradient-based automatic differentiation (which often struggles in nonnegative settings), choose between a limited set of methods with mature implementations, or implement their own model from scratch. As an alternative, we introduce NNEinFact, an einsum-based multiplicative update algorithm that fits any nonnegative tensor factorization expressible as a tensor contraction by minimizing one of many user-specified loss functions (including the $(α,β)$-divergence). To use NNEinFact, the researcher simply specifies their model with a string. NNEinFact converges to a local minimum of the loss, supports missing data, and fits to tensors with hundreds of millions of entries in seconds. Empirically, NNEinFact fits custom models which outperform standard ones in heldout prediction tasks on real-world tensor data by over $37\%$ and attains less than half the test loss of gradient-based methods while converging up to 90 times faster.
Broad Spectrum Structure Discovery in Large-Scale Higher-Order Networks
May 27, 2025Abstract:Complex systems are often driven by higher-order interactions among multiple units, naturally represented as hypergraphs. Understanding dependency structures within these hypergraphs is crucial for understanding and predicting the behavior of complex systems but is made challenging by their combinatorial complexity and computational demands. In this paper, we introduce a class of probabilistic models that efficiently represents and discovers a broad spectrum of mesoscale structure in large-scale hypergraphs. The key insight enabling this approach is to treat classes of similar units as themselves nodes in a latent hypergraph. By modeling observed node interactions through latent interactions among classes using low-rank representations, our approach tractably captures rich structural patterns while ensuring model identifiability. This allows for direct interpretation of distinct node- and class-level structures. Empirically, our model improves link prediction over state-of-the-art methods and discovers interpretable structures in diverse real-world systems, including pharmacological and social networks, advancing the ability to incorporate large-scale higher-order data into the scientific process.
The AL$\ell_0$CORE Tensor Decomposition for Sparse Count Data
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces AL$\ell_0$CORE, a new form of probabilistic non-negative tensor decomposition. AL$\ell_0$CORE is a Tucker decomposition where the number of non-zero elements (i.e., the $\ell_0$-norm) of the core tensor is constrained to a preset value $Q$ much smaller than the size of the core. While the user dictates the total budget $Q$, the locations and values of the non-zero elements are latent variables and allocated across the core tensor during inference. AL$\ell_0$CORE -- i.e., $allo$cated $\ell_0$-$co$nstrained $core$-- thus enjoys both the computational tractability of CP decomposition and the qualitatively appealing latent structure of Tucker. In a suite of real-data experiments, we demonstrate that AL$\ell_0$CORE typically requires only tiny fractions (e.g.,~1%) of the full core to achieve the same results as full Tucker decomposition at only a correspondingly tiny fraction of the cost.
Model-assisted deep learning of rare extreme events from partial observations
Nov 04, 2021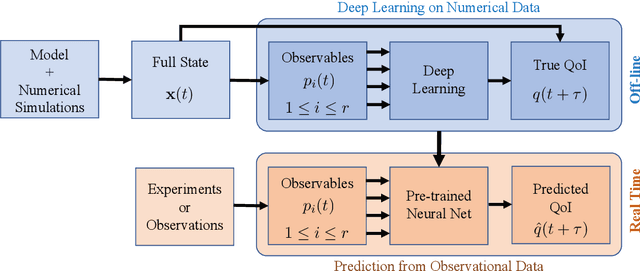
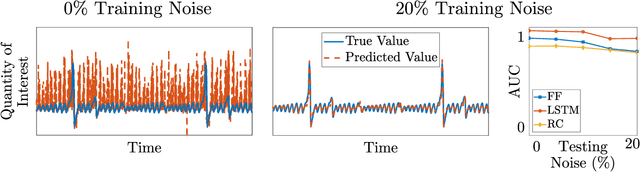
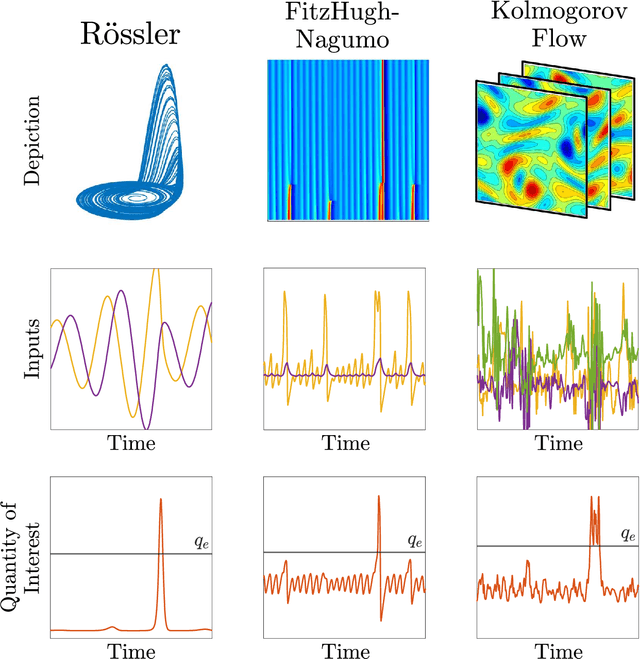
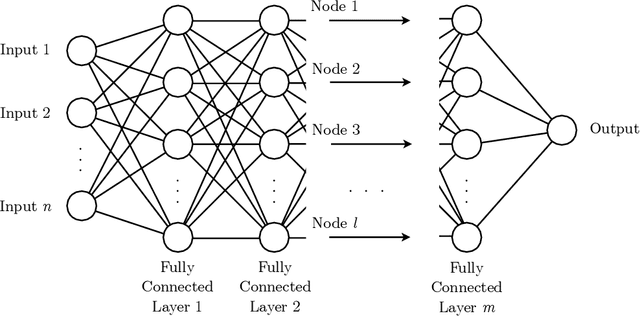
Abstract:To predict rare extreme events using deep neural networks, one encounters the so-called small data problem because even long-term observations often contain few extreme events. Here, we investigate a model-assisted framework where the training data is obtained from numerical simulations, as opposed to observations, with adequate samples from extreme events. However, to ensure the trained networks are applicable in practice, the training is not performed on the full simulation data; instead we only use a small subset of observable quantities which can be measured in practice. We investigate the feasibility of this model-assisted framework on three different dynamical systems (Rossler attractor, FitzHugh--Nagumo model, and a turbulent fluid flow) and three different deep neural network architectures (feedforward, long short-term memory, and reservoir computing). In each case, we study the prediction accuracy, robustness to noise, reproducibility under repeated training, and sensitivity to the type of input data. In particular, we find long short-term memory networks to be most robust to noise and to yield relatively accurate predictions, while requiring minimal fine-tuning of the hyperparameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge