Johann Schaible
Overview of LiLAS 2020 -- Living Labs for Academic Search
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Academic Search is a timeless challenge that the field of Information Retrieval has been dealing with for many years. Even today, the search for academic material is a broad field of research that recently started working on problems like the COVID-19 pandemic. However, test collections and specialized data sets like CORD-19 only allow for system-oriented experiments, while the evaluation of algorithms in real-world environments is only available to researchers from industry. In LiLAS, we open up two academic search platforms to allow participating research to evaluate their systems in a Docker-based research environment. This overview paper describes the motivation, infrastructure, and two systems LIVIVO and GESIS Search that are part of this CLEF lab.
* Manuscript version of the CLEF 2020 proceedings paper
Living Lab Evaluation for Life and Social Sciences Search Platforms -- LiLAS at CLEF 2021
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Meta-evaluation studies of system performances in controlled offline evaluation campaigns, like TREC and CLEF, show a need for innovation in evaluating IR-systems. The field of academic search is no exception to this. This might be related to the fact that relevance in academic search is multilayered and therefore the aspect of user-centric evaluation is becoming more and more important. The Living Labs for Academic Search (LiLAS) lab aims to strengthen the concept of user-centric living labs for the domain of academic search by allowing participants to evaluate their retrieval approaches in two real-world academic search systems from the life sciences and the social sciences. To this end, we provide participants with metadata on the systems' content as well as candidate lists with the task to rank the most relevant candidate to the top. Using the STELLA-infrastructure, we allow participants to easily integrate their approaches into the real-world systems and provide the possibility to compare different approaches at the same time.
Online Information Retrieval Evaluation using the STELLA Framework
Oct 24, 2022
Abstract:Involving users in early phases of software development has become a common strategy as it enables developers to consider user needs from the beginning. Once a system is in production, new opportunities to observe, evaluate and learn from users emerge as more information becomes available. Gathering information from users to continuously evaluate their behavior is a common practice for commercial software, while the Cranfield paradigm remains the preferred option for Information Retrieval (IR) and recommendation systems in the academic world. Here we introduce the Infrastructures for Living Labs STELLA project which aims to create an evaluation infrastructure allowing experimental systems to run along production web-based academic search systems with real users. STELLA combines user interactions and log files analyses to enable large-scale A/B experiments for academic search.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2203.05430
Overview of LiLAS 2021 -- Living Labs for Academic Search
Mar 10, 2022


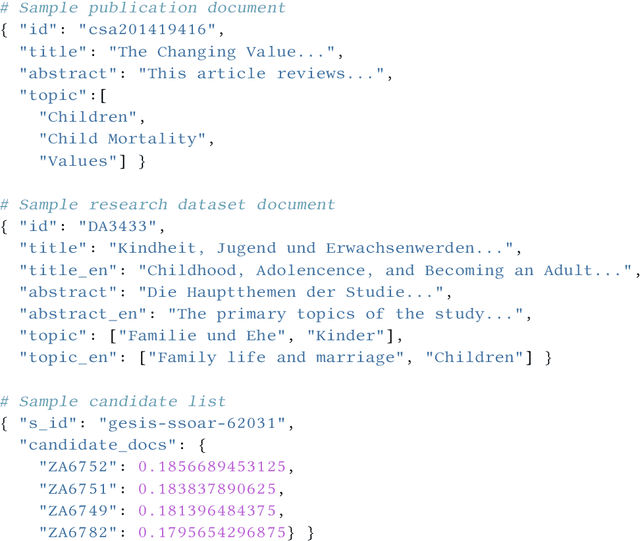
Abstract:The Living Labs for Academic Search (LiLAS) lab aims to strengthen the concept of user-centric living labs for academic search. The methodological gap between real-world and lab-based evaluation should be bridged by allowing lab participants to evaluate their retrieval approaches in two real-world academic search systems from life sciences and social sciences. This overview paper outlines the two academic search systems LIVIVO and GESIS Search, and their corresponding tasks within LiLAS, which are ad-hoc retrieval and dataset recommendation. The lab is based on a new evaluation infrastructure named STELLA that allows participants to submit results corresponding to their experimental systems in the form of pre-computed runs and Docker containers that can be integrated into production systems and generate experimental results in real-time. Both submission types are interleaved with the results provided by the productive systems allowing for a seamless presentation and evaluation. The evaluation of results and a meta-analysis of the different tasks and submission types complement this overview.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge