João Macedo
Attention over Scene Graphs: Indoor Scene Representations Toward CSAI Classification
Sep 30, 2025



Abstract:Indoor scene classification is a critical task in computer vision, with wide-ranging applications that go from robotics to sensitive content analysis, such as child sexual abuse imagery (CSAI) classification. The problem is particularly challenging due to the intricate relationships between objects and complex spatial layouts. In this work, we propose the Attention over Scene Graphs for Sensitive Content Analysis (ASGRA), a novel framework that operates on structured graph representations instead of raw pixels. By first converting images into Scene Graphs and then employing a Graph Attention Network for inference, ASGRA directly models the interactions between a scene's components. This approach offers two key benefits: (i) inherent explainability via object and relationship identification, and (ii) privacy preservation, enabling model training without direct access to sensitive images. On Places8, we achieve 81.27% balanced accuracy, surpassing image-based methods. Real-world CSAI evaluation with law enforcement yields 74.27% balanced accuracy. Our results establish structured scene representations as a robust paradigm for indoor scene classification and CSAI classification. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/tutuzeraa/ASGRA.
Minimizing Risk Through Minimizing Model-Data Interaction: A Protocol For Relying on Proxy Tasks When Designing Child Sexual Abuse Imagery Detection Models
May 10, 2025Abstract:The distribution of child sexual abuse imagery (CSAI) is an ever-growing concern of our modern world; children who suffered from this heinous crime are revictimized, and the growing amount of illegal imagery distributed overwhelms law enforcement agents (LEAs) with the manual labor of categorization. To ease this burden researchers have explored methods for automating data triage and detection of CSAI, but the sensitive nature of the data imposes restricted access and minimal interaction between real data and learning algorithms, avoiding leaks at all costs. In observing how these restrictions have shaped the literature we formalize a definition of "Proxy Tasks", i.e., the substitute tasks used for training models for CSAI without making use of CSA data. Under this new terminology we review current literature and present a protocol for making conscious use of Proxy Tasks together with consistent input from LEAs to design better automation in this field. Finally, we apply this protocol to study -- for the first time -- the task of Few-shot Indoor Scene Classification on CSAI, showing a final model that achieves promising results on a real-world CSAI dataset whilst having no weights actually trained on sensitive data.
Leveraging Self-Supervised Learning for Scene Recognition in Child Sexual Abuse Imagery
Mar 02, 2024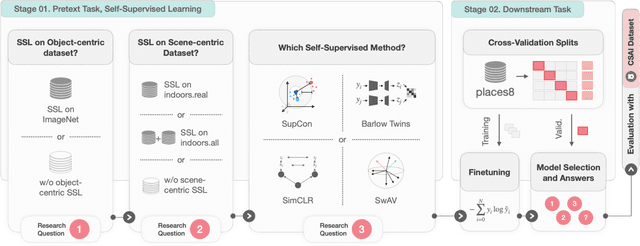
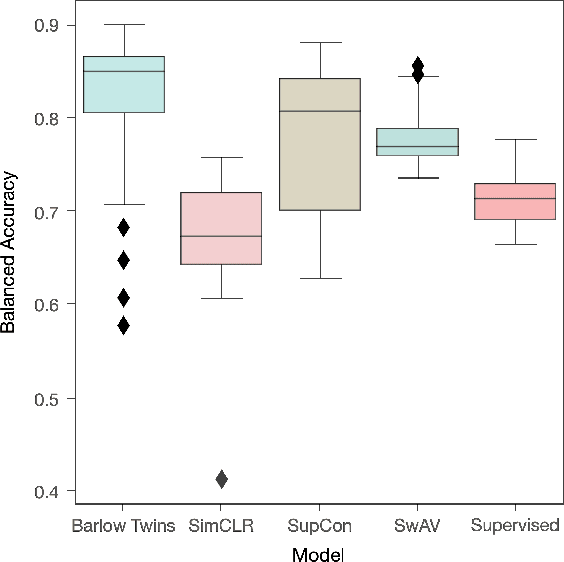

Abstract:Crime in the 21st century is split into a virtual and real world. However, the former has become a global menace to people's well-being and security in the latter. The challenges it presents must be faced with unified global cooperation, and we must rely more than ever on automated yet trustworthy tools to combat the ever-growing nature of online offenses. Over 10 million child sexual abuse reports are submitted to the US National Center for Missing & Exploited Children every year, and over 80% originated from online sources. Therefore, investigation centers and clearinghouses cannot manually process and correctly investigate all imagery. In light of that, reliable automated tools that can securely and efficiently deal with this data are paramount. In this sense, the scene recognition task looks for contextual cues in the environment, being able to group and classify child sexual abuse data without requiring to be trained on sensitive material. The scarcity and limitations of working with child sexual abuse images lead to self-supervised learning, a machine-learning methodology that leverages unlabeled data to produce powerful representations that can be more easily transferred to target tasks. This work shows that self-supervised deep learning models pre-trained on scene-centric data can reach 71.6% balanced accuracy on our indoor scene classification task and, on average, 2.2 percentage points better performance than a fully supervised version. We cooperate with Brazilian Federal Police experts to evaluate our indoor classification model on actual child abuse material. The results demonstrate a notable discrepancy between the features observed in widely used scene datasets and those depicted on sensitive materials.
Seeing without Looking: Analysis Pipeline for Child Sexual Abuse Datasets
Apr 29, 2022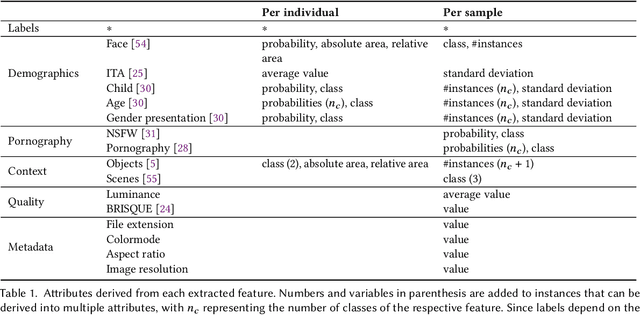
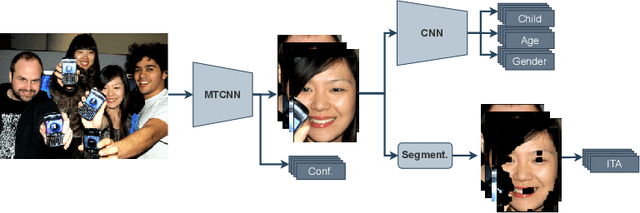
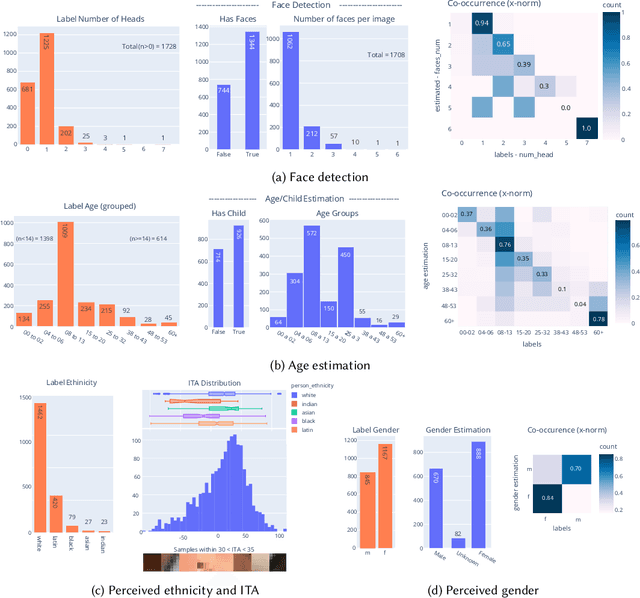
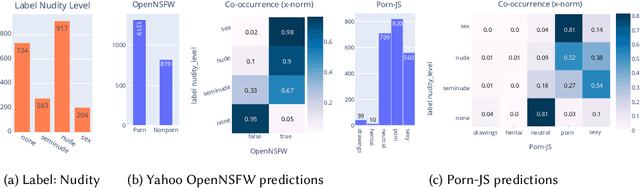
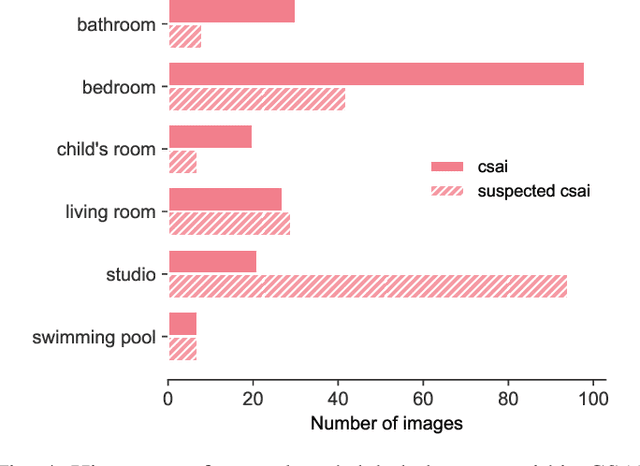
Abstract:The online sharing and viewing of Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) are growing fast, such that human experts can no longer handle the manual inspection. However, the automatic classification of CSAM is a challenging field of research, largely due to the inaccessibility of target data that is - and should forever be - private and in sole possession of law enforcement agencies. To aid researchers in drawing insights from unseen data and safely providing further understanding of CSAM images, we propose an analysis template that goes beyond the statistics of the dataset and respective labels. It focuses on the extraction of automatic signals, provided both by pre-trained machine learning models, e.g., object categories and pornography detection, as well as image metrics such as luminance and sharpness. Only aggregated statistics of sparse signals are provided to guarantee the anonymity of children and adolescents victimized. The pipeline allows filtering the data by applying thresholds to each specified signal and provides the distribution of such signals within the subset, correlations between signals, as well as a bias evaluation. We demonstrated our proposal on the Region-based annotated Child Pornography Dataset (RCPD), one of the few CSAM benchmarks in the literature, composed of over 2000 samples among regular and CSAM images, produced in partnership with Brazil's Federal Police. Although noisy and limited in several senses, we argue that automatic signals can highlight important aspects of the overall distribution of data, which is valuable for databases that can not be disclosed. Our goal is to safely publicize the characteristics of CSAM datasets, encouraging researchers to join the field and perhaps other institutions to provide similar reports on their benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge