Jiyang Guan
Do We Really Need Curated Malicious Data for Safety Alignment in Multi-modal Large Language Models?
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) have made significant progress, yet their safety alignment remains limited. Typically, current open-source MLLMs rely on the alignment inherited from their language module to avoid harmful generations. However, the lack of safety measures specifically designed for multi-modal inputs creates an alignment gap, leaving MLLMs vulnerable to vision-domain attacks such as typographic manipulation. Current methods utilize a carefully designed safety dataset to enhance model defense capability, while the specific knowledge or patterns acquired from the high-quality dataset remain unclear. Through comparison experiments, we find that the alignment gap primarily arises from data distribution biases, while image content, response quality, or the contrastive behavior of the dataset makes little contribution to boosting multi-modal safety. To further investigate this and identify the key factors in improving MLLM safety, we propose finetuning MLLMs on a small set of benign instruct-following data with responses replaced by simple, clear rejection sentences. Experiments show that, without the need for labor-intensive collection of high-quality malicious data, model safety can still be significantly improved, as long as a specific fraction of rejection data exists in the finetuning set, indicating the security alignment is not lost but rather obscured during multi-modal pretraining or instruction finetuning. Simply correcting the underlying data bias could narrow the safety gap in the vision domain.
Sample Correlation for Fingerprinting Deep Face Recognition
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:Face recognition has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years, thanks to the development of deep learning techniques.However, an off-the-shelf face recognition model as a commercial service could be stolen by model stealing attacks, posing great threats to the rights of the model owner.Model fingerprinting, as a model stealing detection method, aims to verify whether a suspect model is stolen from the victim model, gaining more and more attention nowadays.Previous methods always utilize transferable adversarial examples as the model fingerprint, but this method is known to be sensitive to adversarial defense and transfer learning techniques.To address this issue, we consider the pairwise relationship between samples instead and propose a novel yet simple model stealing detection method based on SAmple Correlation (SAC).Specifically, we present SAC-JC that selects JPEG compressed samples as model inputs and calculates the correlation matrix among their model outputs.Extensive results validate that SAC successfully defends against various model stealing attacks in deep face recognition, encompassing face verification and face emotion recognition, exhibiting the highest performance in terms of AUC, p-value and F1 score.Furthermore, we extend our evaluation of SAC-JC to object recognition datasets including Tiny-ImageNet and CIFAR10, which also demonstrates the superior performance of SAC-JC to previous methods.The code will be available at \url{https://github.com/guanjiyang/SAC_JC}.
Rethinking Local Perception in Lightweight Vision Transformer
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have been shown to be effective in various vision tasks. However, resizing them to a mobile-friendly size leads to significant performance degradation. Therefore, developing lightweight vision transformers has become a crucial area of research. This paper introduces CloFormer, a lightweight vision transformer that leverages context-aware local enhancement. CloFormer explores the relationship between globally shared weights often used in vanilla convolutional operators and token-specific context-aware weights appearing in attention, then proposes an effective and straightforward module to capture high-frequency local information. In CloFormer, we introduce AttnConv, a convolution operator in attention's style. The proposed AttnConv uses shared weights to aggregate local information and deploys carefully designed context-aware weights to enhance local features. The combination of the AttnConv and vanilla attention which uses pooling to reduce FLOPs in CloFormer enables the model to perceive high-frequency and low-frequency information. Extensive experiments were conducted in image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation, demonstrating the superiority of CloFormer.
Few-shot Backdoor Defense Using Shapley Estimation
Dec 30, 2021
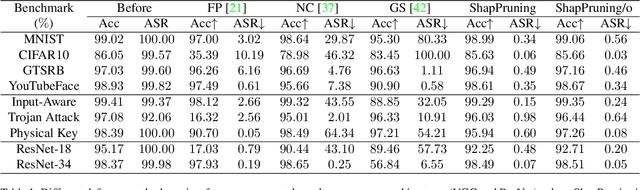

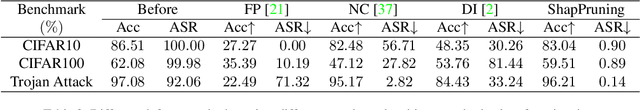
Abstract:Deep neural networks have achieved impressive performance in a variety of tasks over the last decade, such as autonomous driving, face recognition, and medical diagnosis. However, prior works show that deep neural networks are easily manipulated into specific, attacker-decided behaviors in the inference stage by backdoor attacks which inject malicious small hidden triggers into model training, raising serious security threats. To determine the triggered neurons and protect against backdoor attacks, we exploit Shapley value and develop a new approach called Shapley Pruning (ShapPruning) that successfully mitigates backdoor attacks from models in a data-insufficient situation (1 image per class or even free of data). Considering the interaction between neurons, ShapPruning identifies the few infected neurons (under 1% of all neurons) and manages to protect the model's structure and accuracy after pruning as many infected neurons as possible. To accelerate ShapPruning, we further propose discarding threshold and $\epsilon$-greedy strategy to accelerate Shapley estimation, making it possible to repair poisoned models with only several minutes. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method against various attacks and tasks compared to existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge