Jingya Zhang
Multi-modal Evidential Fusion Network for Trusted PET/CT Tumor Segmentation
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:Accurate segmentation of tumors in PET/CT images is important in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The key issue of such a segmentation problem lies in the effective integration of complementary information from PET and CT images. However, the quality of PET and CT images varies widely in clinical settings, which leads to uncertainty in the modality information extracted by networks. To take the uncertainty into account in multi-modal information fusion, this paper proposes a novel Multi-modal Evidential Fusion Network (MEFN) comprising a Cross-Modal Feature Learning (CFL) module and a Multi-modal Trusted Fusion (MTF) module. The CFL module reduces the domain gap upon modality conversion and highlights common tumor features, thereby alleviating the needs of the segmentation module to handle modality specificity. The MTF module utilizes mutual attention mechanisms and an uncertainty calibrator to fuse modality features based on modality uncertainty and then fuse the segmentation results under the guidance of Dempster-Shafer Theory. Besides, a new uncertainty perceptual loss is introduced to force the model focusing on uncertain features and hence improve its ability to extract trusted modality information. Extensive comparative experiments are conducted on two publicly available PET/CT datasets to evaluate the performance of our proposed method whose results demonstrate that our MEFN significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods with improvements of 2.15% and 3.23% in DSC scores on the AutoPET dataset and the Hecktor dataset, respectively. More importantly, our model can provide radiologists with credible uncertainty of the segmentation results for their decision in accepting or rejecting the automatic segmentation results, which is particularly important for clinical applications. Our code will be available at https://github.com/QPaws/MEFN.
Bayesian geoacoustic inversion using mixture density network
Aug 19, 2020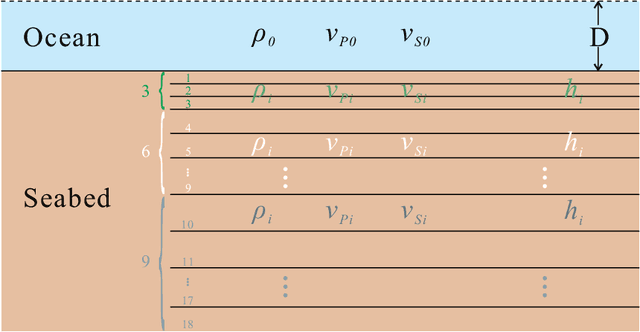
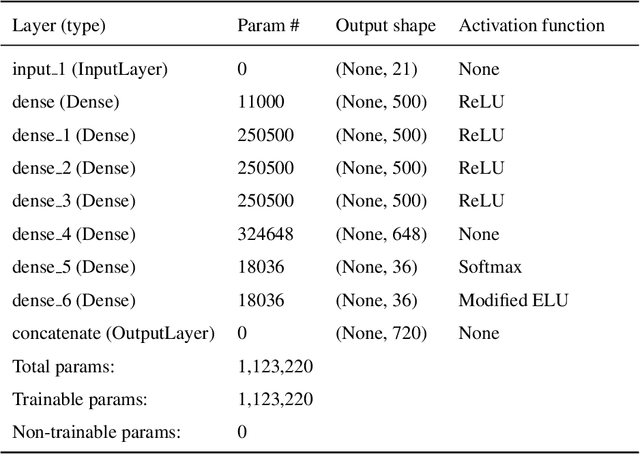
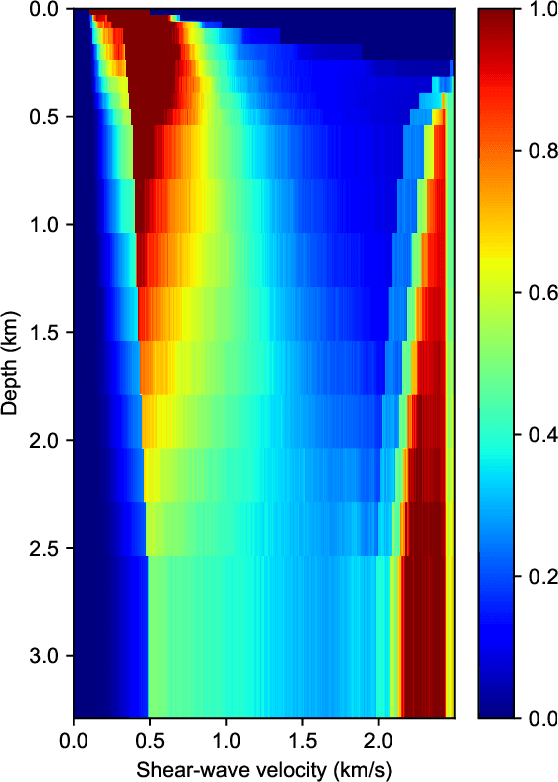
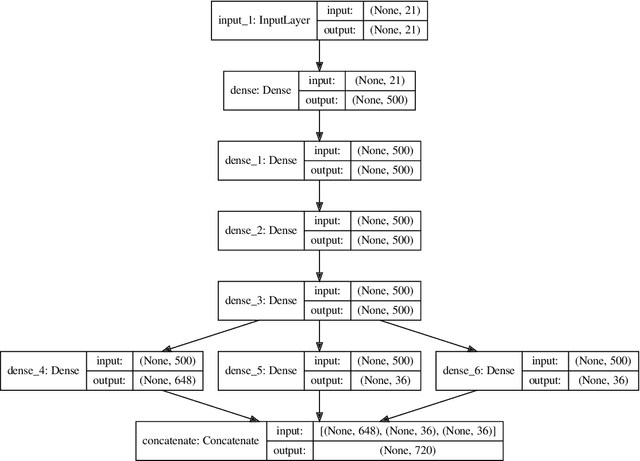
Abstract:Bayesian geoacoustic inversion problems are conventionally solved by Markov chain Monte Carlo methods or its variants, which are computationally expensive. This paper extends the classic Bayesian geoacoustic inversion framework using the mixture density network (MDN), which provides a much more efficient way to solve geoacoustic inversion problems in Bayesian inference framework. Some important geoacoustic statistics of Bayesian geoacoustic inversion are derived from the multidimensional posterior probability density (PPD) using the MDN theory. These statistics make it convenient to train the network directly on the whole parameter space and get the multidimensional PPD of model parameters. The network is trained on a simulated dataset of surface-wave dispersion curves with shear-wave velocities as labels. The results show that the network gives reliable predictions and has good generalization performance on unseen data. Once trained, the network can rapidly (within seconds) give a fully probabilistic solution which is comparable to Monte Carlo methods. It provides an promissing approach for real-time inversion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge