Jingqin Gao
Traffic Prediction considering Multiple Levels of Spatial-temporal Information: A Multi-scale Graph Wavelet-based Approach
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Although traffic prediction has been receiving considerable attention with a number of successes in the context of intelligent transportation systems, the prediction of traffic states over a complex transportation network that contains different road types has remained a challenge. This study proposes a multi-scale graph wavelet temporal convolution network (MSGWTCN) to predict the traffic states in complex transportation networks. Specifically, a multi-scale spatial block is designed to simultaneously capture the spatial information at different levels, and the gated temporal convolution network is employed to extract the temporal dependencies of the data. The model jointly learns to mount multiple levels of the spatial interactions by stacking graph wavelets with different scales. Two real-world datasets are used in this study to investigate the model performance, including a highway network in Seattle and a dense road network of Manhattan in New York City. Experiment results show that the proposed model outperforms other baseline models. Furthermore, different scales of graph wavelets are found to be effective in extracting local, intermediate and global information at the same time and thus enable the model to learn a complex transportation network topology with various types of road segments. By carefully customizing the scales of wavelets, the model is able to improve the prediction performance and better adapt to different network configurations.
Informed along the road: roadway capacity driven graph convolution network for network-wide traffic prediction
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:While deep learning has shown success in predicting traffic states, most methods treat it as a general prediction task without considering transportation aspects. Recently, graph neural networks have proven effective for this task, but few incorporate external factors that impact roadway capacity and traffic flow. This study introduces the Roadway Capacity Driven Graph Convolution Network (RCDGCN) model, which incorporates static and dynamic roadway capacity attributes in spatio-temporal settings to predict network-wide traffic states. The model was evaluated on two real-world datasets with different transportation factors: the ICM-495 highway network and an urban network in Manhattan, New York City. Results show RCDGCN outperformed baseline methods in forecasting accuracy. Analyses, including ablation experiments, weight analysis, and case studies, investigated the effect of capacity-related factors. The study demonstrates the potential of using RCDGCN for transportation system management.
Agent-based Simulation Model and Deep Learning Techniques to Evaluate and Predict Transportation Trends around COVID-19
Sep 23, 2020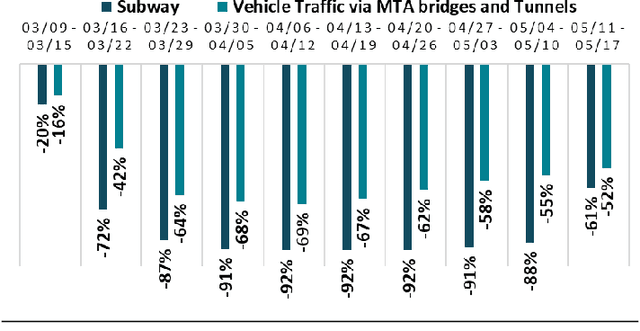
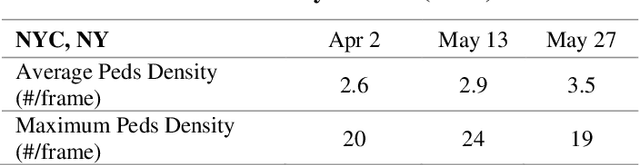
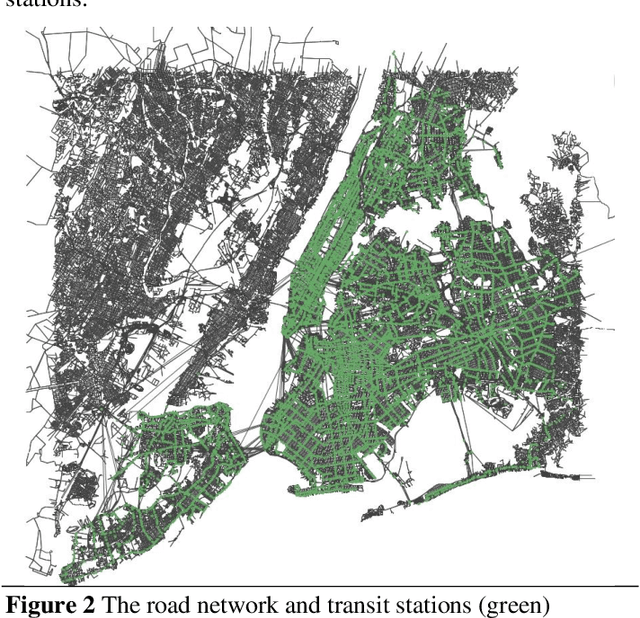
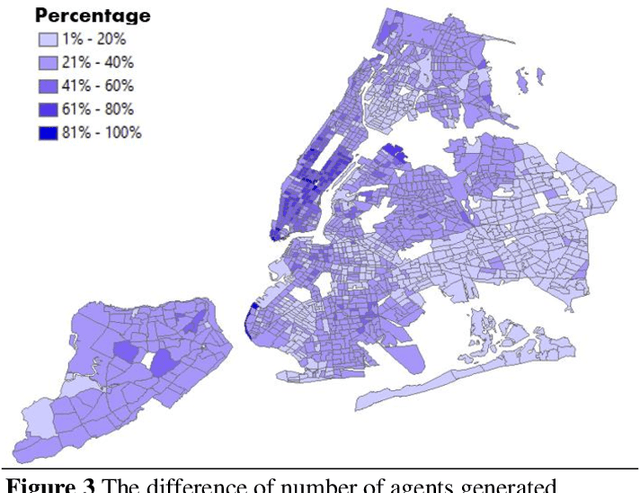
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has affected travel behaviors and transportation system operations, and cities are grappling with what policies can be effective for a phased reopening shaped by social distancing. This edition of the white paper updates travel trends and highlights an agent-based simulation model's results to predict the impact of proposed phased reopening strategies. It also introduces a real-time video processing method to measure social distancing through cameras on city streets.
An Interactive Data Visualization and Analytics Tool to Evaluate Mobility and Sociability Trends During COVID-19
Jun 26, 2020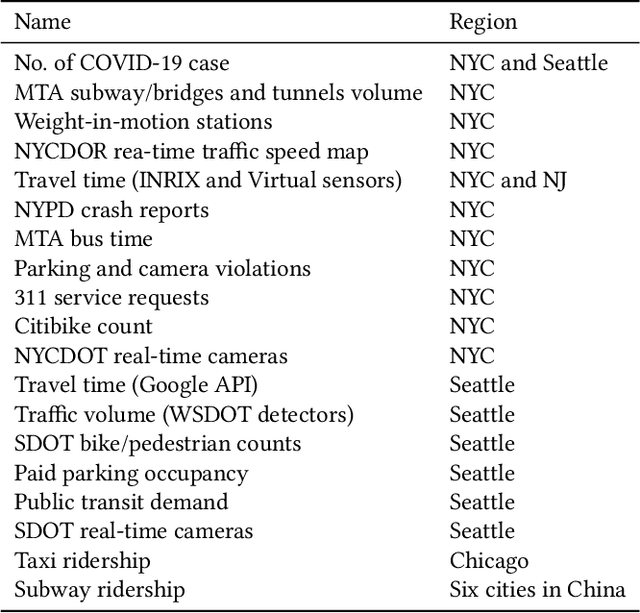
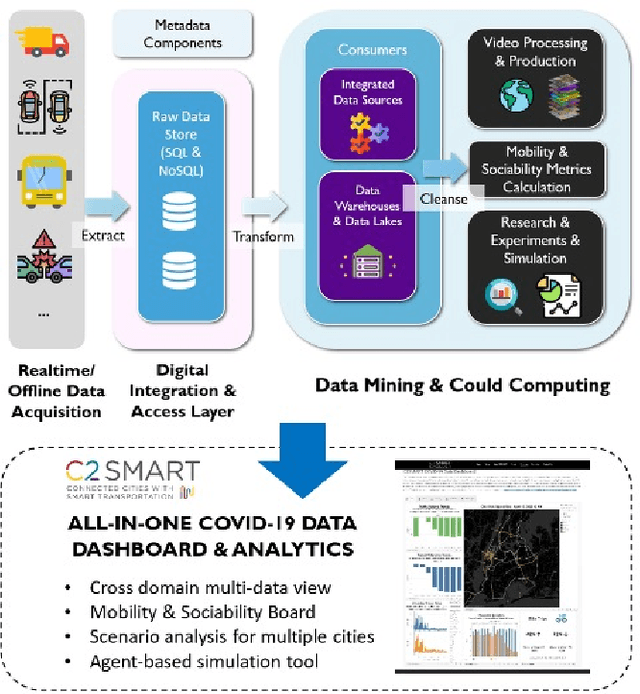
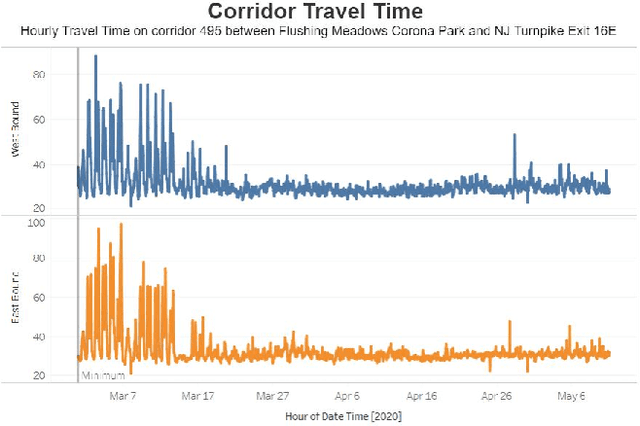
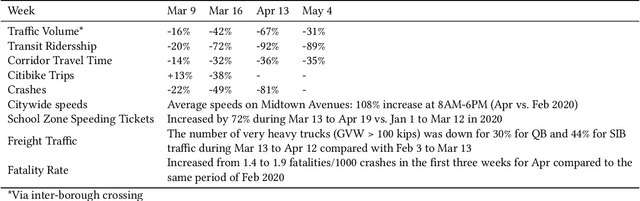
Abstract:The COVID-19 outbreak has dramatically changed travel behavior in affected cities. The C2SMART research team has been investigating the impact of COVID-19 on mobility and sociability. New York City (NYC) and Seattle, two of the cities most affected by COVID-19 in the U.S. were included in our initial study. An all-in-one dashboard with data mining and cloud computing capabilities was developed for interactive data analytics and visualization to facilitate the understanding of the impact of the outbreak and corresponding policies such as social distancing on transportation systems. This platform is updated regularly and continues to evolve with the addition of new data, impact metrics, and visualizations to assist public and decision-makers to make informed decisions. This paper presents the architecture of the COVID related mobility data dashboard and preliminary mobility and sociability metrics for NYC and Seattle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge