Jinghuan Yu
NFL: Robust Learned Index via Distribution Transformation
May 24, 2022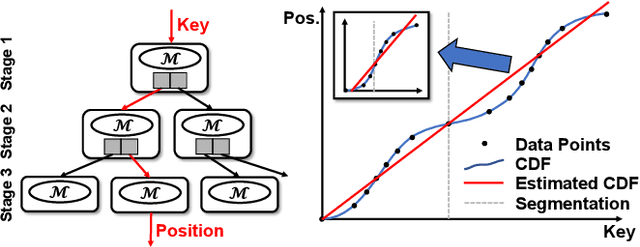
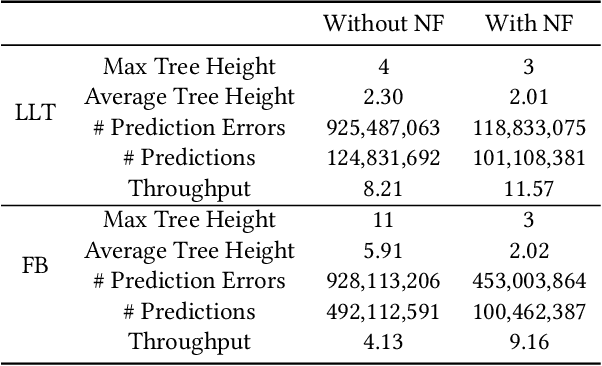
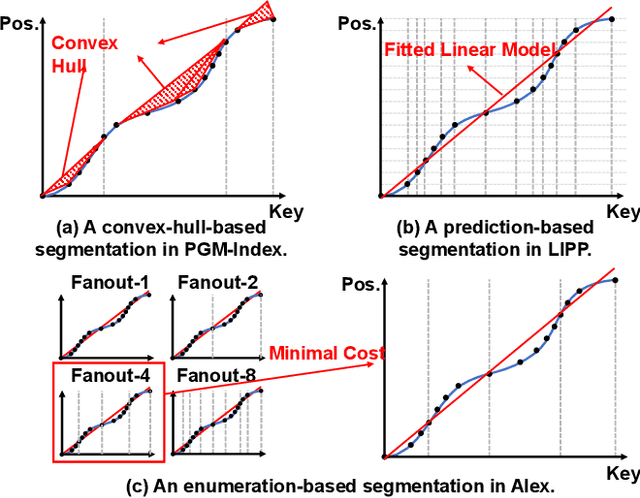
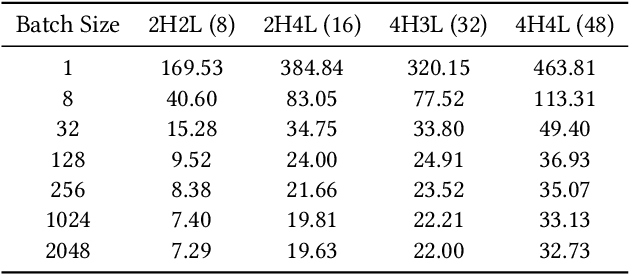
Abstract:Recent works on learned index open a new direction for the indexing field. The key insight of the learned index is to approximate the mapping between keys and positions with piece-wise linear functions. Such methods require partitioning key space for a better approximation. Although lots of heuristics are proposed to improve the approximation quality, the bottleneck is that the segmentation overheads could hinder the overall performance. This paper tackles the approximation problem by applying a \textit{distribution transformation} to the keys before constructing the learned index. A two-stage Normalizing-Flow-based Learned index framework (NFL) is proposed, which first transforms the original complex key distribution into a near-uniform distribution, then builds a learned index leveraging the transformed keys. For effective distribution transformation, we propose a Numerical Normalizing Flow (Numerical NF). Based on the characteristics of the transformed keys, we propose a robust After-Flow Learned Index (AFLI). To validate the performance, comprehensive evaluations are conducted on both synthetic and real-world workloads, which shows that the proposed NFL produces the highest throughput and the lowest tail latency compared to the state-of-the-art learned indexes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge