Jiaying Zou
Zero-shot stance detection based on cross-domain feature enhancement by contrastive learning
Oct 07, 2022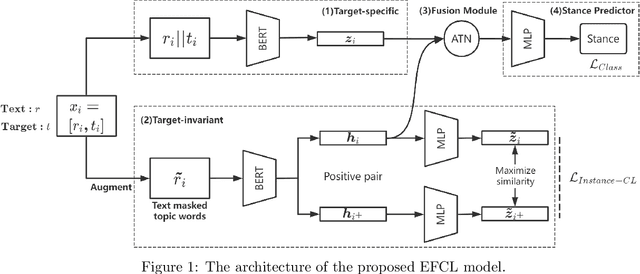
Abstract:Zero-shot stance detection is challenging because it requires detecting the stance of previously unseen targets in the inference phase. The ability to learn transferable target-invariant features is critical for zero-shot stance detection. In this work, we propose a stance detection approach that can efficiently adapt to unseen targets, the core of which is to capture target-invariant syntactic expression patterns as transferable knowledge. Specifically, we first augment the data by masking the topic words of sentences, and then feed the augmented data to an unsupervised contrastive learning module to capture transferable features. Then, to fit a specific target, we encode the raw texts as target-specific features. Finally, we adopt an attention mechanism, which combines syntactic expression patterns with target-specific features to obtain enhanced features for predicting previously unseen targets. Experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms competitive baselines on four benchmark datasets.
Adversarial Learning-based Stance Classifier for COVID-19-related Health Policies
Sep 13, 2022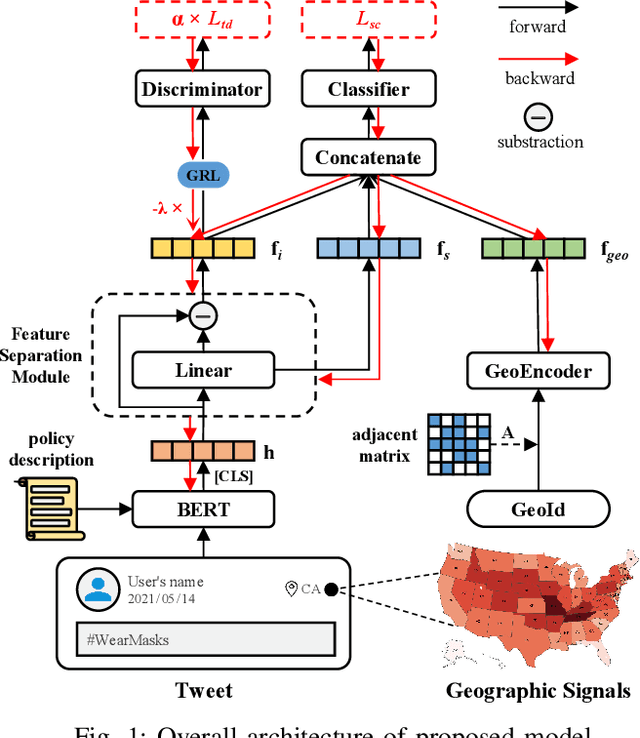
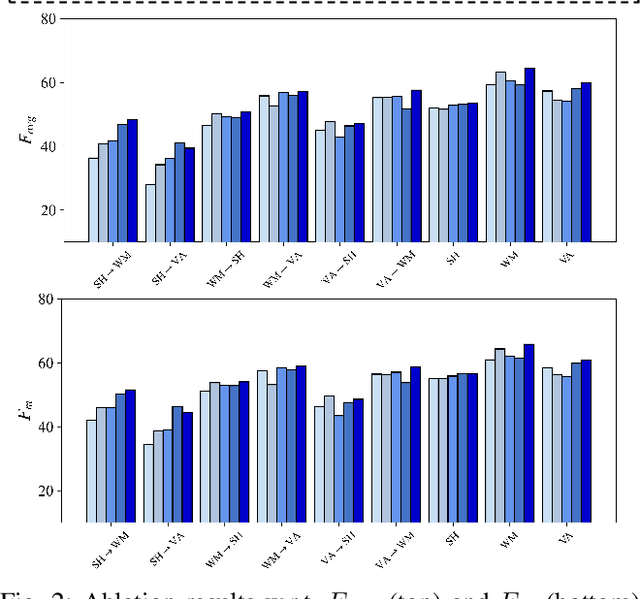
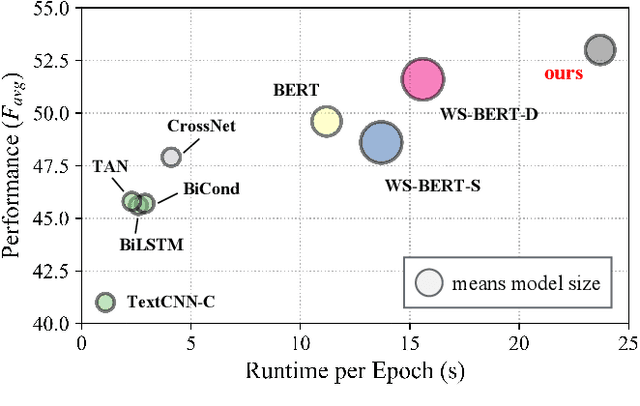
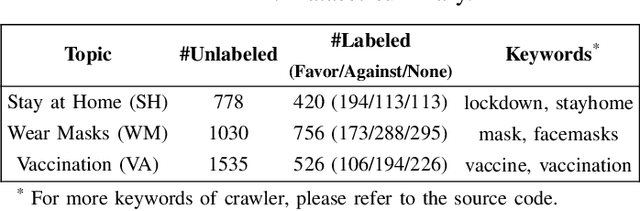
Abstract:The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has caused immeasurable losses for people worldwide. To contain the spread of virus and further alleviate the crisis, various health policies (e.g., stay-at-home orders) have been issued which spark heat discussion as users turn to share their attitudes on social media. In this paper, we consider a more realistic scenario on stance detection (i.e., cross-target and zero-shot settings) for the pandemic and propose an adversarial learning-based stance classifier to automatically identify the public attitudes toward COVID-19-related health policies. Specifically, we adopt adversarial learning which allows the model to train on a large amount of labeled data and capture transferable knowledge from source topics, so as to enable generalize to the emerging health policy with sparse labeled data. Meanwhile, a GeoEncoder is designed which encourages model to learn unobserved contextual factors specified by each region and represents them as non-text information to enhance model's deeper understanding. We evaluate the performance of a broad range of baselines in stance detection task for COVID-19-related policies, and experimental results show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both cross-target and zero-shot settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge