Jianning Pei
Distribution Matching Variational AutoEncoder
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Most visual generative models compress images into a latent space before applying diffusion or autoregressive modelling. Yet, existing approaches such as VAEs and foundation model aligned encoders implicitly constrain the latent space without explicitly shaping its distribution, making it unclear which types of distributions are optimal for modeling. We introduce \textbf{Distribution-Matching VAE} (\textbf{DMVAE}), which explicitly aligns the encoder's latent distribution with an arbitrary reference distribution via a distribution matching constraint. This generalizes beyond the Gaussian prior of conventional VAEs, enabling alignment with distributions derived from self-supervised features, diffusion noise, or other prior distributions. With DMVAE, we can systematically investigate which latent distributions are more conducive to modeling, and we find that SSL-derived distributions provide an excellent balance between reconstruction fidelity and modeling efficiency, reaching gFID equals 3.2 on ImageNet with only 64 training epochs. Our results suggest that choosing a suitable latent distribution structure (achieved via distribution-level alignment), rather than relying on fixed priors, is key to bridging the gap between easy-to-model latents and high-fidelity image synthesis. Code is avaliable at https://github.com/sen-ye/dmvae.
Optimal Stepsize for Diffusion Sampling
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models achieve remarkable generation quality but suffer from computational intensive sampling due to suboptimal step discretization. While existing works focus on optimizing denoising directions, we address the principled design of stepsize schedules. This paper proposes Optimal Stepsize Distillation, a dynamic programming framework that extracts theoretically optimal schedules by distilling knowledge from reference trajectories. By reformulating stepsize optimization as recursive error minimization, our method guarantees global discretization bounds through optimal substructure exploitation. Crucially, the distilled schedules demonstrate strong robustness across architectures, ODE solvers, and noise schedules. Experiments show 10x accelerated text-to-image generation while preserving 99.4% performance on GenEval. Our code is available at https://github.com/bebebe666/OptimalSteps.
AgMTR: Agent Mining Transformer for Few-shot Segmentation in Remote Sensing
Sep 26, 2024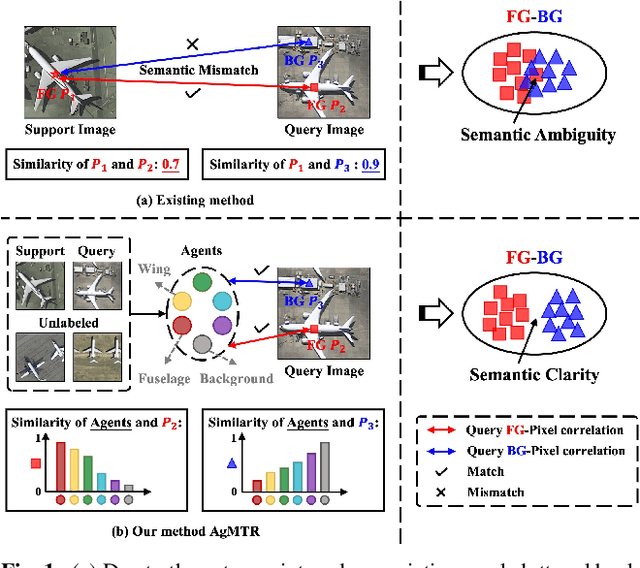
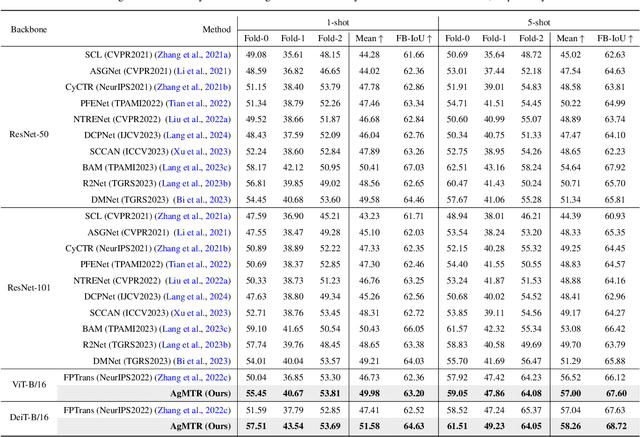
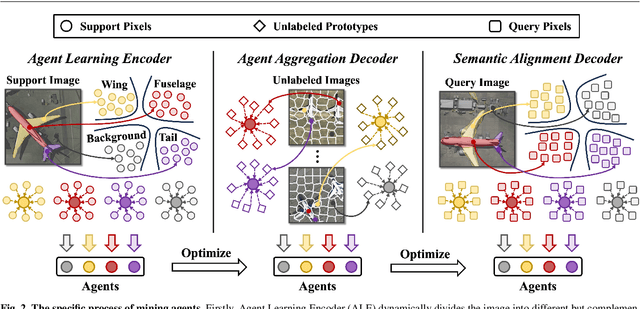
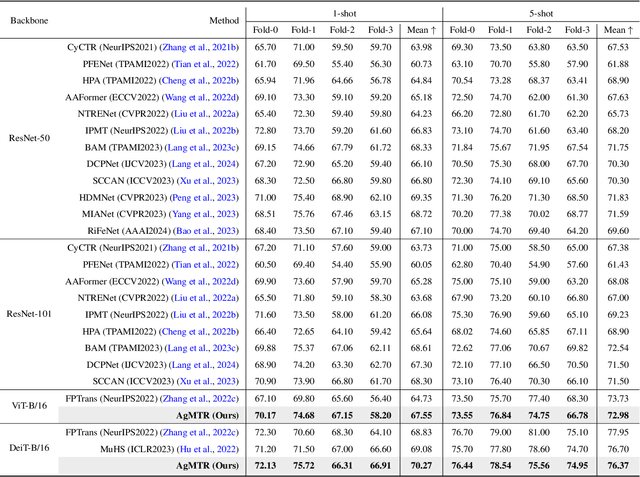
Abstract:Few-shot Segmentation (FSS) aims to segment the interested objects in the query image with just a handful of labeled samples (i.e., support images). Previous schemes would leverage the similarity between support-query pixel pairs to construct the pixel-level semantic correlation. However, in remote sensing scenarios with extreme intra-class variations and cluttered backgrounds, such pixel-level correlations may produce tremendous mismatches, resulting in semantic ambiguity between the query foreground (FG) and background (BG) pixels. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel Agent Mining Transformer (AgMTR), which adaptively mines a set of local-aware agents to construct agent-level semantic correlation. Compared with pixel-level semantics, the given agents are equipped with local-contextual information and possess a broader receptive field. At this point, different query pixels can selectively aggregate the fine-grained local semantics of different agents, thereby enhancing the semantic clarity between query FG and BG pixels. Concretely, the Agent Learning Encoder (ALE) is first proposed to erect the optimal transport plan that arranges different agents to aggregate support semantics under different local regions. Then, for further optimizing the agents, the Agent Aggregation Decoder (AAD) and the Semantic Alignment Decoder (SAD) are constructed to break through the limited support set for mining valuable class-specific semantics from unlabeled data sources and the query image itself, respectively. Extensive experiments on the remote sensing benchmark iSAID indicate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance. Surprisingly, our method remains quite competitive when extended to more common natural scenarios, i.e., PASCAL-5i and COCO-20i.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge