Jiangyi Wang
Beyond Surface Reasoning: Unveiling the True Long Chain-of-Thought Capacity of Diffusion Large Language Models
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Recently, Diffusion Large Language Models (DLLMs) have offered high throughput and effective sequential reasoning, making them a competitive alternative to autoregressive LLMs (ALLMs). However, parallel decoding, which enables simultaneous token updates, conflicts with the causal order often required for rigorous reasoning. We first identify this conflict as the core Parallel-Sequential Contradiction (PSC). Behavioral analyses in both simple and complex reasoning tasks show that DLLMs exhibit genuine parallelism only for directly decidable outputs. As task difficulty increases, they revert to autoregressive-like behavior, a limitation exacerbated by autoregressive prompting, which nearly doubles the number of decoding steps with remasking without improving quality. Moreover, PSC restricts DLLMs' self-reflection, reasoning depth, and exploratory breadth. To further characterize PSC, we introduce three scaling dimensions for DLLMs: parallel, diffusion, and sequential. Empirically, while parallel scaling yields consistent improvements, diffusion and sequential scaling are constrained by PSC. Based on these findings, we propose several practical mitigations, parallel-oriented prompting, diffusion early stopping, and parallel scaling, to reduce PSC-induced ineffectiveness and inefficiencies.
Uncertainty Meets Diversity: A Comprehensive Active Learning Framework for Indoor 3D Object Detection
Mar 20, 2025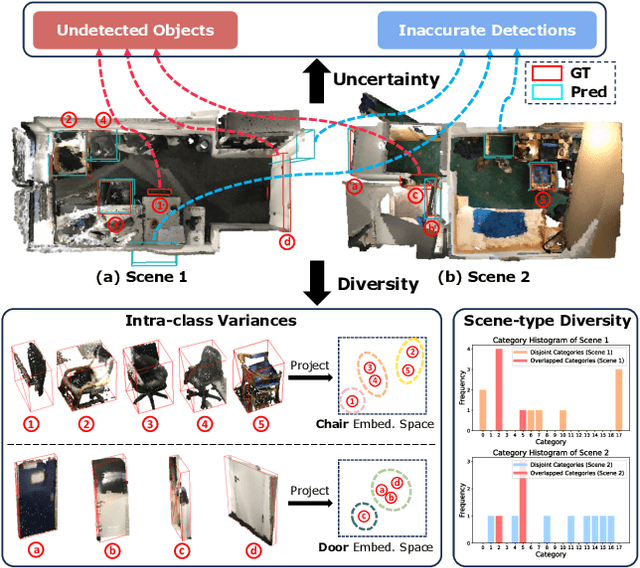

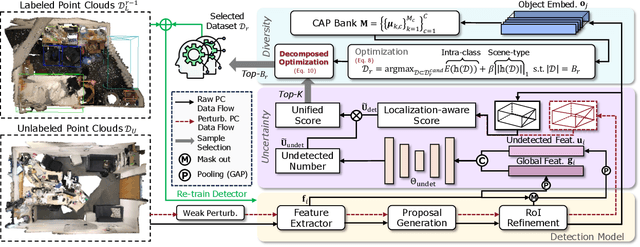
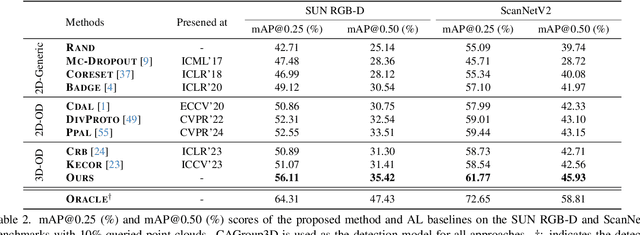
Abstract:Active learning has emerged as a promising approach to reduce the substantial annotation burden in 3D object detection tasks, spurring several initiatives in outdoor environments. However, its application in indoor environments remains unexplored. Compared to outdoor 3D datasets, indoor datasets face significant challenges, including fewer training samples per class, a greater number of classes, more severe class imbalance, and more diverse scene types and intra-class variances. This paper presents the first study on active learning for indoor 3D object detection, where we propose a novel framework tailored for this task. Our method incorporates two key criteria - uncertainty and diversity - to actively select the most ambiguous and informative unlabeled samples for annotation. The uncertainty criterion accounts for both inaccurate detections and undetected objects, ensuring that the most ambiguous samples are prioritized. Meanwhile, the diversity criterion is formulated as a joint optimization problem that maximizes the diversity of both object class distributions and scene types, using a new Class-aware Adaptive Prototype (CAP) bank. The CAP bank dynamically allocates representative prototypes to each class, helping to capture varying intra-class diversity across different categories. We evaluate our method on SUN RGB-D and ScanNetV2, where it outperforms baselines by a significant margin, achieving over 85% of fully-supervised performance with just 10% of the annotation budget.
On-the-fly Point Feature Representation for Point Clouds Analysis
Jul 31, 2024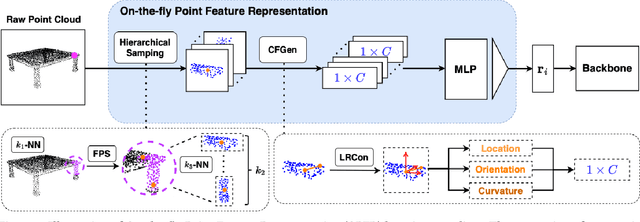

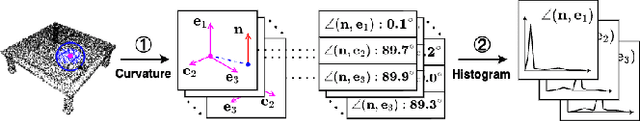

Abstract:Point cloud analysis is challenging due to its unique characteristics of unorderness, sparsity and irregularity. Prior works attempt to capture local relationships by convolution operations or attention mechanisms, exploiting geometric information from coordinates implicitly. These methods, however, are insufficient to describe the explicit local geometry, e.g., curvature and orientation. In this paper, we propose On-the-fly Point Feature Representation (OPFR), which captures abundant geometric information explicitly through Curve Feature Generator module. This is inspired by Point Feature Histogram (PFH) from computer vision community. However, the utilization of vanilla PFH encounters great difficulties when applied to large datasets and dense point clouds, as it demands considerable time for feature generation. In contrast, we introduce the Local Reference Constructor module, which approximates the local coordinate systems based on triangle sets. Owing to this, our OPFR only requires extra 1.56ms for inference (65x faster than vanilla PFH) and 0.012M more parameters, and it can serve as a versatile plug-and-play module for various backbones, particularly MLP-based and Transformer-based backbones examined in this study. Additionally, we introduce the novel Hierarchical Sampling module aimed at enhancing the quality of triangle sets, thereby ensuring robustness of the obtained geometric features. Our proposed method improves overall accuracy (OA) on ModelNet40 from 90.7% to 94.5% (+3.8%) for classification, and OA on S3DIS Area-5 from 86.4% to 90.0% (+3.6%) for semantic segmentation, respectively, building upon PointNet++ backbone. When integrated with Point Transformer backbone, we achieve state-of-the-art results on both tasks: 94.8% OA on ModelNet40 and 91.7% OA on S3DIS Area-5.
Improving 3D Occupancy Prediction through Class-balancing Loss and Multi-scale Representation
May 25, 2024Abstract:3D environment recognition is essential for autonomous driving systems, as autonomous vehicles require a comprehensive understanding of surrounding scenes. Recently, the predominant approach to define this real-life problem is through 3D occupancy prediction. It attempts to predict the occupancy states and semantic labels for all voxels in 3D space, which enhances the perception capability. Birds-Eye-View(BEV)-based perception has achieved the SOTA performance for this task. Nonetheless, this architecture fails to represent various scales of BEV features. In this paper, inspired by the success of UNet in semantic segmentation tasks, we introduce a novel UNet-like Multi-scale Occupancy Head module to relieve this issue. Furthermore, we propose the class-balancing loss to compensate for rare classes in the dataset. The experimental results on nuScenes 3D occupancy challenge dataset show the superiority of our proposed approach over baseline and SOTA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge