Jiangyi Lin
Multi-Granularity Prompts for Topic Shift Detection in Dialogue
May 23, 2023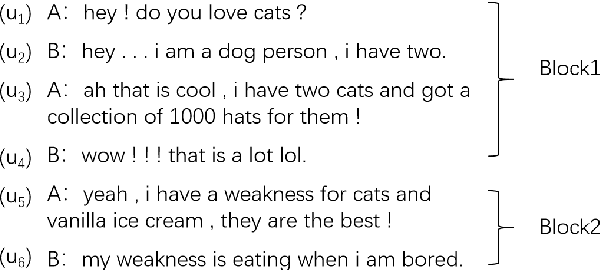
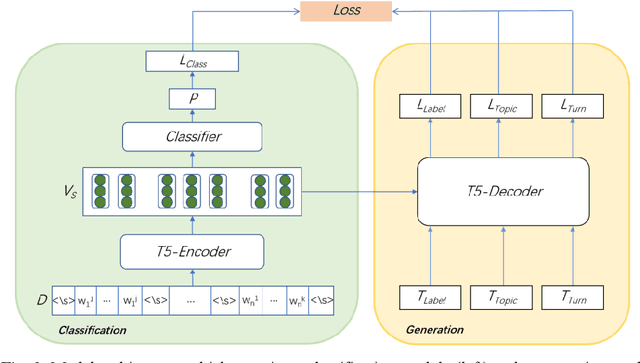
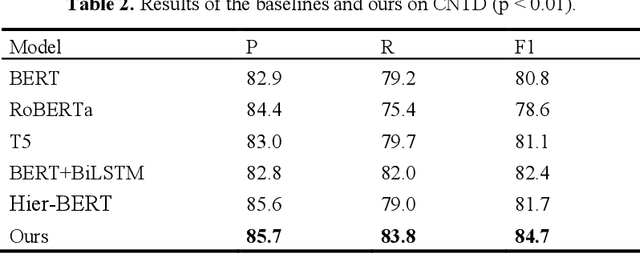
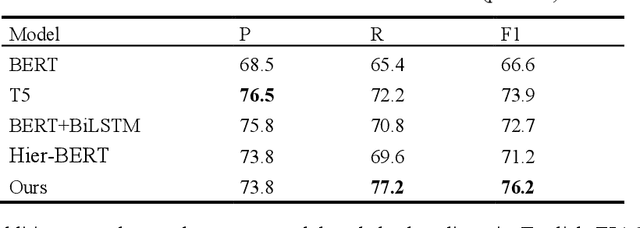
Abstract:The goal of dialogue topic shift detection is to identify whether the current topic in a conversation has changed or needs to change. Previous work focused on detecting topic shifts using pre-trained models to encode the utterance, failing to delve into the various levels of topic granularity in the dialogue and understand dialogue contents. To address the above issues, we take a prompt-based approach to fully extract topic information from dialogues at multiple-granularity, i.e., label, turn, and topic. Experimental results on our annotated Chinese Natural Topic Dialogue dataset CNTD and the publicly available English TIAGE dataset show that the proposed model outperforms the baselines. Further experiments show that the information extracted at different levels of granularity effectively helps the model comprehend the conversation topics.
Topic Shift Detection in Chinese Dialogues: Corpus and Benchmark
May 02, 2023Abstract:Dialogue topic shift detection is to detect whether an ongoing topic has shifted or should shift in a dialogue, which can be divided into two categories, i.e., response-known task and response-unknown task. Currently, only a few investigated the latter, because it is still a challenge to predict the topic shift without the response information. In this paper, we first annotate a Chinese Natural Topic Dialogue (CNTD) corpus consisting of 1308 dialogues to fill the gap in the Chinese natural conversation topic corpus. And then we focus on the response-unknown task and propose a teacher-student framework based on hierarchical contrastive learning to predict the topic shift without the response. Specifically, the response at high-level teacher-student is introduced to build the contrastive learning between the response and the context, while the label contrastive learning is constructed at low-level student. The experimental results on our Chinese CNTD and English TIAGE show the effectiveness of our proposed model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge