Jiang Lin
FreeControl: Efficient, Training-Free Structural Control via One-Step Attention Extraction
Nov 07, 2025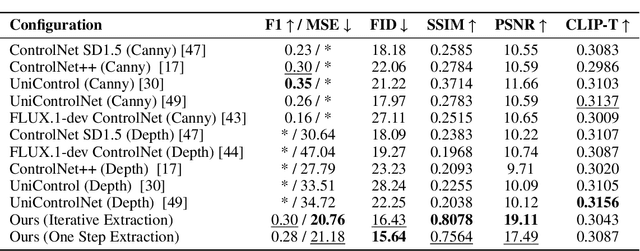
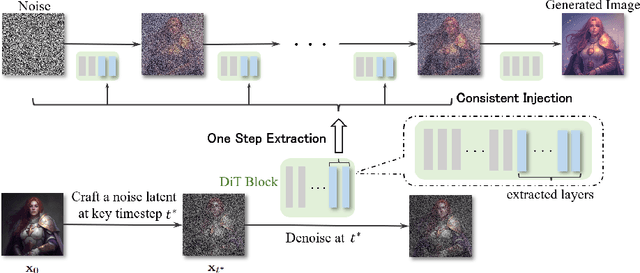
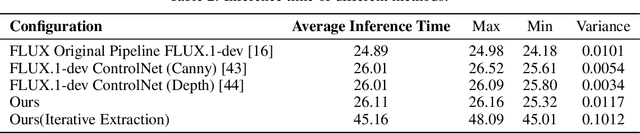

Abstract:Controlling the spatial and semantic structure of diffusion-generated images remains a challenge. Existing methods like ControlNet rely on handcrafted condition maps and retraining, limiting flexibility and generalization. Inversion-based approaches offer stronger alignment but incur high inference cost due to dual-path denoising. We present FreeControl, a training-free framework for semantic structural control in diffusion models. Unlike prior methods that extract attention across multiple timesteps, FreeControl performs one-step attention extraction from a single, optimally chosen key timestep and reuses it throughout denoising. This enables efficient structural guidance without inversion or retraining. To further improve quality and stability, we introduce Latent-Condition Decoupling (LCD): a principled separation of the key timestep and the noised latent used in attention extraction. LCD provides finer control over attention quality and eliminates structural artifacts. FreeControl also supports compositional control via reference images assembled from multiple sources - enabling intuitive scene layout design and stronger prompt alignment. FreeControl introduces a new paradigm for test-time control, enabling structurally and semantically aligned, visually coherent generation directly from raw images, with the flexibility for intuitive compositional design and compatibility with modern diffusion models at approximately 5 percent additional cost.
OmniStyle: Filtering High Quality Style Transfer Data at Scale
May 20, 2025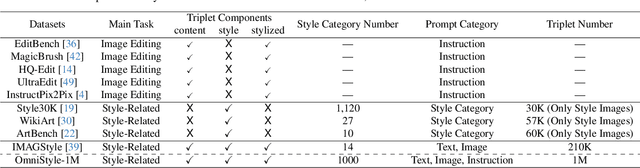
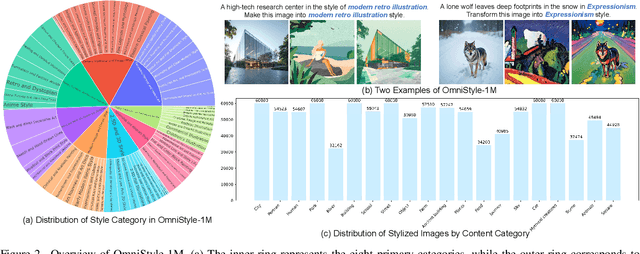
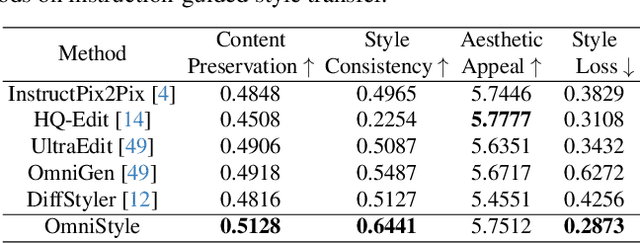
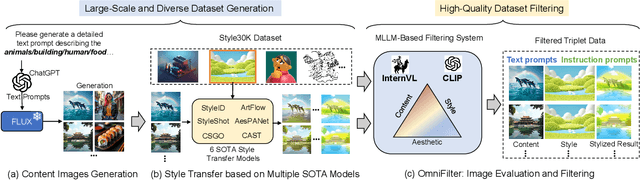
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce OmniStyle-1M, a large-scale paired style transfer dataset comprising over one million content-style-stylized image triplets across 1,000 diverse style categories, each enhanced with textual descriptions and instruction prompts. We show that OmniStyle-1M can not only enable efficient and scalable of style transfer models through supervised training but also facilitate precise control over target stylization. Especially, to ensure the quality of the dataset, we introduce OmniFilter, a comprehensive style transfer quality assessment framework, which filters high-quality triplets based on content preservation, style consistency, and aesthetic appeal. Building upon this foundation, we propose OmniStyle, a framework based on the Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture designed for high-quality and efficient style transfer. This framework supports both instruction-guided and image-guided style transfer, generating high resolution outputs with exceptional detail. Extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate OmniStyle's superior performance compared to existing approaches, highlighting its efficiency and versatility. OmniStyle-1M and its accompanying methodologies provide a significant contribution to advancing high-quality style transfer, offering a valuable resource for the research community.
Inversion-Free Video Style Transfer with Trajectory Reset Attention Control and Content-Style Bridging
Mar 10, 2025
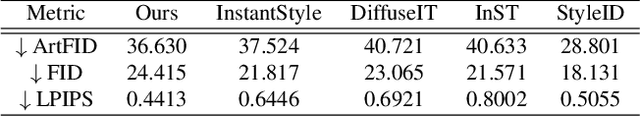
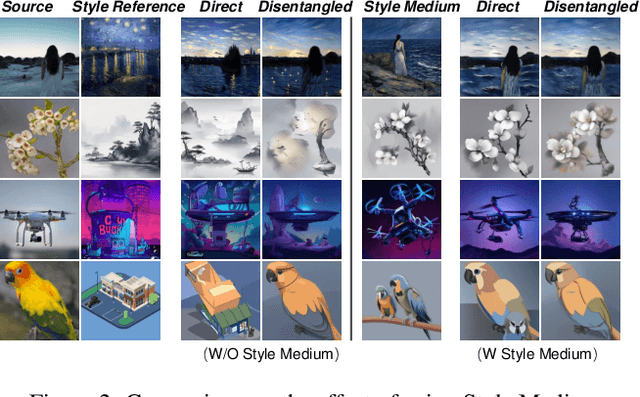
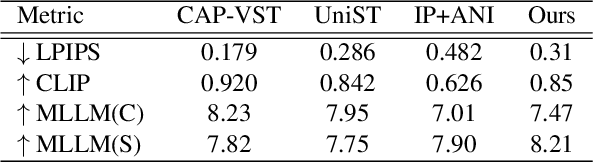
Abstract:Video style transfer aims to alter the style of a video while preserving its content. Previous methods often struggle with content leakage and style misalignment, particularly when using image-driven approaches that aim to transfer precise styles. In this work, we introduce Trajectory Reset Attention Control (TRAC), a novel method that allows for high-quality style transfer while preserving content integrity. TRAC operates by resetting the denoising trajectory and enforcing attention control, thus enhancing content consistency while significantly reducing the computational costs against inversion-based methods. Additionally, a concept termed Style Medium is introduced to bridge the gap between content and style, enabling a more precise and harmonious transfer of stylistic elements. Building upon these concepts, we present a tuning-free framework that offers a stable, flexible, and efficient solution for both image and video style transfer. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework accommodates a wide range of stylized outputs, from precise content preservation to the production of visually striking results with vibrant and expressive styles.
A Comprehensive Augmentation Framework for Anomaly Detection
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:Data augmentation methods are commonly integrated into the training of anomaly detection models. Previous approaches have primarily focused on replicating real-world anomalies or enhancing diversity, without considering that the standard of anomaly varies across different classes, potentially leading to a biased training distribution.This paper analyzes crucial traits of simulated anomalies that contribute to the training of reconstructive networks and condenses them into several methods, thus creating a comprehensive framework by selectively utilizing appropriate combinations.Furthermore, we integrate this framework with a reconstruction-based approach and concurrently propose a split training strategy that alleviates the issue of overfitting while avoiding introducing interference to the reconstruction process. The evaluations conducted on the MVTec anomaly detection dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art approach, particularly in terms of object classes. To evaluate generalizability, we generate a simulated dataset comprising anomalies with diverse characteristics since the original test samples only include specific types of anomalies and may lead to biased evaluations. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach exhibits promising potential for generalizing effectively to various unforeseen anomalies encountered in real-world scenarios.
Robust Defect Detection with Contrastive Localization
Jun 19, 2023Abstract:Defect detection aims to detect and localize regions out of the normal distribution. Previous works rely on modeling the normality to identify the defective regions, which may lead to non-ideal generalizability. This paper proposed a one-stage framework that detects defective patterns directly without the modeling process. This ability is adopted through the joint efforts of three parties: a generative adversarial network (GAN), a newly proposed scaled pattern loss, and a dynamic masked cycle-consistent auxiliary network. Explicit information that could indicate the position of defects is intentionally excluded to avoid learning any direct mapping. Experimental results on the texture class of the challenging MVTec AD dataset show that the proposed method is 2.9\% higher than the SOTA methods in F1-Score, while substantially outperforming SOTA methods in generalizability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge