Jialv He
Sensing Urban Land-Use Patterns By Integrating Google Tensorflow And Scene-Classification Models
Aug 04, 2017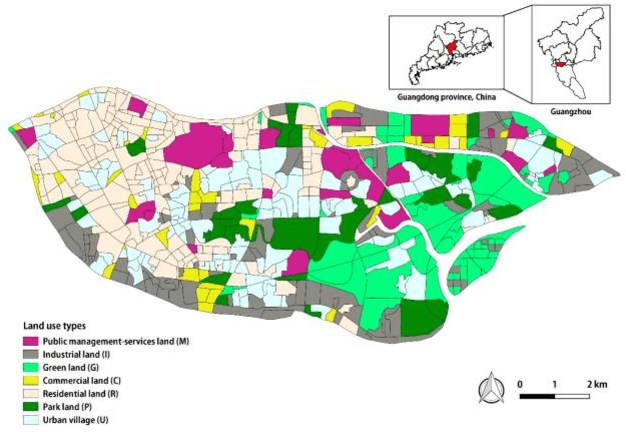
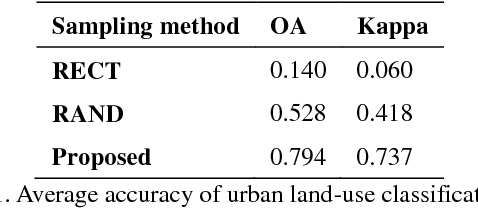
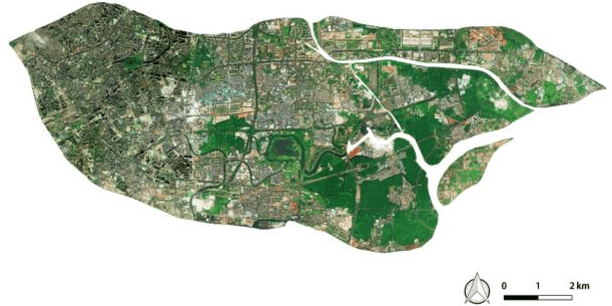
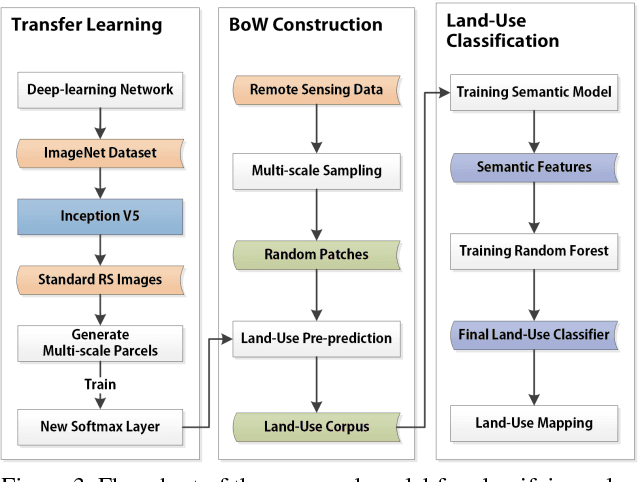
Abstract:With the rapid progress of China's urbanization, research on the automatic detection of land-use patterns in Chinese cities is of substantial importance. Deep learning is an effective method to extract image features. To take advantage of the deep-learning method in detecting urban land-use patterns, we applied a transfer-learning-based remote-sensing image approach to extract and classify features. Using the Google Tensorflow framework, a powerful convolution neural network (CNN) library was created. First, the transferred model was previously trained on ImageNet, one of the largest object-image data sets, to fully develop the model's ability to generate feature vectors of standard remote-sensing land-cover data sets (UC Merced and WHU-SIRI). Then, a random-forest-based classifier was constructed and trained on these generated vectors to classify the actual urban land-use pattern on the scale of traffic analysis zones (TAZs). To avoid the multi-scale effect of remote-sensing imagery, a large random patch (LRP) method was used. The proposed method could efficiently obtain acceptable accuracy (OA = 0.794, Kappa = 0.737) for the study area. In addition, the results show that the proposed method can effectively overcome the multi-scale effect that occurs in urban land-use classification at the irregular land-parcel level. The proposed method can help planners monitor dynamic urban land use and evaluate the impact of urban-planning schemes.
Extracting urban impervious surface from GF-1 imagery using one-class classifiers
May 13, 2017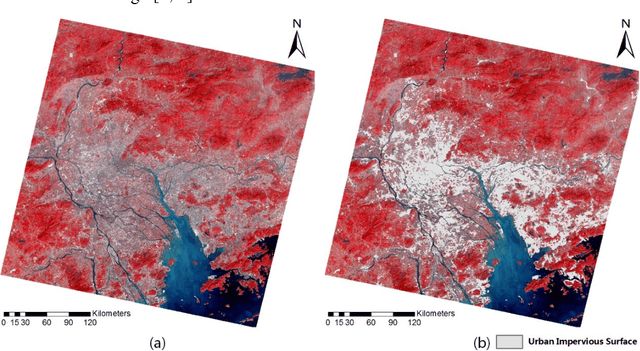
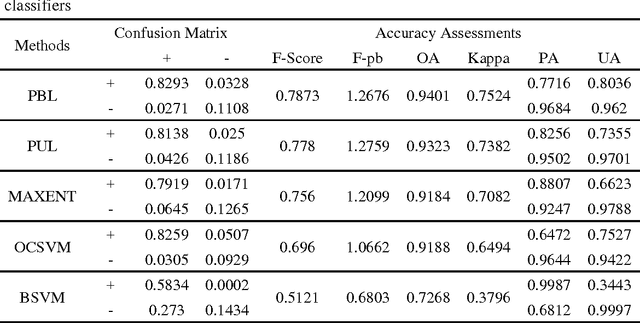
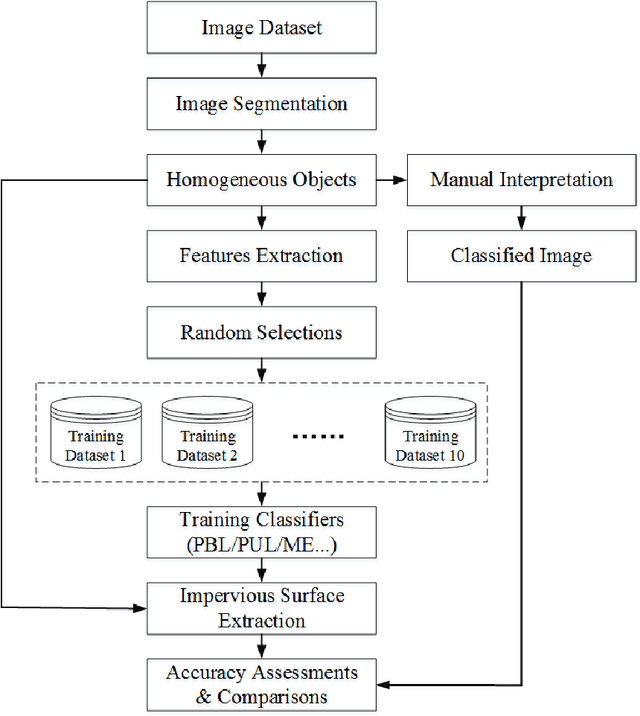
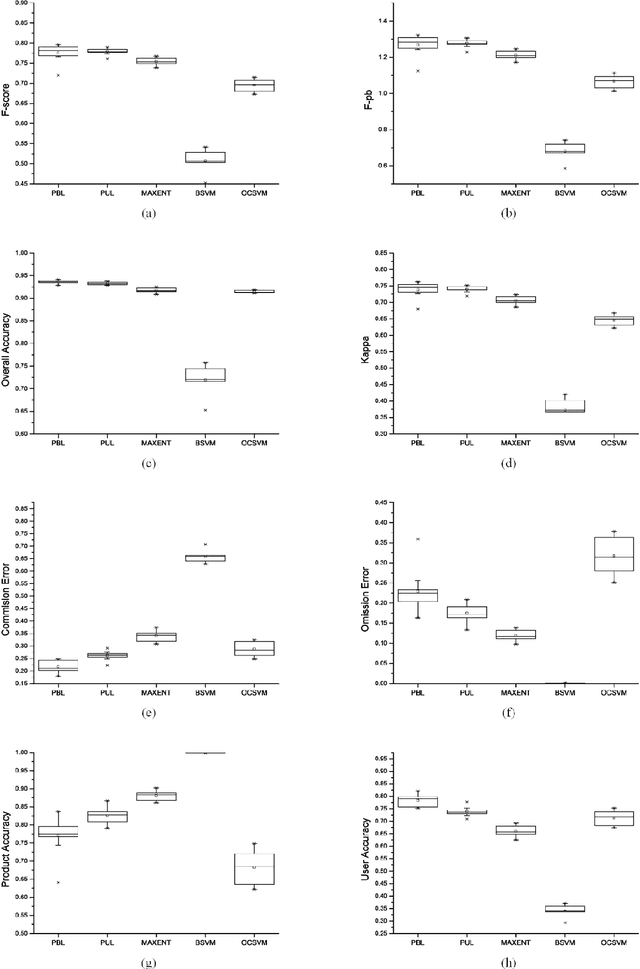
Abstract:Impervious surface area is a direct consequence of the urbanization, which also plays an important role in urban planning and environmental management. With the rapidly technical development of remote sensing, monitoring urban impervious surface via high spatial resolution (HSR) images has attracted unprecedented attention recently. Traditional multi-classes models are inefficient for impervious surface extraction because it requires labeling all needed and unneeded classes that occur in the image exhaustively. Therefore, we need to find a reliable one-class model to classify one specific land cover type without labeling other classes. In this study, we investigate several one-class classifiers, such as Presence and Background Learning (PBL), Positive Unlabeled Learning (PUL), OCSVM, BSVM and MAXENT, to extract urban impervious surface area using high spatial resolution imagery of GF-1, China's new generation of high spatial remote sensing satellite, and evaluate the classification accuracy based on artificial interpretation results. Compared to traditional multi-classes classifiers (ANN and SVM), the experimental results indicate that PBL and PUL provide higher classification accuracy, which is similar to the accuracy provided by ANN model. Meanwhile, PBL and PUL outperforms OCSVM, BSVM, MAXENT and SVM models. Hence, the one-class classifiers only need a small set of specific samples to train models without losing predictive accuracy, which is supposed to gain more attention on urban impervious surface extraction or other one specific land cover type.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge