Jiachen Wei
Beyond Target-Level: ISAC-Enabled Event-Level Sensing for Behavioral Intention Prediction
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) holds great promise for enabling event-level sensing, such as behavioral intention prediction (BIP) in autonomous driving, particularly under non-line-of-sight (NLoS) or adverse weather conditions where conventional sensors degrade. However, as a key instance of event-level sensing, ISAC-based BIP remains unexplored. To address this gap, we propose an ISAC-enabled BIP framework and validate its feasibility and effectiveness through extensive simulations. Our framework achieves robust performance in safety-critical scenarios, improving the F1-score by 11.4% over sensor-based baselines in adverse weather, thereby demonstrating ISAC's potential for intelligent event-level sensing.
UAV's Rotor Micro-Doppler Feature Extraction Using Integrated Sensing and Communication Signal: Algorithm Design and Testbed Evaluation
Aug 29, 2024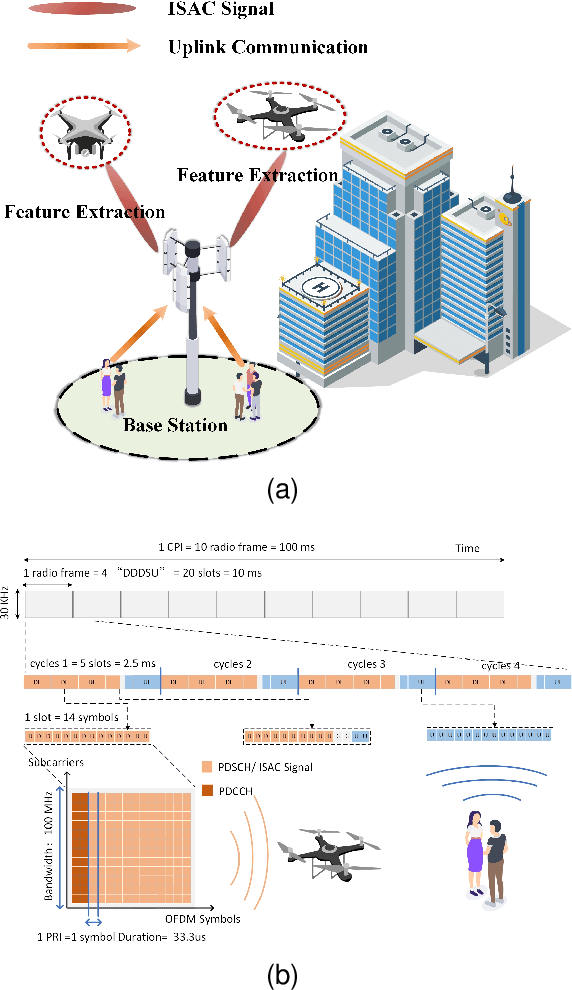
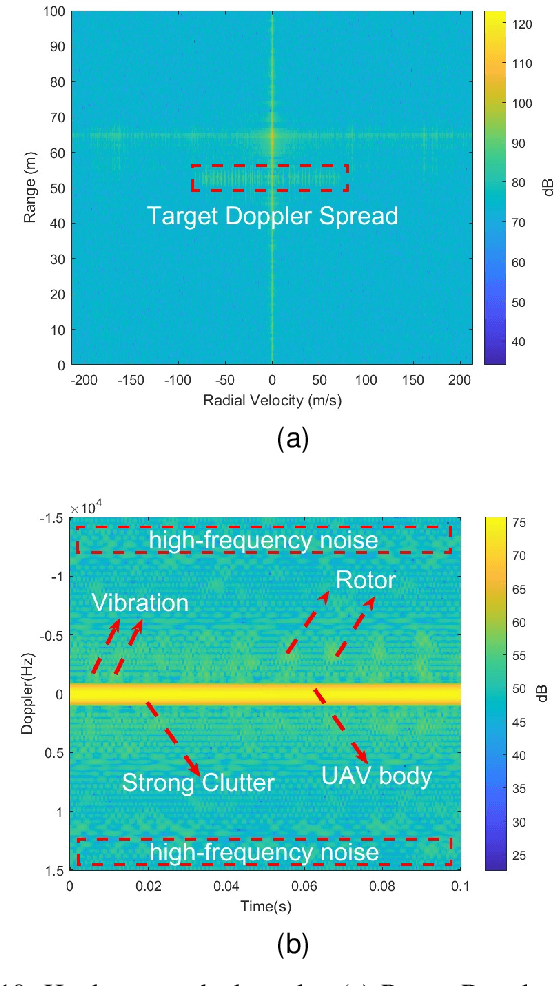
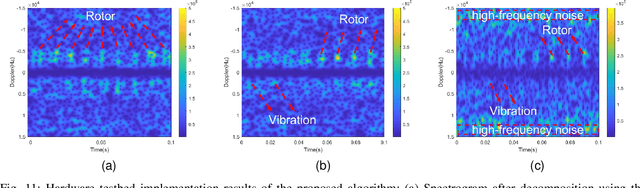
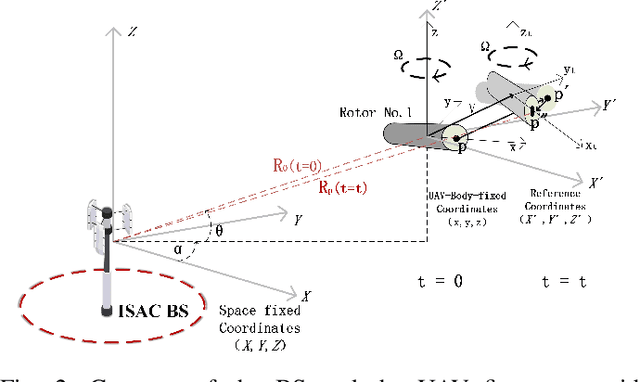
Abstract:With the rapid application of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in urban areas, the identification and tracking of hovering UAVs have become critical challenges, significantly impacting the safety of aircraft take-off and landing operations. As a promising technology for 6G mobile systems, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) can be used to detect high-mobility UAVs with a low deployment cost. The micro-Doppler signals from UAV rotors can be leveraged to address the detection of low-mobility and hovering UAVs using ISAC signals. However, determining whether the frame structure of the ISAC system can be used to identify UAVs, and how to accurately capture the weak rotor micro-Doppler signals of UAVs in complex environments, remain two challenging problems. This paper first proposes a novel frame structure for UAV micro-Doppler extraction and the representation of UAV micro-Doppler signals within the channel state information (CSI). Furthermore, to address complex environments and the interference caused by UAV body vibrations, the rotor micro-Doppler null space pursuit (rmD-NSP) algorithm and the feature extraction algorithm synchroextracting transform (SET) are designed to effectively separate UAV's rotor micro-Doppler signals and enhance their features in the spectrogram. Finally, both simulation and hardware testbed demonstrate that the proposed rmD-NSP algorithm enables the ISAC base station (BS) to accurately and completely extract UAV's rotor micro-Doppler signals. Within a 0.1s observation period, ISAC BS successfully captures eight rotations of the DJI M300 RTK UAV's rotor in urban environments. Compared to the existing AM-FM NSP and NSP signal decomposition algorithms, the integrity of the rotor micro-Doppler features is improved by 60%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge