Jiace Sun
Molecular-orbital-based Machine Learning for Open-shell and Multi-reference Systems with Kernel Addition Gaussian Process Regression
Jul 17, 2022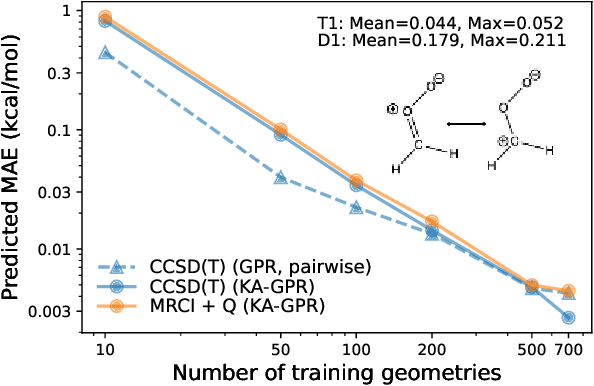
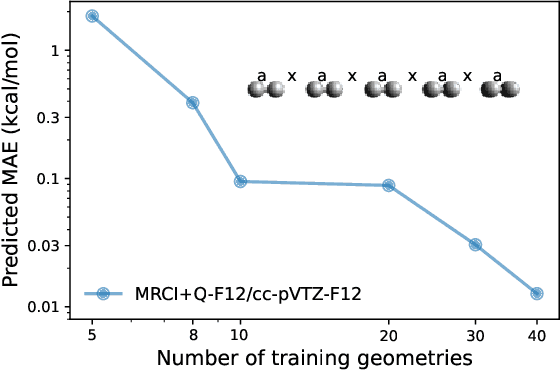
Abstract:We introduce a novel machine learning strategy, kernel addition Gaussian process regression (KA-GPR), in molecular-orbital-based machine learning (MOB-ML) to learn the total correlation energies of general electronic structure theories for closed- and open-shell systems by introducing a machine learning strategy. The learning efficiency of MOB-ML (KA-GPR) is the same as the original MOB-ML method for the smallest criegee molecule, which is a closed-shell molecule with multi-reference characters. In addition, the prediction accuracies of different small free radicals could reach the chemical accuracy of 1 kcal/mol by training on one example structure. Accurate potential energy surfaces for the H10 chain (closed-shell) and water OH bond dissociation (open-shell) could also be generated by MOB-ML (KA-GPR). To explore the breadth of chemical systems that KA-GPR can describe, we further apply MOB-ML to accurately predict the large benchmark datasets for closed- (QM9, QM7b-T, GDB-13-T) and open-shell (QMSpin) molecules.
Molecular Dipole Moment Learning via Rotationally Equivariant Gaussian Process Regression with Derivatives in Molecular-orbital-based Machine Learning
May 31, 2022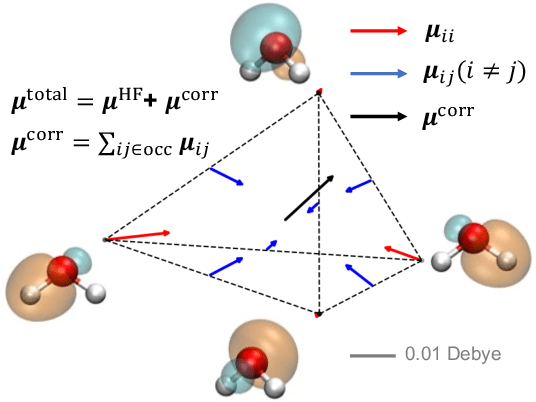
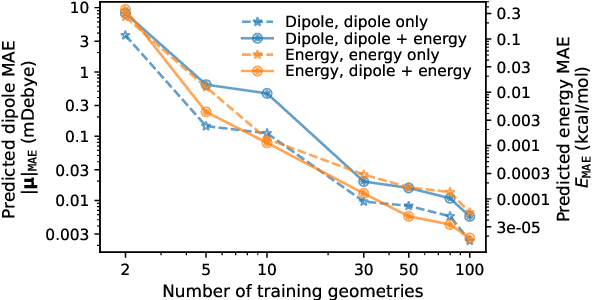
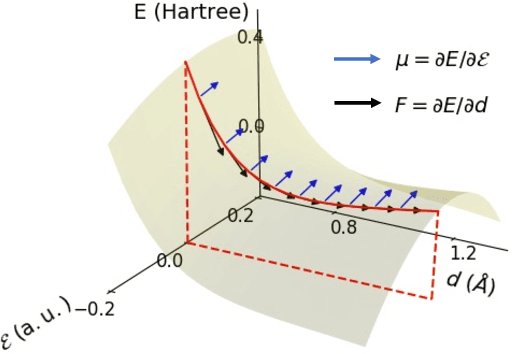
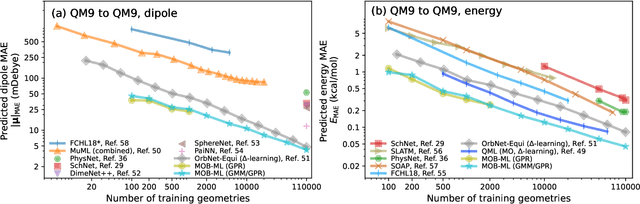
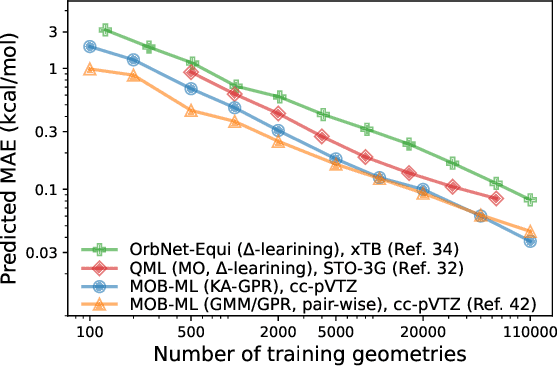
Abstract:This study extends the accurate and transferable molecular-orbital-based machine learning (MOB-ML) approach to modeling the contribution of electron correlation to dipole moments at the cost of Hartree-Fock computations. A molecular-orbital-based (MOB) pairwise decomposition of the correlation part of the dipole moment is applied, and these pair dipole moments could be further regressed as a universal function of molecular orbitals (MOs). The dipole MOB features consist of the energy MOB features and their responses to electric fields. An interpretable and rotationally equivariant Gaussian process regression (GPR) with derivatives algorithm is introduced to learn the dipole moment more efficiently. The proposed problem setup, feature design, and ML algorithm are shown to provide highly-accurate models for both dipole moment and energies on water and fourteen small molecules. To demonstrate the ability of MOB-ML to function as generalized density-matrix functionals for molecular dipole moments and energies of organic molecules, we further apply the proposed MOB-ML approach to train and test the molecules from the QM9 dataset. The application of local scalable GPR with Gaussian mixture model unsupervised clustering (GMM/GPR) scales up MOB-ML to a large-data regime while retaining the prediction accuracy. In addition, compared with literature results, MOB-ML provides the best test MAEs of 4.21 mDebye and 0.045 kcal/mol for dipole moment and energy models, respectively, when training on 110000 QM9 molecules. The excellent transferability of the resulting QM9 models is also illustrated by the accurate predictions for four different series of peptides.
Accurate Molecular-Orbital-Based Machine Learning Energies via Unsupervised Clustering of Chemical Space
Apr 21, 2022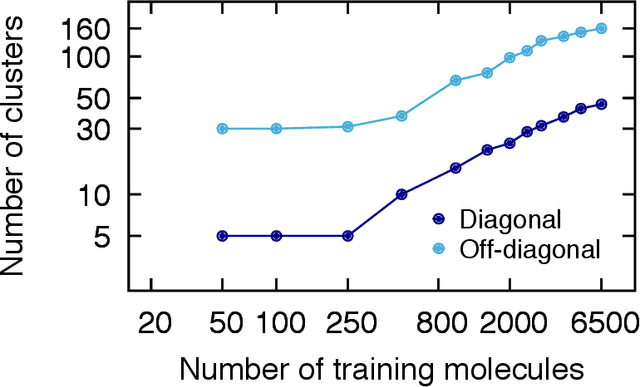
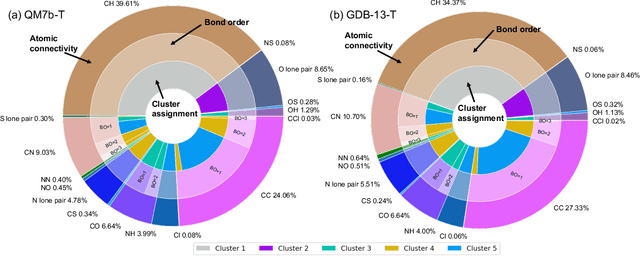
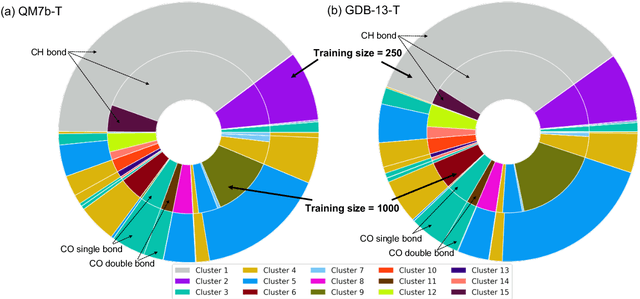
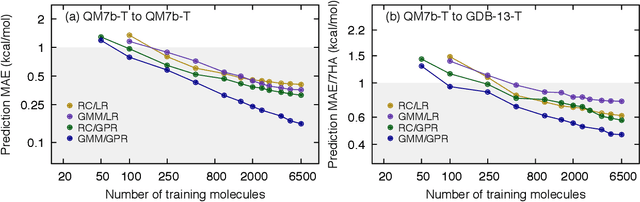
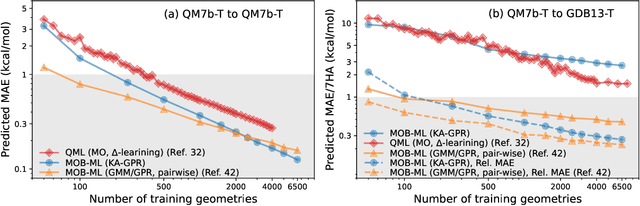
Abstract:We introduce an unsupervised clustering algorithm to improve training efficiency and accuracy in predicting energies using molecular-orbital-based machine learning (MOB-ML). This work determines clusters via the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) in an entirely automatic manner and simplifies an earlier supervised clustering approach [J. Chem. Theory Comput., 15, 6668 (2019)] by eliminating both the necessity for user-specified parameters and the training of an additional classifier. Unsupervised clustering results from GMM have the advantage of accurately reproducing chemically intuitive groupings of frontier molecular orbitals and having improved performance with an increasing number of training examples. The resulting clusters from supervised or unsupervised clustering is further combined with scalable Gaussian process regression (GPR) or linear regression (LR) to learn molecular energies accurately by generating a local regression model in each cluster. Among all four combinations of regressors and clustering methods, GMM combined with scalable exact Gaussian process regression (GMM/GPR) is the most efficient training protocol for MOB-ML. The numerical tests of molecular energy learning on thermalized datasets of drug-like molecules demonstrate the improved accuracy, transferability, and learning efficiency of GMM/GPR over not only other training protocols for MOB-ML, i.e., supervised regression-clustering combined with GPR(RC/GPR) and GPR without clustering. GMM/GPR also provide the best molecular energy predictions compared with the ones from literature on the same benchmark datasets. With a lower scaling, GMM/GPR has a 10.4-fold speedup in wall-clock training time compared with scalable exact GPR with a training size of 6500 QM7b-T molecules.
Molecular Energy Learning Using Alternative Blackbox Matrix-Matrix Multiplication Algorithm for Exact Gaussian Process
Sep 20, 2021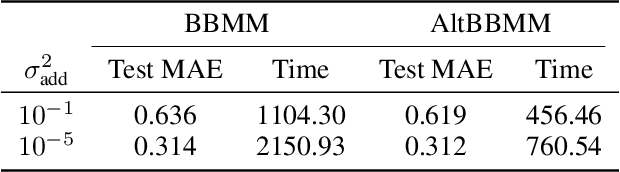
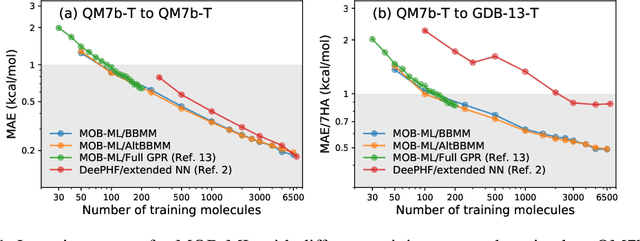

Abstract:We present an application of the blackbox matrix-matrix multiplication (BBMM) algorithm to scale up the Gaussian Process (GP) training of molecular energies in the molecular-orbital based machine learning (MOB-ML) framework. An alternative implementation of BBMM (AltBBMM) is also proposed to train more efficiently (over four-fold speedup) with the same accuracy and transferability as the original BBMM implementation. The training of MOB-ML was limited to 220 molecules, and BBMM and AltBBMM scale the training of MOB-ML up by over 30 times to 6500 molecules (more than a million pair energies). The accuracy and transferability of both algorithms are examined on the benchmark datasets of organic molecules with 7 and 13 heavy atoms. These lower-scaling implementations of the GP preserve the state-of-the-art learning efficiency in the low-data regime while extending it to the large-data regime with better accuracy than other available machine learning works on molecular energies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge