Jessica Leu
Autonomous Vehicle Parking in Dynamic Environments: An Integrated System with Prediction and Motion Planning
Apr 26, 2022



Abstract:This paper presents an integrated motion planning system for autonomous vehicle (AV) parking in the presence of other moving vehicles. The proposed system includes 1) a hybrid environment predictor that predicts the motions of the surrounding vehicles and 2) a strategic motion planner that reacts to the predictions. The hybrid environment predictor performs short-term predictions via an extended Kalman filter and an adaptive observer. It also combines short-term predictions with a driver behavior cost-map to make long-term predictions. The strategic motion planner comprises 1) a model predictive control-based safety controller for trajectory tracking; 2) a search-based retreating planner for finding an evasion path in an emergency; 3) an optimization-based repairing planner for planning a new path when the original path is invalidated. Simulation validation demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method in terms of initial planning, motion prediction, safe tracking, retreating in an emergency, and trajectory repairing.
Long-Horizon Motion Planning via Sampling and Segmented Trajectory Optimization
Apr 17, 2022
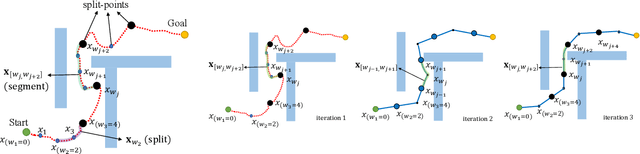
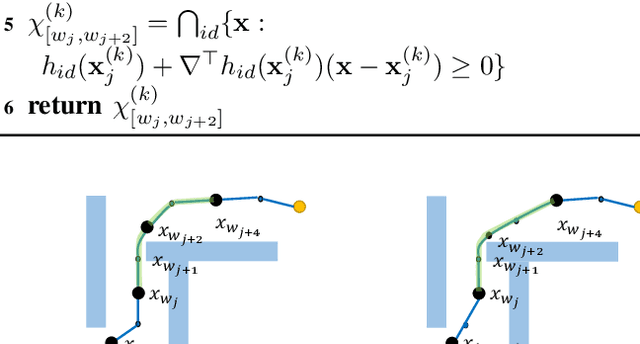
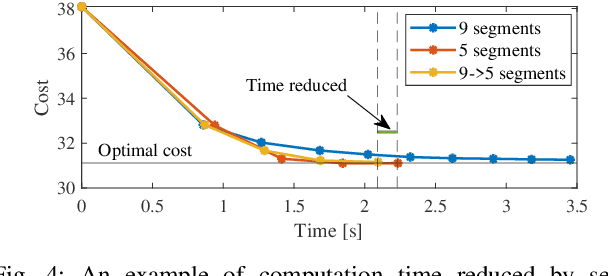
Abstract:This paper presents a hybrid robot motion planner that generates long-horizon motion plans for robot navigation in environments with obstacles. We propose a hybrid planner, RRT* with segmented trajectory optimization (RRT*-sOpt), which combines the merits of sampling-based planning, optimization-based planning, and trajectory splitting to quickly plan for a collision-free and dynamically-feasible motion plan. When generating a plan, the RRT* layer quickly samples a semi-optimal path and sets it as an initial reference path. Then, the sOpt layer splits the reference path and performs optimization on each segment. It then splits the new trajectory again and repeats the process until the whole trajectory converges. We also propose to reduce the number of segments before convergence with the aim of further reducing computation time. Simulation results show that RRT*-sOpt benefits from the hybrid structure with trajectory splitting and performs robustly in various robot platforms and scenarios.
Robust Task Planning for Assembly Lines with Human-Robot Collaboration
Apr 17, 2022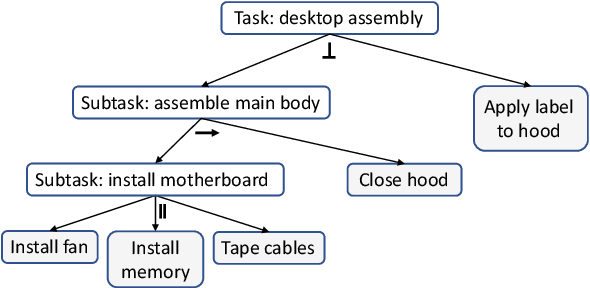
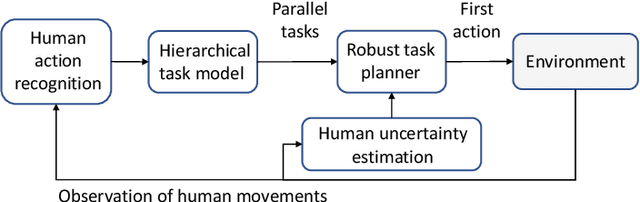
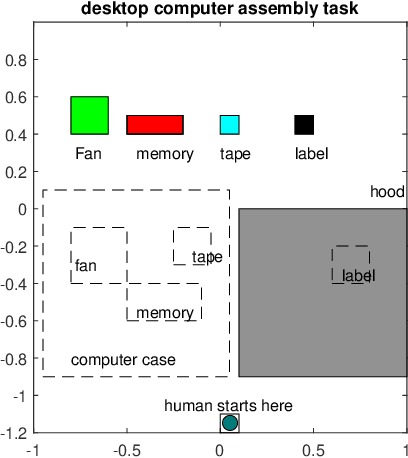
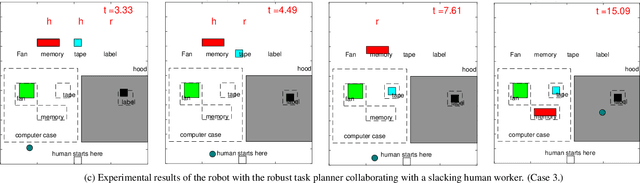
Abstract:Efficient and robust task planning for a human-robot collaboration (HRC) system remains challenging. The human-aware task planner needs to assign jobs to both robots and human workers so that they can work collaboratively to achieve better time efficiency. However, the complexity of the tasks and the stochastic nature of the human collaborators bring challenges to such task planning. To reduce the complexity of the planning problem, we utilize the hierarchical task model, which explicitly captures the sequential and parallel relationships of the task. We model human movements with the sigma-lognormal functions to account for human-induced uncertainties. A human action model adaptation scheme is applied during run-time, and it provides a measure for modeling the human-induced uncertainties. We propose a sampling-based method to estimate human job completion time uncertainties. Next, we propose a robust task planner, which formulates the planning problem as a robust optimization problem by considering the task structure and the uncertainties. We conduct simulations of a robot arm collaborating with a human worker in an electronics assembly setting. The results show that our proposed planner can reduce task completion time when human-induced uncertainties occur compared to the baseline planner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge