Jessica Borja-Diaz
Grounding Language with Visual Affordances over Unstructured Data
Oct 10, 2022



Abstract:Recent works have shown that Large Language Models (LLMs) can be applied to ground natural language to a wide variety of robot skills. However, in practice, learning multi-task, language-conditioned robotic skills typically requires large-scale data collection and frequent human intervention to reset the environment or help correcting the current policies. In this work, we propose a novel approach to efficiently learn general-purpose language-conditioned robot skills from unstructured, offline and reset-free data in the real world by exploiting a self-supervised visuo-lingual affordance model, which requires annotating as little as 1% of the total data with language. We evaluate our method in extensive experiments both in simulated and real-world robotic tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the challenging CALVIN benchmark and learning over 25 distinct visuomotor manipulation tasks with a single policy in the real world. We find that when paired with LLMs to break down abstract natural language instructions into subgoals via few-shot prompting, our method is capable of completing long-horizon, multi-tier tasks in the real world, while requiring an order of magnitude less data than previous approaches. Code and videos are available at http://hulc2.cs.uni-freiburg.de
Affordance Learning from Play for Sample-Efficient Policy Learning
Mar 01, 2022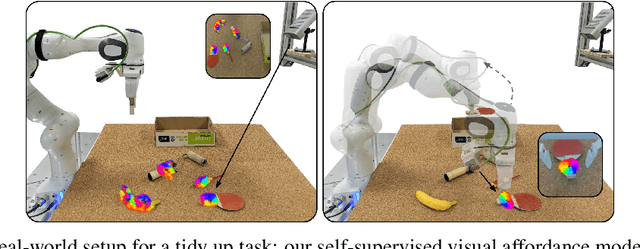
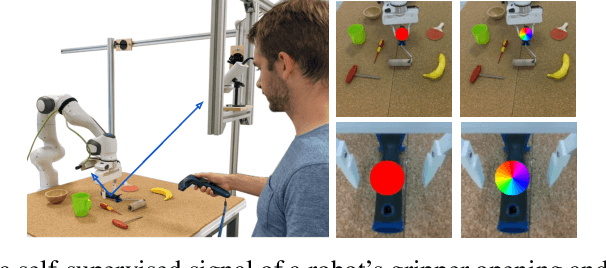
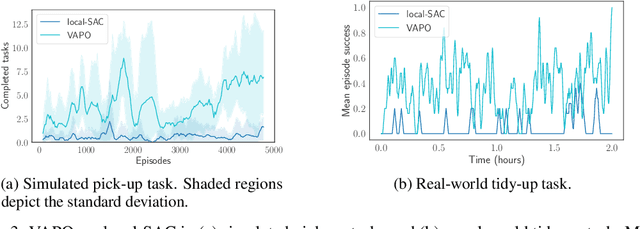
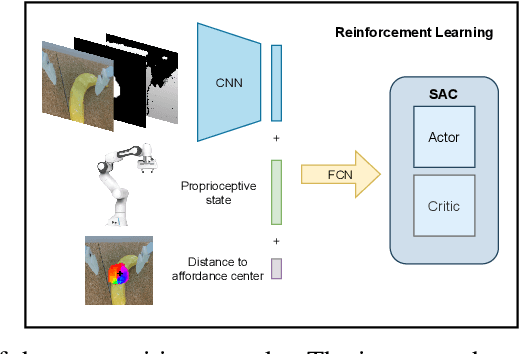
Abstract:Robots operating in human-centered environments should have the ability to understand how objects function: what can be done with each object, where this interaction may occur, and how the object is used to achieve a goal. To this end, we propose a novel approach that extracts a self-supervised visual affordance model from human teleoperated play data and leverages it to enable efficient policy learning and motion planning. We combine model-based planning with model-free deep reinforcement learning (RL) to learn policies that favor the same object regions favored by people, while requiring minimal robot interactions with the environment. We evaluate our algorithm, Visual Affordance-guided Policy Optimization (VAPO), with both diverse simulation manipulation tasks and real world robot tidy-up experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our affordance-guided policies. We find that our policies train 4x faster than the baselines and generalize better to novel objects because our visual affordance model can anticipate their affordance regions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge