Jeroen D. Hol
Using Inertial Sensors for Position and Orientation Estimation
Jun 10, 2018



Abstract:In recent years, MEMS inertial sensors (3D accelerometers and 3D gyroscopes) have become widely available due to their small size and low cost. Inertial sensor measurements are obtained at high sampling rates and can be integrated to obtain position and orientation information. These estimates are accurate on a short time scale, but suffer from integration drift over longer time scales. To overcome this issue, inertial sensors are typically combined with additional sensors and models. In this tutorial we focus on the signal processing aspects of position and orientation estimation using inertial sensors. We discuss different modeling choices and a selected number of important algorithms. The algorithms include optimization-based smoothing and filtering as well as computationally cheaper extended Kalman filter and complementary filter implementations. The quality of their estimates is illustrated using both experimental and simulated data.
* 90 pages, 38 figures
A Scalable and Distributed Solution to the Inertial Motion Capture Problem
Aug 18, 2016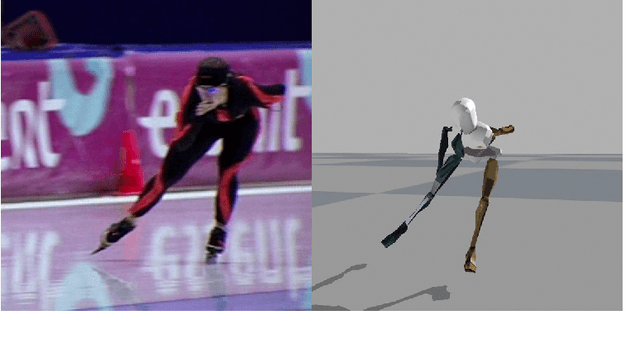
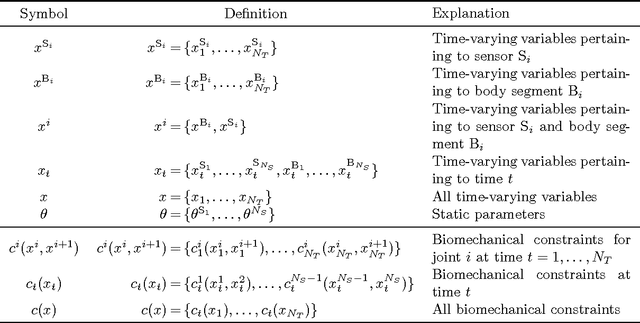
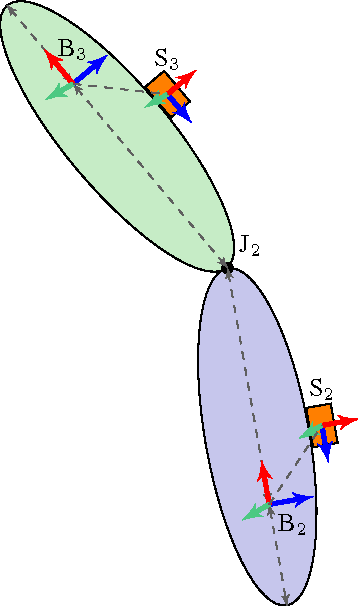
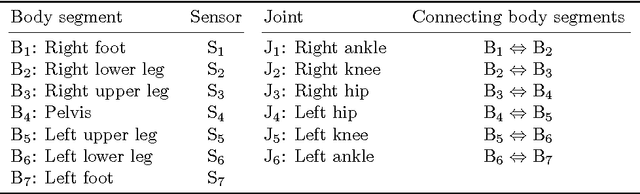
Abstract:In inertial motion capture, a multitude of body segments are equipped with inertial sensors, consisting of 3D accelerometers and 3D gyroscopes. Using an optimization-based approach to solve the motion capture problem allows for natural inclusion of biomechanical constraints and for modeling the connection of the body segments at the joint locations. The computational complexity of solving this problem grows both with the length of the data set and with the number of sensors and body segments considered. In this work, we present a scalable and distributed solution to this problem using tailored message passing, capable of exploiting the structure that is inherent in the problem. As a proof-of-concept we apply our algorithm to data from a lower body configuration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge