Jeremy Morgan
SyncTwin: Fast Digital Twin Construction and Synchronization for Safe Robotic Grasping
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Accurate and safe grasping under dynamic and visually occluded conditions remains a core challenge in real-world robotic manipulation. We present SyncTwin, a digital twin framework that unifies fast 3D scene reconstruction and real-to-sim synchronization for robust and safety-aware grasping in such environments. In the offline stage, we employ VGGT to rapidly reconstruct object-level 3D assets from RGB images, forming a reusable geometry library for simulation. During execution, SyncTwin continuously synchronizes the digital twin by tracking real-world object states via point cloud segmentation updates and aligning them through colored-ICP registration. The updated twin enables motion planners to compute collision-free and dynamically feasible trajectories in simulation, which are safely executed on the real robot through a closed real-to-sim-to-real loop. Experiments in dynamic and occluded scenes show that SyncTwin improves grasp accuracy and motion safety, demonstrating the effectiveness of digital-twin synchronization for real-world robotic execution.
CppFlow: Generative Inverse Kinematics for Efficient and Robust Cartesian Path Planning
Sep 16, 2023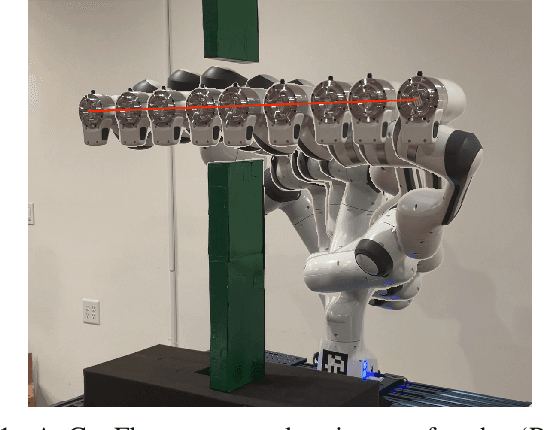
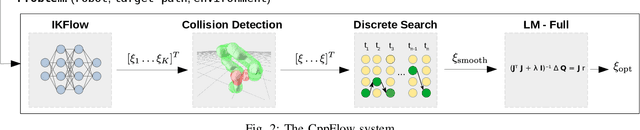
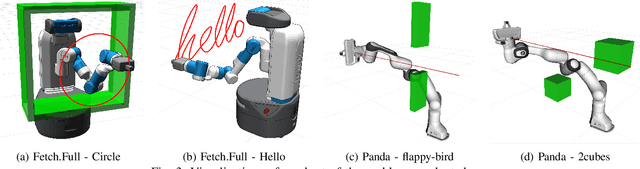
Abstract:In this work we present CppFlow - a novel and performant planner for the Cartesian Path Planning problem, which finds valid trajectories up to 129x faster than current methods, while also succeeding on more difficult problems where others fail. At the core of the proposed algorithm is the use of a learned, generative Inverse Kinematics solver, which is able to efficiently produce promising entire candidate solution trajectories on the GPU. Precise, valid solutions are then found through classical approaches such as differentiable programming, global search, and optimization. In combining approaches from these two paradigms we get the best of both worlds - efficient approximate solutions from generative AI which are made exact using the guarantees of traditional planning and optimization. We evaluate our system against other state of the art methods on a set of established baselines as well as new ones introduced in this work and find that our method significantly outperforms others in terms of the time to find a valid solution and planning success rate, and performs comparably in terms of trajectory length over time. The work is made open source and available for use upon acceptance.
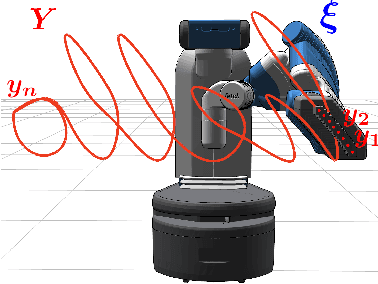
IKFlow: Generating Diverse Inverse Kinematics Solutions
Nov 17, 2021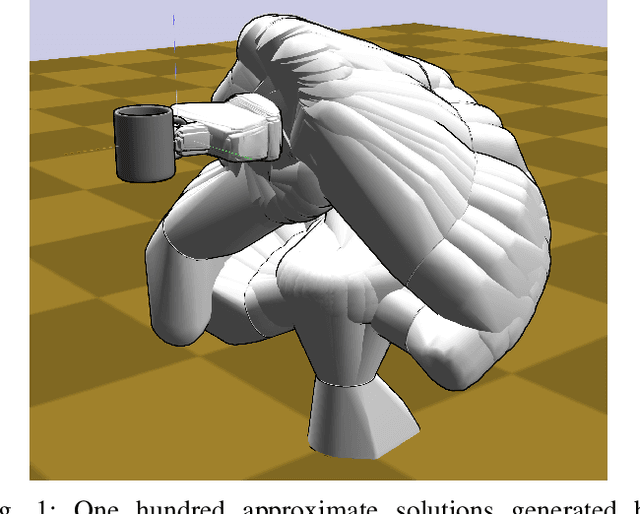
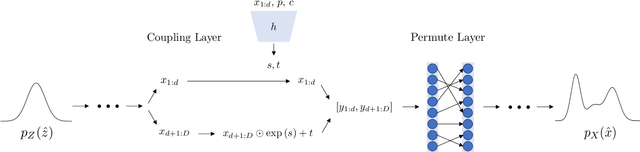
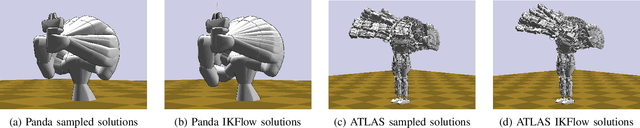
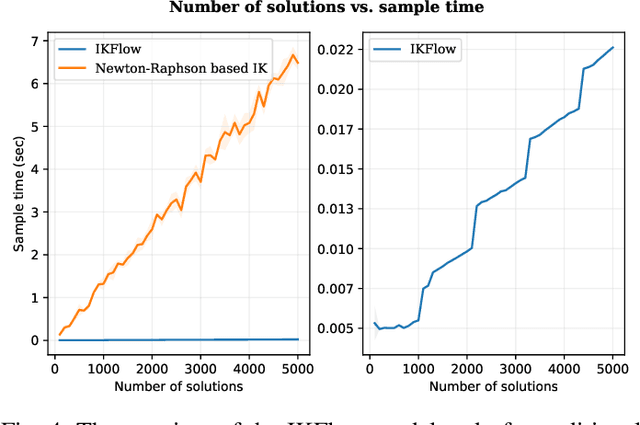
Abstract:Inverse kinematics - finding joint poses that reach a given Cartesian-space end-effector pose - is a common operation in robotics, since goals and waypoints are typically defined in Cartesian space, but robots must be controlled in joint space. However, existing inverse kinematics solvers return a single solution pose, where systems with more than 6 degrees of freedom support infinitely many such solutions, which can be useful in the presence of constraints, pose preferences, or obstacles. We introduce a method that uses a deep neural network to learn to generate a diverse set of samples from the solution space of such kinematic chains. The resulting samples can be generated quickly (2000 solutions in under 10ms) and accurately (to within 10 millimeters and 2 degrees of an exact solution) and can be rapidly refined by classical methods if necessary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge