Jennifer Villareale
Improving Fairness in Adaptive Social Exergames via Shapley Bandits
Feb 21, 2023Abstract:Algorithmic fairness is an essential requirement as AI becomes integrated in society. In the case of social applications where AI distributes resources, algorithms often must make decisions that will benefit a subset of users, sometimes repeatedly or exclusively, while attempting to maximize specific outcomes. How should we design such systems to serve users more fairly? This paper explores this question in the case where a group of users works toward a shared goal in a social exergame called Step Heroes. We identify adverse outcomes in traditional multi-armed bandits (MABs) and formalize the Greedy Bandit Problem. We then propose a solution based on a new type of fairness-aware multi-armed bandit, Shapley Bandits. It uses the Shapley Value for increasing overall player participation and intervention adherence rather than the maximization of total group output, which is traditionally achieved by favoring only high-performing participants. We evaluate our approach via a user study (n=46). Our results indicate that our Shapley Bandits effectively mediates the Greedy Bandit Problem and achieves better user retention and motivation across the participants.
Dealing with Adversarial Player Strategies in the Neural Network Game iNNk through Ensemble Learning
Jul 05, 2021
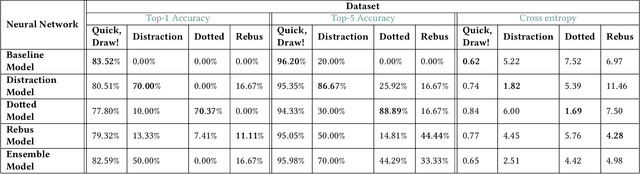
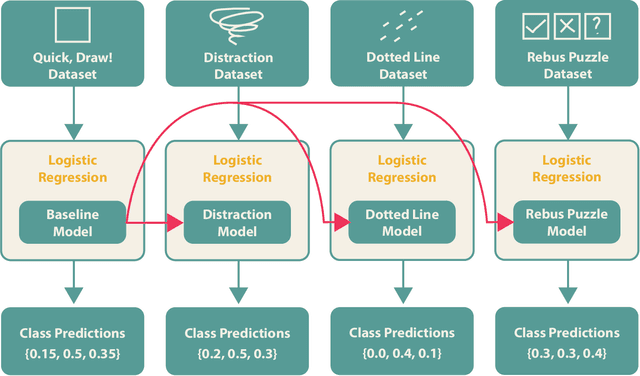
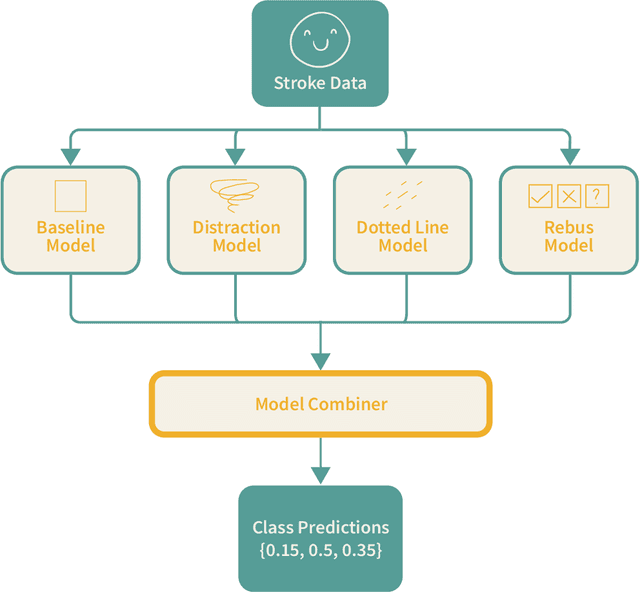
Abstract:Applying neural network (NN) methods in games can lead to various new and exciting game dynamics not previously possible. However, they also lead to new challenges such as the lack of large, clean datasets, varying player skill levels, and changing gameplay strategies. In this paper, we focus on the adversarial player strategy aspect in the game iNNk, in which players try to communicate secret code words through drawings with the goal of not being deciphered by a NN. Some strategies exploit weaknesses in the NN that consistently trick it into making incorrect classifications, leading to unbalanced gameplay. We present a method that combines transfer learning and ensemble methods to obtain a data-efficient adaptation to these strategies. This combination significantly outperforms the baseline NN across all adversarial player strategies despite only being trained on a limited set of adversarial examples. We expect the methods developed in this paper to be useful for the rapidly growing field of NN-based games, which will require new approaches to deal with unforeseen player creativity.
Personalization Paradox in Behavior Change Apps: Lessons from a Social Comparison-Based Personalized App for Physical Activity
Feb 11, 2021
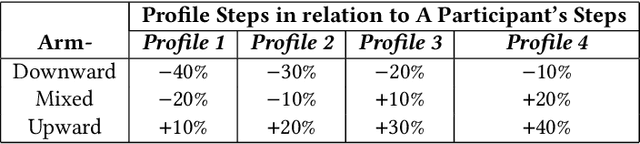
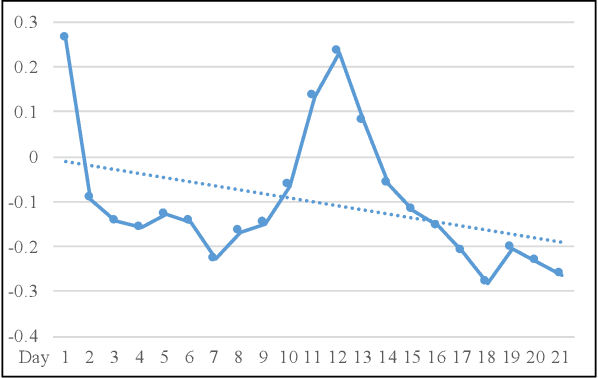
Abstract:Social comparison-based features are widely used in social computing apps. However, most existing apps are not grounded in social comparison theories and do not consider individual differences in social comparison preferences and reactions. This paper is among the first to automatically personalize social comparison targets. In the context of an m-health app for physical activity, we use artificial intelligence (AI) techniques of multi-armed bandits. Results from our user study (n=53) indicate that there is some evidence that motivation can be increased using the AI-based personalization of social comparison. The detected effects achieved small-to-moderate effect sizes, illustrating the real-world implications of the intervention for enhancing motivation and physical activity. In addition to design implications for social comparison features in social apps, this paper identified the personalization paradox, the conflict between user modeling and adaptation, as a key design challenge of personalized applications for behavior change. Additionally, we propose research directions to mitigate this Personalization Paradox.
Player-AI Interaction: What Neural Network Games Reveal About AI as Play
Jan 18, 2021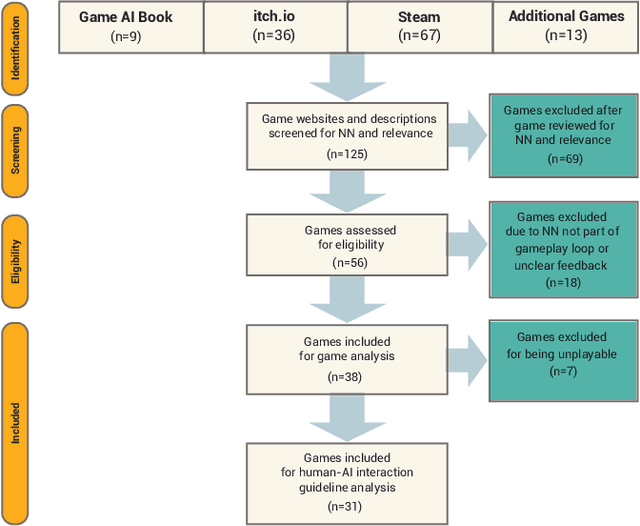
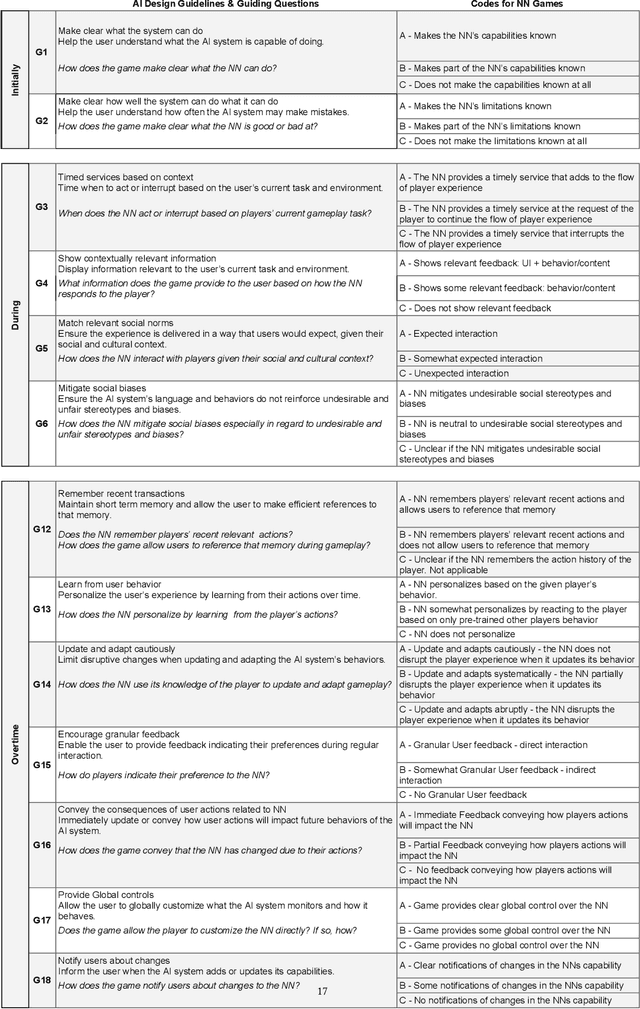
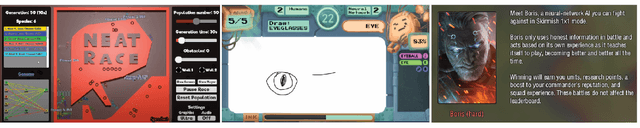
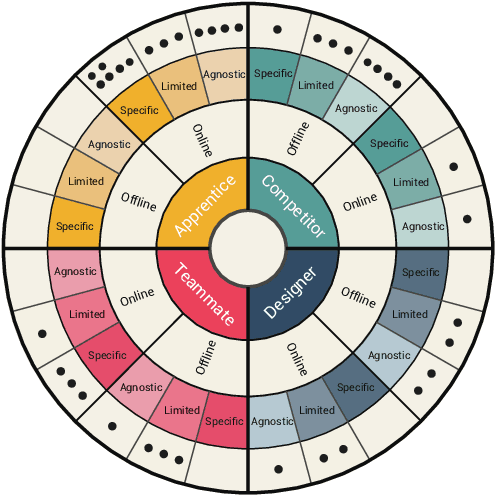
Abstract:The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) bring human-AI interaction to the forefront of HCI research. This paper argues that games are an ideal domain for studying and experimenting with how humans interact with AI. Through a systematic survey of neural network games (n = 38), we identified the dominant interaction metaphors and AI interaction patterns in these games. In addition, we applied existing human-AI interaction guidelines to further shed light on player-AI interaction in the context of AI-infused systems. Our core finding is that AI as play can expand current notions of human-AI interaction, which are predominantly productivity-based. In particular, our work suggests that game and UX designers should consider flow to structure the learning curve of human-AI interaction, incorporate discovery-based learning to play around with the AI and observe the consequences, and offer users an invitation to play to explore new forms of human-AI interaction.
iNNk: A Multi-Player Game to Deceive a Neural Network
Jul 17, 2020

Abstract:This paper presents \textit{iNNK}, a multiplayer drawing game where human players team up against an NN. The players need to successfully communicate a secret code word to each other through drawings, without being deciphered by the NN. With this game, we aim to foster a playful environment where players can, in a small way, go from passive consumers of NN applications to creative thinkers and critical challengers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge