Jana G. Delfino
Knowledge-based anomaly detection for identifying network-induced shape artifacts
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Synthetic data provides a promising approach to address data scarcity for training machine learning models; however, adoption without proper quality assessments may introduce artifacts, distortions, and unrealistic features that compromise model performance and clinical utility. This work introduces a novel knowledge-based anomaly detection method for detecting network-induced shape artifacts in synthetic images. The introduced method utilizes a two-stage framework comprising (i) a novel feature extractor that constructs a specialized feature space by analyzing the per-image distribution of angle gradients along anatomical boundaries, and (ii) an isolation forest-based anomaly detector. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the method for identifying network-induced shape artifacts in two synthetic mammography datasets from models trained on CSAW-M and VinDr-Mammo patient datasets respectively. Quantitative evaluation shows that the method successfully concentrates artifacts in the most anomalous partition (1st percentile), with AUC values of 0.97 (CSAW-syn) and 0.91 (VMLO-syn). In addition, a reader study involving three imaging scientists confirmed that images identified by the method as containing network-induced shape artifacts were also flagged by human readers with mean agreement rates of 66% (CSAW-syn) and 68% (VMLO-syn) for the most anomalous partition, approximately 1.5-2 times higher than the least anomalous partition. Kendall-Tau correlations between algorithmic and human rankings were 0.45 and 0.43 for the two datasets, indicating reasonable agreement despite the challenging nature of subtle artifact detection. This method is a step forward in the responsible use of synthetic data, as it allows developers to evaluate synthetic images for known anatomic constraints and pinpoint and address specific issues to improve the overall quality of a synthetic dataset.
Out-of-Distribution Detection and Data Drift Monitoring using Statistical Process Control
Feb 12, 2024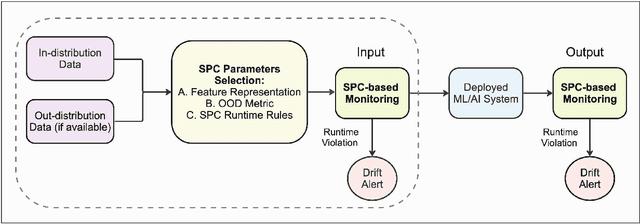
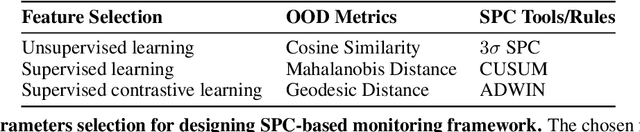
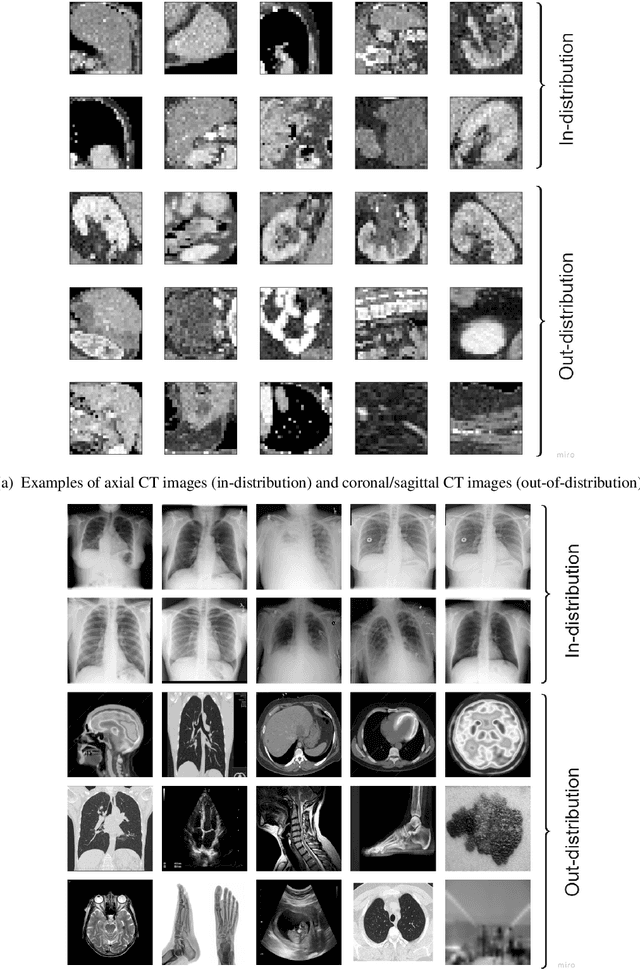
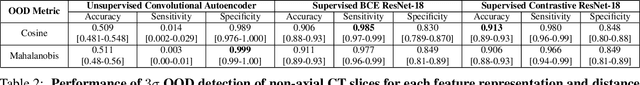
Abstract:Background: Machine learning (ML) methods often fail with data that deviates from their training distribution. This is a significant concern for ML-enabled devices in clinical settings, where data drift may cause unexpected performance that jeopardizes patient safety. Method: We propose a ML-enabled Statistical Process Control (SPC) framework for out-of-distribution (OOD) detection and drift monitoring. SPC is advantageous as it visually and statistically highlights deviations from the expected distribution. To demonstrate the utility of the proposed framework for monitoring data drift in radiological images, we investigated different design choices, including methods for extracting feature representations, drift quantification, and SPC parameter selection. Results: We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework for two tasks: 1) differentiating axial vs. non-axial computed tomography (CT) images and 2) separating chest x-ray (CXR) from other modalities. For both tasks, we achieved high accuracy in detecting OOD inputs, with 0.913 in CT and 0.995 in CXR, and sensitivity of 0.980 in CT and 0.984 in CXR. Our framework was also adept at monitoring data streams and identifying the time a drift occurred. In a simulation with 100 daily CXR cases, we detected a drift in OOD input percentage from 0-1% to 3-5% within two days, maintaining a low false-positive rate. Through additional experimental results, we demonstrate the framework's data-agnostic nature and independence from the underlying model's structure. Conclusion: We propose a framework for OOD detection and drift monitoring that is agnostic to data, modality, and model. The framework is customizable and can be adapted for specific applications.
Knowledge-based in silico models and dataset for the comparative evaluation of mammography AI for a range of breast characteristics, lesion conspicuities and doses
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:To generate evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of artificial intelligence (AI) enabled medical devices, AI models need to be evaluated on a diverse population of patient cases, some of which may not be readily available. We propose an evaluation approach for testing medical imaging AI models that relies on in silico imaging pipelines in which stochastic digital models of human anatomy (in object space) with and without pathology are imaged using a digital replica imaging acquisition system to generate realistic synthetic image datasets. Here, we release M-SYNTH, a dataset of cohorts with four breast fibroglandular density distributions imaged at different exposure levels using Monte Carlo x-ray simulations with the publicly available Virtual Imaging Clinical Trial for Regulatory Evaluation (VICTRE) toolkit. We utilize the synthetic dataset to analyze AI model performance and find that model performance decreases with increasing breast density and increases with higher mass density, as expected. As exposure levels decrease, AI model performance drops with the highest performance achieved at exposure levels lower than the nominal recommended dose for the breast type.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge