Jan von der Assen
DMPA: Model Poisoning Attacks on Decentralized Federated Learning for Model Differences
Feb 07, 2025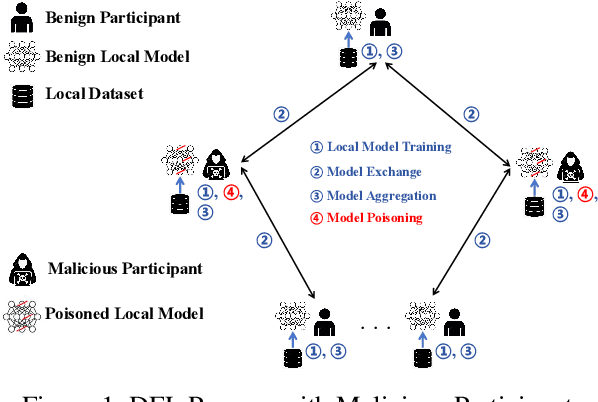
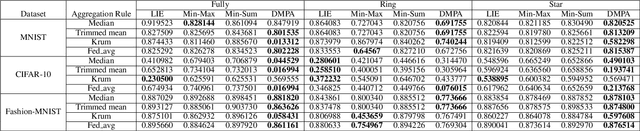
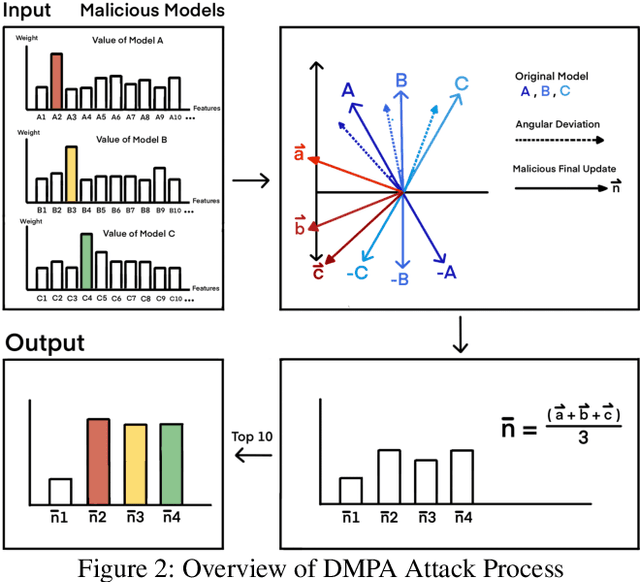
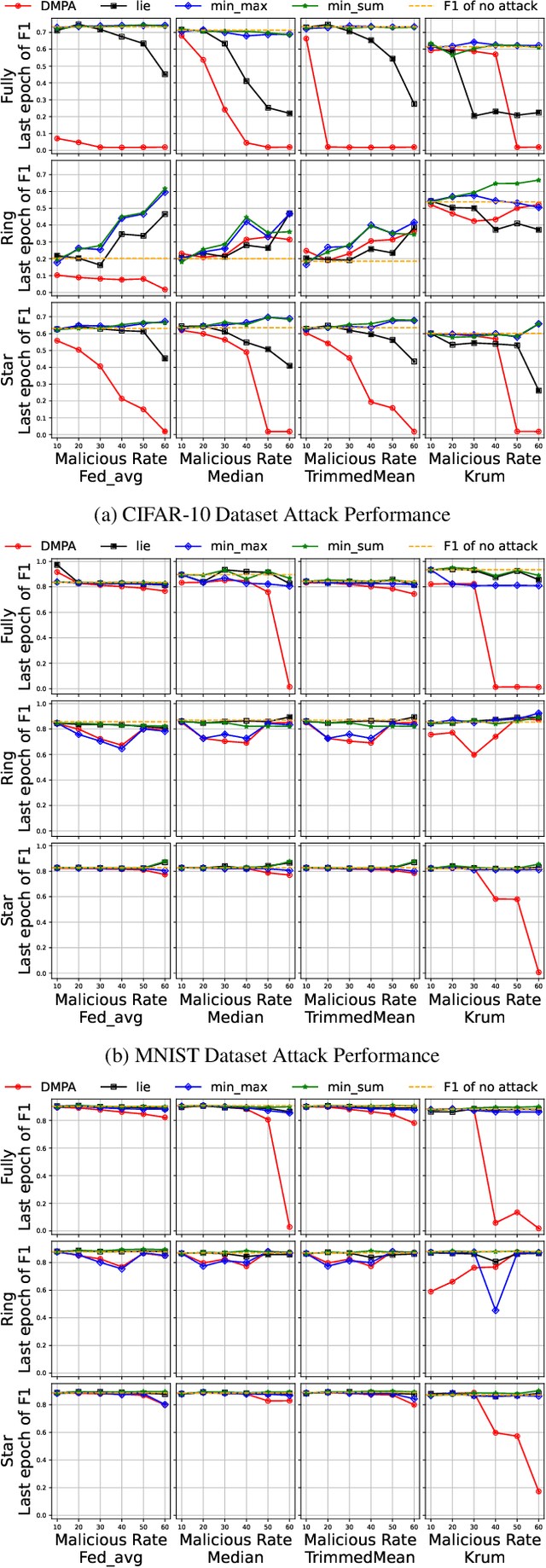
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has garnered significant attention as a prominent privacy-preserving Machine Learning (ML) paradigm. Decentralized FL (DFL) eschews traditional FL's centralized server architecture, enhancing the system's robustness and scalability. However, these advantages of DFL also create new vulnerabilities for malicious participants to execute adversarial attacks, especially model poisoning attacks. In model poisoning attacks, malicious participants aim to diminish the performance of benign models by creating and disseminating the compromised model. Existing research on model poisoning attacks has predominantly concentrated on undermining global models within the Centralized FL (CFL) paradigm, while there needs to be more research in DFL. To fill the research gap, this paper proposes an innovative model poisoning attack called DMPA. This attack calculates the differential characteristics of multiple malicious client models and obtains the most effective poisoning strategy, thereby orchestrating a collusive attack by multiple participants. The effectiveness of this attack is validated across multiple datasets, with results indicating that the DMPA approach consistently surpasses existing state-of-the-art FL model poisoning attack strategies.
FedEP: Tailoring Attention to Heterogeneous Data Distribution with Entropy Pooling for Decentralized Federated Learning
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) performance is highly influenced by data distribution across clients, and non-Independent and Identically Distributed (non-IID) leads to a slower convergence of the global model and a decrease in model effectiveness. The existing algorithms for solving the non-IID problem are focused on the traditional centralized FL (CFL), where a central server is used for model aggregation. However, in decentralized FL (DFL), nodes lack the overall vision of the federation. To address the non-IID problem in DFL, this paper proposes a novel DFL aggregation algorithm, Federated Entropy Pooling (FedEP). FedEP mitigates the client drift problem by incorporating the statistical characteristics of local distributions instead of any actual data. Prior to training, each client conducts a local distribution fitting using a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and shares the resulting statistical characteristics with its neighbors. After receiving the statistical characteristics shared by its neighbors, each node tries to fit the global data distribution. In the aggregation phase, each node calculates the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergences of the local data distribution over the fitted global data distribution, giving the weights to generate the aggregated model. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that FedEP can achieve faster convergence and show higher test performance than state-of-the-art approaches.
CyberForce: A Federated Reinforcement Learning Framework for Malware Mitigation
Aug 11, 2023Abstract:The expansion of the Internet-of-Things (IoT) paradigm is inevitable, but vulnerabilities of IoT devices to malware incidents have become an increasing concern. Recent research has shown that the integration of Reinforcement Learning with Moving Target Defense (MTD) mechanisms can enhance cybersecurity in IoT devices. Nevertheless, the numerous new malware attacks and the time that agents take to learn and select effective MTD techniques make this approach impractical for real-world IoT scenarios. To tackle this issue, this work presents CyberForce, a framework that employs Federated Reinforcement Learning (FRL) to collectively and privately determine suitable MTD techniques for mitigating diverse zero-day attacks. CyberForce integrates device fingerprinting and anomaly detection to reward or penalize MTD mechanisms chosen by an FRL-based agent. The framework has been evaluated in a federation consisting of ten devices of a real IoT platform. A pool of experiments with six malware samples affecting the devices has demonstrated that CyberForce can precisely learn optimum MTD mitigation strategies. When all clients are affected by all attacks, the FRL agent exhibits high accuracy and reduced training time when compared to a centralized RL agent. In cases where different clients experience distinct attacks, the CyberForce clients gain benefits through the transfer of knowledge from other clients and similar attack behavior. Additionally, CyberForce showcases notable robustness against data poisoning attacks.
RCVaR: an Economic Approach to Estimate Cyberattacks Costs using Data from Industry Reports
Jul 20, 2023



Abstract:Digitization increases business opportunities and the risk of companies being victims of devastating cyberattacks. Therefore, managing risk exposure and cybersecurity strategies is essential for digitized companies that want to survive in competitive markets. However, understanding company-specific risks and quantifying their associated costs is not trivial. Current approaches fail to provide individualized and quantitative monetary estimations of cybersecurity impacts. Due to limited resources and technical expertise, SMEs and even large companies are affected and struggle to quantify their cyberattack exposure. Therefore, novel approaches must be placed to support the understanding of the financial loss due to cyberattacks. This article introduces the Real Cyber Value at Risk (RCVaR), an economical approach for estimating cybersecurity costs using real-world information from public cybersecurity reports. RCVaR identifies the most significant cyber risk factors from various sources and combines their quantitative results to estimate specific cyberattacks costs for companies. Furthermore, RCVaR extends current methods to achieve cost and risk estimations based on historical real-world data instead of only probability-based simulations. The evaluation of the approach on unseen data shows the accuracy and efficiency of the RCVaR in predicting and managing cyber risks. Thus, it shows that the RCVaR is a valuable addition to cybersecurity planning and risk management processes.
RansomAI: AI-powered Ransomware for Stealthy Encryption
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:Cybersecurity solutions have shown promising performance when detecting ransomware samples that use fixed algorithms and encryption rates. However, due to the current explosion of Artificial Intelligence (AI), sooner than later, ransomware (and malware in general) will incorporate AI techniques to intelligently and dynamically adapt its encryption behavior to be undetected. It might result in ineffective and obsolete cybersecurity solutions, but the literature lacks AI-powered ransomware to verify it. Thus, this work proposes RansomAI, a Reinforcement Learning-based framework that can be integrated into existing ransomware samples to adapt their encryption behavior and stay stealthy while encrypting files. RansomAI presents an agent that learns the best encryption algorithm, rate, and duration that minimizes its detection (using a reward mechanism and a fingerprinting intelligent detection system) while maximizing its damage function. The proposed framework was validated in a ransomware, Ransomware-PoC, that infected a Raspberry Pi 4, acting as a crowdsensor. A pool of experiments with Deep Q-Learning and Isolation Forest (deployed on the agent and detection system, respectively) has demonstrated that RansomAI evades the detection of Ransomware-PoC affecting the Raspberry Pi 4 in a few minutes with >90% accuracy.
RL and Fingerprinting to Select Moving Target Defense Mechanisms for Zero-day Attacks in IoT
Dec 30, 2022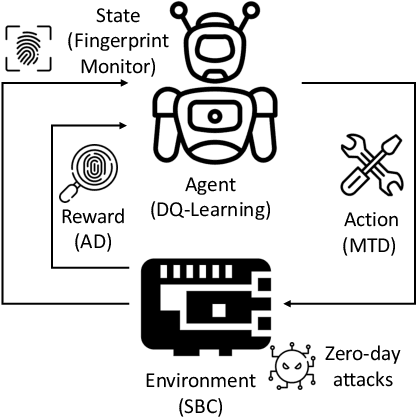
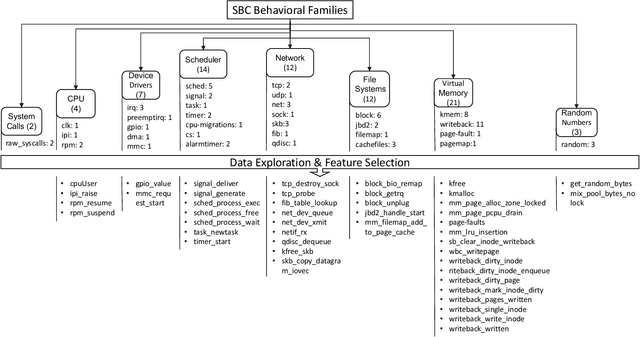
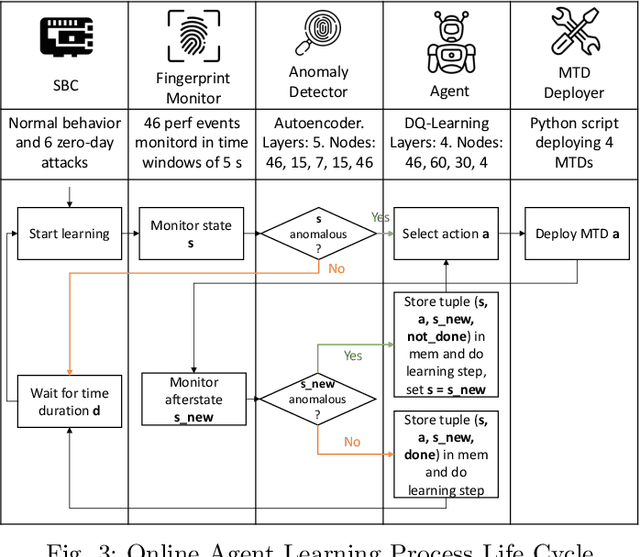
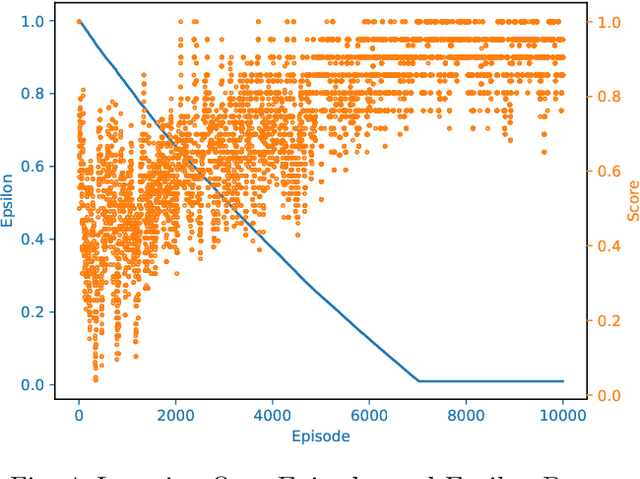
Abstract:Cybercriminals are moving towards zero-day attacks affecting resource-constrained devices such as single-board computers (SBC). Assuming that perfect security is unrealistic, Moving Target Defense (MTD) is a promising approach to mitigate attacks by dynamically altering target attack surfaces. Still, selecting suitable MTD techniques for zero-day attacks is an open challenge. Reinforcement Learning (RL) could be an effective approach to optimize the MTD selection through trial and error, but the literature fails when i) evaluating the performance of RL and MTD solutions in real-world scenarios, ii) studying whether behavioral fingerprinting is suitable for representing SBC's states, and iii) calculating the consumption of resources in SBC. To improve these limitations, the work at hand proposes an online RL-based framework to learn the correct MTD mechanisms mitigating heterogeneous zero-day attacks in SBC. The framework considers behavioral fingerprinting to represent SBCs' states and RL to learn MTD techniques that mitigate each malicious state. It has been deployed on a real IoT crowdsensing scenario with a Raspberry Pi acting as a spectrum sensor. More in detail, the Raspberry Pi has been infected with different samples of command and control malware, rootkits, and ransomware to later select between four existing MTD techniques. A set of experiments demonstrated the suitability of the framework to learn proper MTD techniques mitigating all attacks (except a harmfulness rootkit) while consuming <1 MB of storage and utilizing <55% CPU and <80% RAM.
A Lightweight Moving Target Defense Framework for Multi-purpose Malware Affecting IoT Devices
Oct 14, 2022



Abstract:Malware affecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices is rapidly growing due to the relevance of this paradigm in real-world scenarios. Specialized literature has also detected a trend towards multi-purpose malware able to execute different malicious actions such as remote control, data leakage, encryption, or code hiding, among others. Protecting IoT devices against this kind of malware is challenging due to their well-known vulnerabilities and limitation in terms of CPU, memory, and storage. To improve it, the moving target defense (MTD) paradigm was proposed a decade ago and has shown promising results, but there is a lack of IoT MTD solutions dealing with multi-purpose malware. Thus, this work proposes four MTD mechanisms changing IoT devices' network, data, and runtime environment to mitigate multi-purpose malware. Furthermore, it presents a lightweight and IoT-oriented MTD framework to decide what, when, and how the MTD mechanisms are deployed. Finally, the efficiency and effectiveness of the framework and MTD mechanisms are evaluated in a real-world scenario with one IoT spectrum sensor affected by multi-purpose malware.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge