Jamil Ahmad
FocusSDF: Boundary-Aware Learning for Medical Image Segmentation via Signed Distance Supervision
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Segmentation of medical images constitutes an essential component of medical image analysis, providing the foundation for precise diagnosis and efficient therapeutic interventions in clinical practices. Despite substantial progress, most segmentation models do not explicitly encode boundary information; as a result, making boundary preservation a persistent challenge in medical image segmentation. To address this challenge, we introduce FocusSDF, a novel loss function based on the signed distance functions (SDFs), which redirects the network to concentrate on boundary regions by adaptively assigning higher weights to pixels closer to the lesion or organ boundary, effectively making it boundary aware. To rigorously validate FocusSDF, we perform extensive evaluations against five state-of-the-art medical image segmentation models, including the foundation model MedSAM, using four distance-based loss functions across diverse datasets covering cerebral aneurysm, stroke, liver, and breast tumor segmentation tasks spanning multiple imaging modalities. The experimental results consistently demonstrate the superior performance of FocusSDF over existing distance transform based loss functions.
piSAAC: Extended notion of SAAC feature selection novel method for discrimination of Enzymes model using different machine learning algorithm
Dec 16, 2020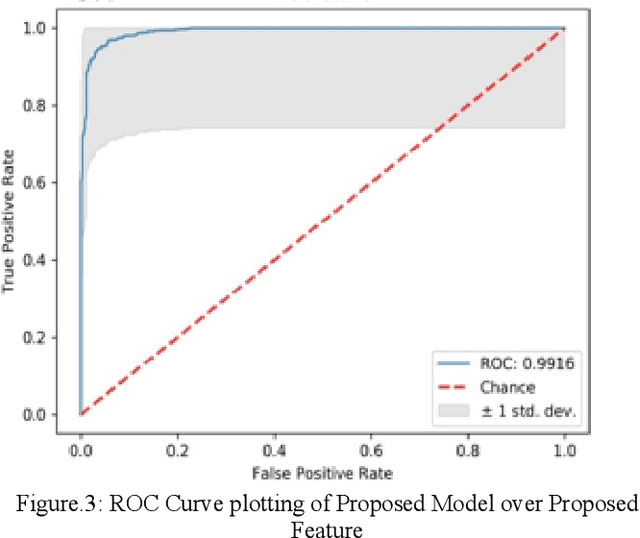
Abstract:Enzymes and proteins are live driven biochemicals, which has a dramatic impact over the environment, in which it is active. So, therefore, it is highly looked-for to build such a robust and highly accurate automatic and computational model to accurately predict enzymes nature. In this study, a novel split amino acid composition model named piSAAC is proposed. In this model, protein sequence is discretized in equal and balanced terminus to fully evaluate the intrinsic correlation properties of the sequence. Several state-of-the-art algorithms have been employed to evaluate the proposed model. A 10-folds cross-validation evaluation is used for finding out the authenticity and robust-ness of the model using different statistical measures e.g. Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F-measure and area un-der ROC curve. The experimental results show that, probabilistic neural network algorithm with piSAAC feature extraction yields an accuracy of 98.01%, sensitivity of 97.12%, specificity of 95.87%, f-measure of 0.9812and AUC 0.95812, over dataset S1, accuracy of 97.85%, sensitivity of 97.54%, specificity of 96.24%, f-measure of 0.9774 and AUC 0.9803 over dataset S2. Evident from these excellent empirical results, the proposed model would be a very useful tool for academic research and drug designing related application areas.
Divide-and-Conquer based Ensemble to Spot Emotions in Speech using MFCC and Random Forest
Oct 05, 2016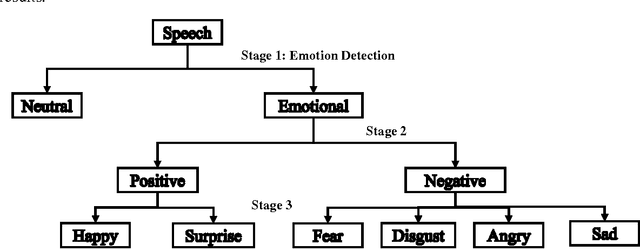
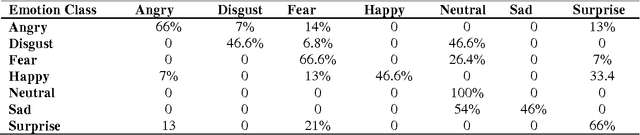
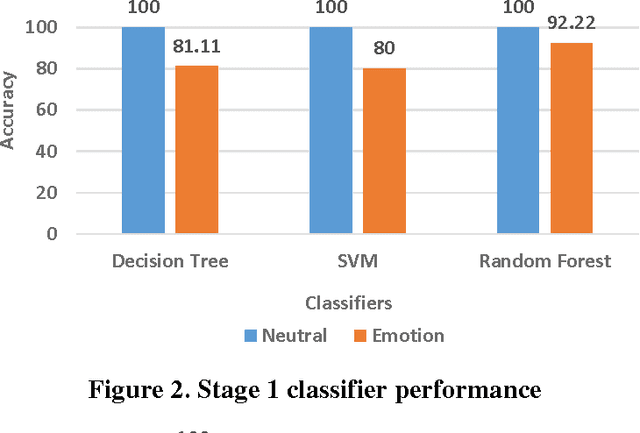
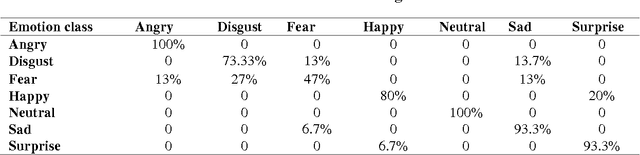
Abstract:Besides spoken words, speech signals also carry information about speaker gender, age, and emotional state which can be used in a variety of speech analysis applications. In this paper, a divide and conquer strategy for ensemble classification has been proposed to recognize emotions in speech. Intrinsic hierarchy in emotions has been utilized to construct an emotions tree, which assisted in breaking down the emotion recognition task into smaller sub tasks. The proposed framework generates predictions in three phases. Firstly, emotions are detected in the input speech signal by classifying it as neutral or emotional. If the speech is classified as emotional, then in the second phase, it is further classified into positive and negative classes. Finally, individual positive or negative emotions are identified based on the outcomes of the previous stages. Several experiments have been performed on a widely used benchmark dataset. The proposed method was able to achieve improved recognition rates as compared to several other approaches.
On Feature based Delaunay Triangulation for Palmprint Recognition
Feb 05, 2016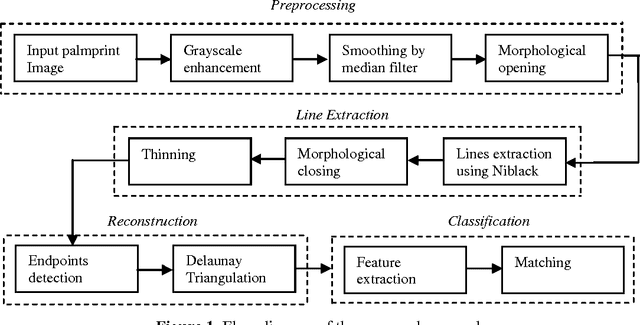
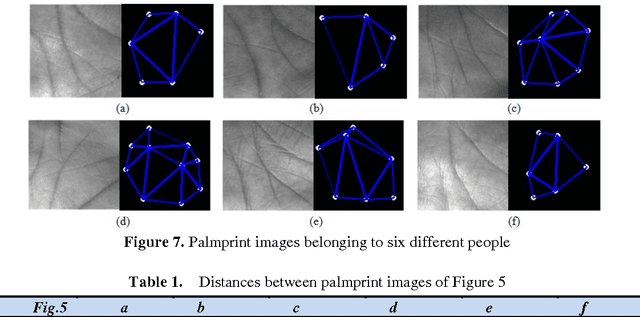
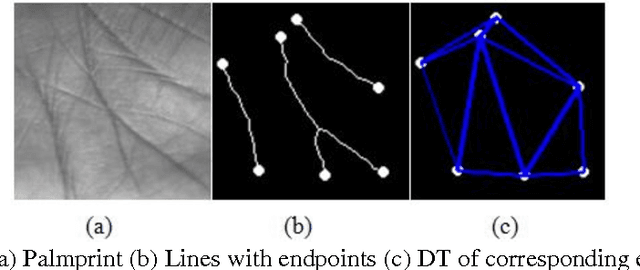
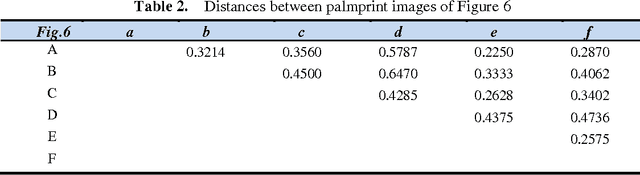
Abstract:Authentication of individuals via palmprint based biometric system is becoming very popular due to its reliability as it contains unique and stable features. In this paper, we present a novel approach for palmprint recognition and its representation. To extract the palm lines, local thresholding technique Niblack binarization algorithm is adopted. The endpoints of these lines are determined and a connection is created among them using the Delaunay triangulation thereby generating a distinct topological structure of each palmprint. Next, we extract different geometric as well as quantitative features from the triangles of the Delaunay triangulation that assist in identifying different individuals. To ensure that the proposed approach is invariant to rotation and scaling, features were made relative to topological and geometrical structure of the palmprint. The similarity of the two palmprints is computed using the weighted sum approach and compared with the k-nearest neighbor. The experimental results obtained reflect the effectiveness of the proposed approach to discriminate between different palmprint images and thus achieved a recognition rate of 90% over large databases.
Describing Colors, Textures and Shapes for Content Based Image Retrieval - A Survey
Feb 25, 2015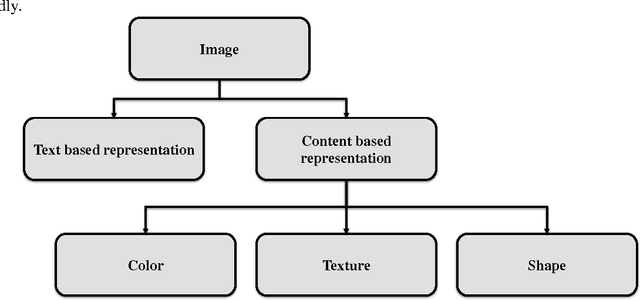
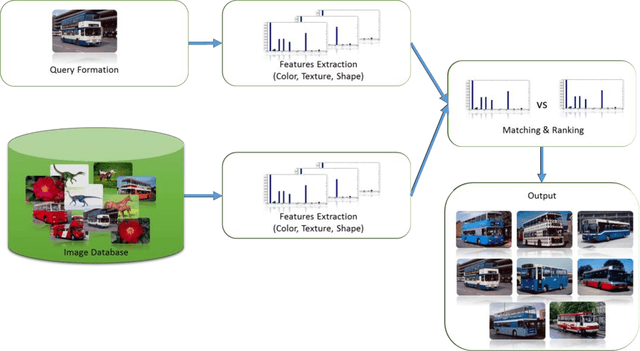
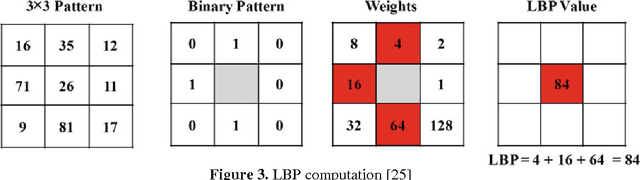
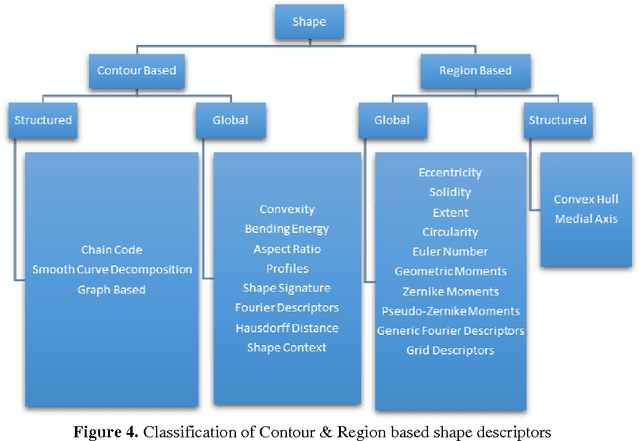
Abstract:Visual media has always been the most enjoyed way of communication. From the advent of television to the modern day hand held computers, we have witnessed the exponential growth of images around us. Undoubtedly it's a fact that they carry a lot of information in them which needs be utilized in an effective manner. Hence intense need has been felt to efficiently index and store large image collections for effective and on- demand retrieval. For this purpose low-level features extracted from the image contents like color, texture and shape has been used. Content based image retrieval systems employing these features has proven very successful. Image retrieval has promising applications in numerous fields and hence has motivated researchers all over the world. New and improved ways to represent visual content are being developed each day. Tremendous amount of research has been carried out in the last decade. In this paper we will present a detailed overview of some of the powerful color, texture and shape descriptors for content based image retrieval. A comparative analysis will also be carried out for providing an insight into outstanding challenges in this field.
A Fusion of Labeled-Grid Shape Descriptors with Weighted Ranking Algorithm for Shapes Recognition
Jun 16, 2014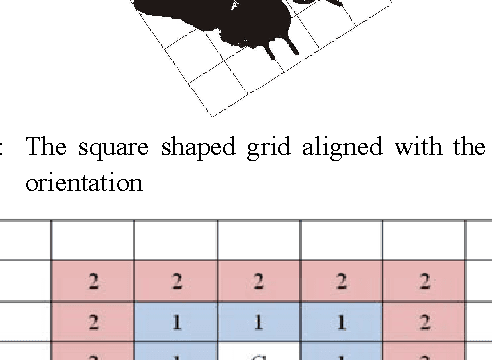
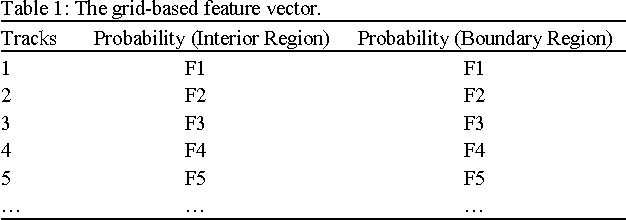
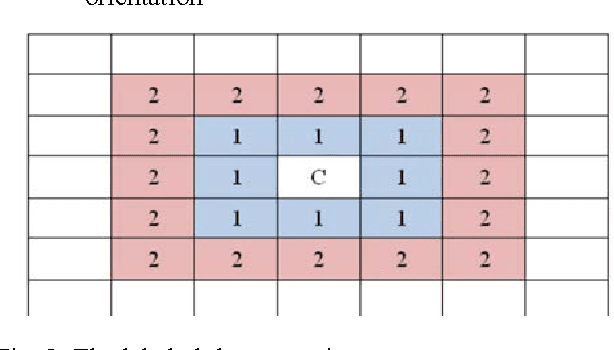
Abstract:Retrieving similar images from a large dataset based on the image content has been a very active research area and is a very challenging task. Studies have shown that retrieving similar images based on their shape is a very effective method. For this purpose a large number of methods exist in literature. The combination of more than one feature has also been investigated for this purpose and has shown promising results. In this paper a fusion based shapes recognition method has been proposed. A set of local boundary based and region based features are derived from the labeled grid based representation of the shape and are combined with a few global shape features to produce a composite shape descriptor. This composite shape descriptor is then used in a weighted ranking algorithm to find similarities among shapes from a large dataset. The experimental analysis has shown that the proposed method is powerful enough to discriminate the geometrically similar shapes from the non-similar ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge