Zanobya N. Khan
Frequency and Spatial domain based Saliency for Pigmented Skin Lesion Segmentation
Oct 08, 2020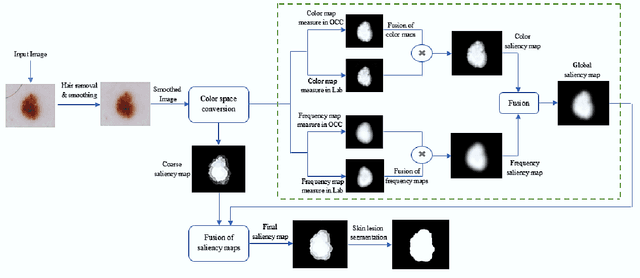
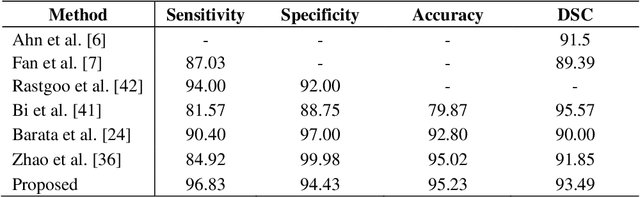
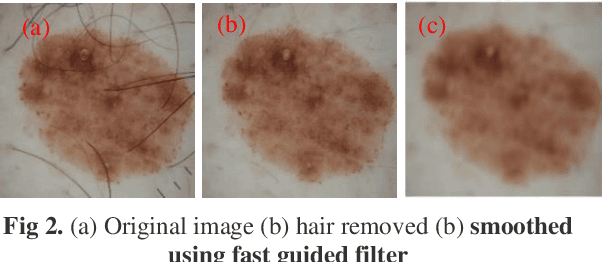
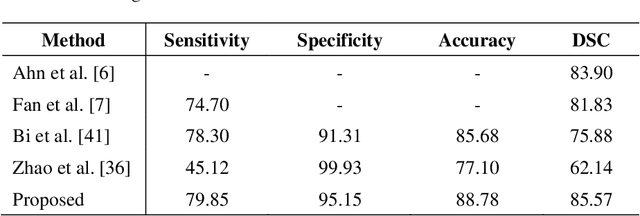
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation can be rather a challenging task owing to the presence of artifacts, low contrast between lesion and boundary, color variegation, fuzzy skin lesion borders and heterogeneous background in dermoscopy images. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective saliency-based approach derived in the frequency and spatial domain to detect pigmented skin lesion. Two color models are utilized for the construction of these maps. We suggest a different metric for each color model to design map in the spatial domain via color features. The map in the frequency domain is generated from aggregated images. We adopt a separate fusion scheme to combine salient features in their respective domains. Finally, two-phase saliency integration scheme is devised to combine these maps using pixelwise multiplication. Performance of the proposed method is assessed on PH2 and ISIC 2016 datasets. The outcome of the experiments suggests that the proposed scheme generate better segmentation result as compared to state-of-the-art methods.
On Feature based Delaunay Triangulation for Palmprint Recognition
Feb 05, 2016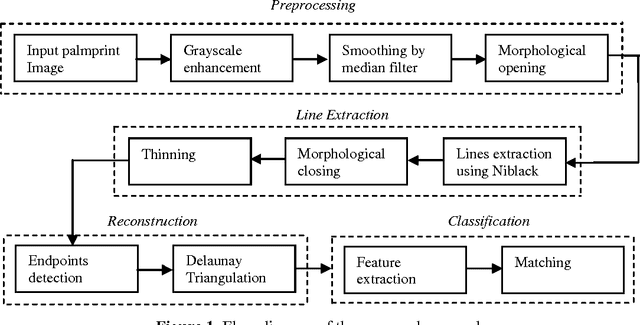
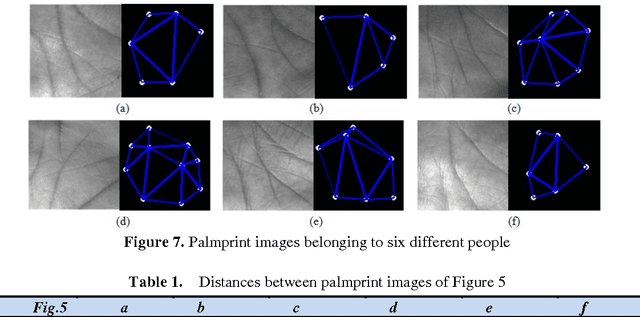
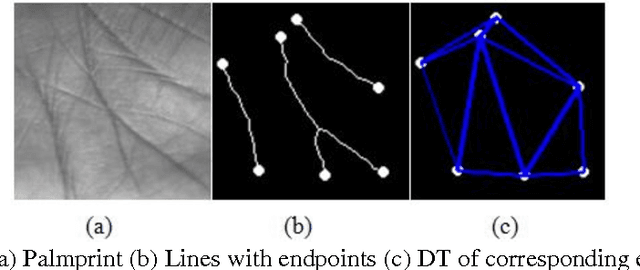
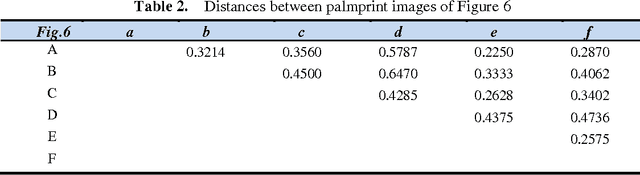
Abstract:Authentication of individuals via palmprint based biometric system is becoming very popular due to its reliability as it contains unique and stable features. In this paper, we present a novel approach for palmprint recognition and its representation. To extract the palm lines, local thresholding technique Niblack binarization algorithm is adopted. The endpoints of these lines are determined and a connection is created among them using the Delaunay triangulation thereby generating a distinct topological structure of each palmprint. Next, we extract different geometric as well as quantitative features from the triangles of the Delaunay triangulation that assist in identifying different individuals. To ensure that the proposed approach is invariant to rotation and scaling, features were made relative to topological and geometrical structure of the palmprint. The similarity of the two palmprints is computed using the weighted sum approach and compared with the k-nearest neighbor. The experimental results obtained reflect the effectiveness of the proposed approach to discriminate between different palmprint images and thus achieved a recognition rate of 90% over large databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge