James Weatherall
Unlocking Historical Clinical Trial Data with ALIGN: A Compositional Large Language Model System for Medical Coding
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:The reuse of historical clinical trial data has significant potential to accelerate medical research and drug development. However, interoperability challenges, particularly with missing medical codes, hinders effective data integration across studies. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising solution for automated coding without labeled data, current approaches face challenges on complex coding tasks. We introduce ALIGN, a novel compositional LLM-based system for automated, zero-shot medical coding. ALIGN follows a three-step process: (1) diverse candidate code generation; (2) self-evaluation of codes and (3) confidence scoring and uncertainty estimation enabling human deferral to ensure reliability. We evaluate ALIGN on harmonizing medication terms into Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) and medical history terms into Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) codes extracted from 22 immunology trials. ALIGN outperformed the LLM baselines, while also providing capabilities for trustworthy deployment. For MedDRA coding, ALIGN achieved high accuracy across all levels, matching RAG and excelling at the most specific levels (87-90% for HLGT). For ATC coding, ALIGN demonstrated superior performance, particularly at lower hierarchy levels (ATC Level 4), with 72-73% overall accuracy and 86-89% accuracy for common medications, outperforming baselines by 7-22%. ALIGN's uncertainty-based deferral improved accuracy by 17% to 90% accuracy with 30% deferral, notably enhancing performance on uncommon medications. ALIGN achieves this cost-efficiently at \$0.0007 and \$0.02 per code for GPT-4o-mini and GPT-4o, reducing barriers to clinical adoption. ALIGN advances automated medical coding for clinical trial data, contributing to enhanced data interoperability and reusability, positioning it as a promising tool to improve clinical research and accelerate drug development.
Ranking Biomarkers Through Mutual Information
Dec 05, 2016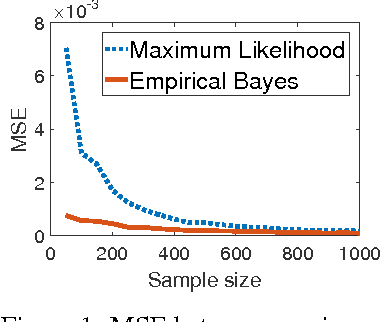
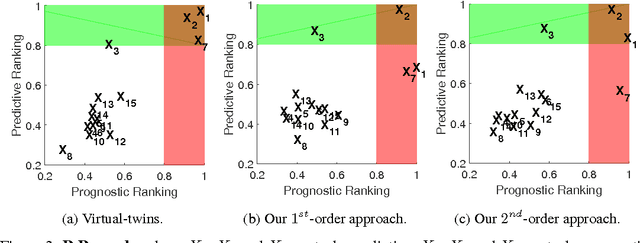
Abstract:We study information theoretic methods for ranking biomarkers. In clinical trials there are two, closely related, types of biomarkers: predictive and prognostic, and disentangling them is a key challenge. Our first step is to phrase biomarker ranking in terms of optimizing an information theoretic quantity. This formalization of the problem will enable us to derive rankings of predictive/prognostic biomarkers, by estimating different, high dimensional, conditional mutual information terms. To estimate these terms, we suggest efficient low dimensional approximations, and we derive an empirical Bayes estimator, which is suitable for small or sparse datasets. Finally, we introduce a new visualisation tool that captures the prognostic and the predictive strength of a set of biomarkers. We believe this representation will prove to be a powerful tool in biomarker discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge