James Storer
RePr: Improved Training of Convolutional Filters
Nov 26, 2018



Abstract:A well-trained Convolutional Neural Network can easily be pruned without significant loss of performance. This is because of unnecessary overlap in the features captured by the network's filters. Innovations in network architecture such as skip/dense connections and Inception units have mitigated this problem to some extent, but these improvements come with increased computation and memory requirements at run-time. We attempt to address this problem from another angle - not by changing the network structure but by altering the training method. We show that by temporarily pruning and then restoring a subset of the model's filters, and repeating this process cyclically, overlap in the learned features is reduced, producing improved generalization. We show that the existing model-pruning criteria are not optimal for selecting filters to prune in this context and introduce inter-filter orthogonality as the ranking criteria to determine under-expressive filters. Our method is applicable both to vanilla convolutional networks and more complex modern architectures, and improves the performance across a variety of tasks, especially when applied to smaller networks.
Deflecting Adversarial Attacks with Pixel Deflection
Mar 30, 2018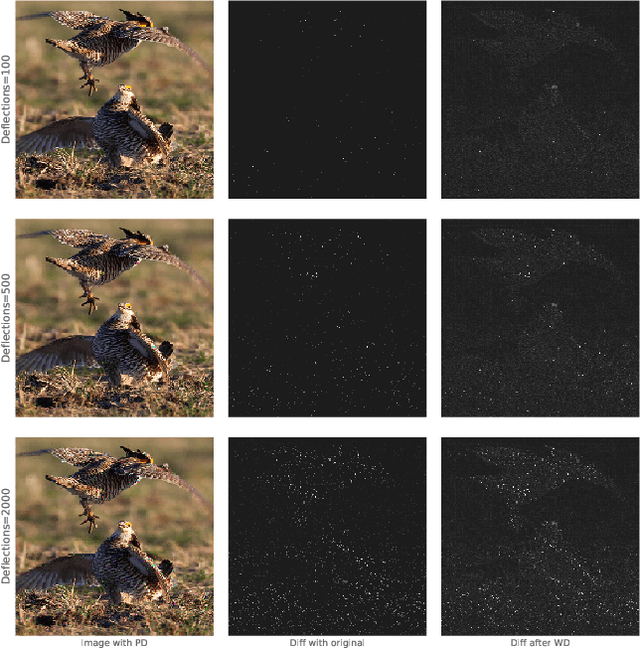
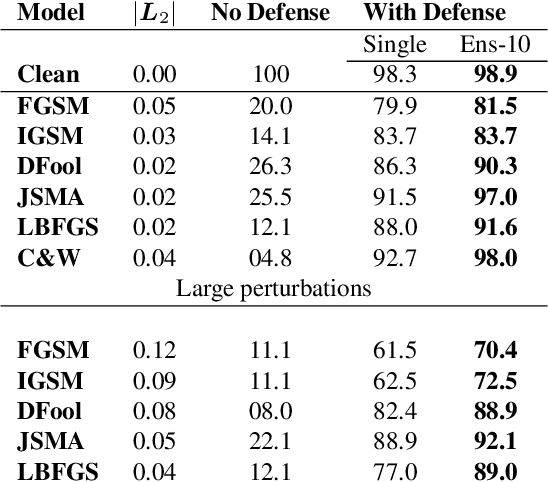
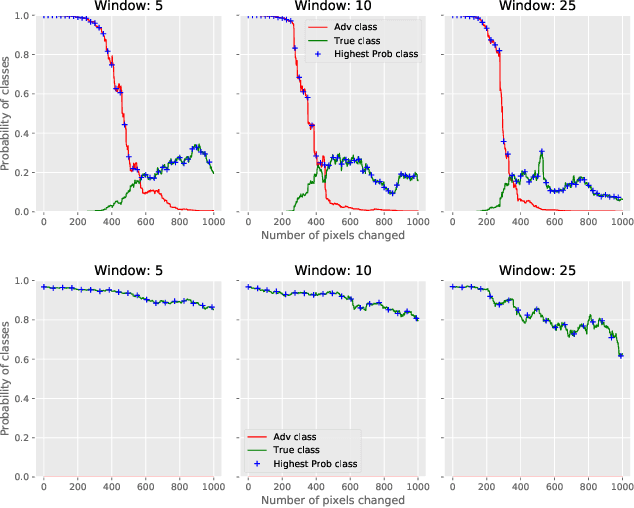
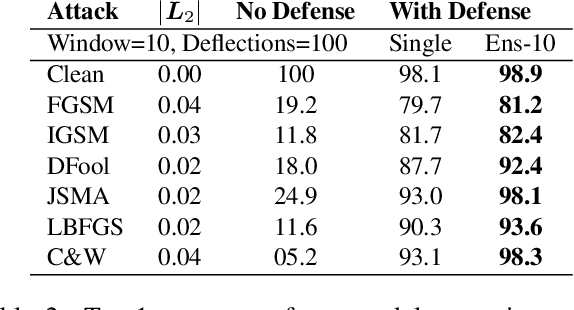
Abstract:CNNs are poised to become integral parts of many critical systems. Despite their robustness to natural variations, image pixel values can be manipulated, via small, carefully crafted, imperceptible perturbations, to cause a model to misclassify images. We present an algorithm to process an image so that classification accuracy is significantly preserved in the presence of such adversarial manipulations. Image classifiers tend to be robust to natural noise, and adversarial attacks tend to be agnostic to object location. These observations motivate our strategy, which leverages model robustness to defend against adversarial perturbations by forcing the image to match natural image statistics. Our algorithm locally corrupts the image by redistributing pixel values via a process we term pixel deflection. A subsequent wavelet-based denoising operation softens this corruption, as well as some of the adversarial changes. We demonstrate experimentally that the combination of these techniques enables the effective recovery of the true class, against a variety of robust attacks. Our results compare favorably with current state-of-the-art defenses, without requiring retraining or modifying the CNN.
Protecting JPEG Images Against Adversarial Attacks
Mar 02, 2018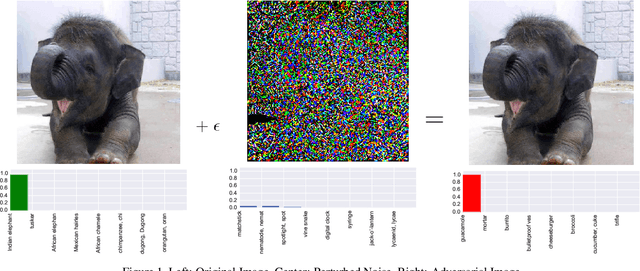
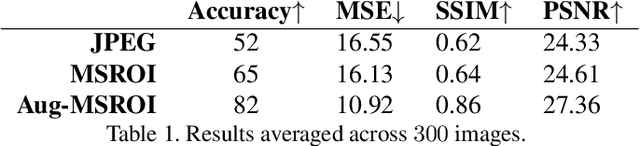
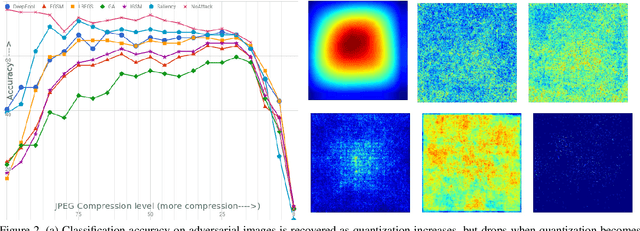
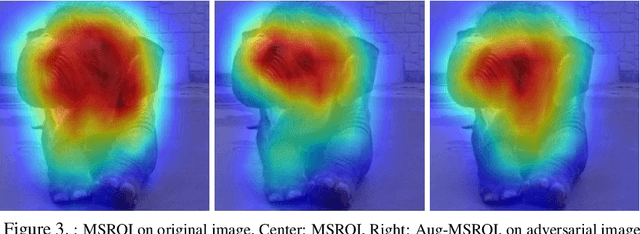
Abstract:As deep neural networks (DNNs) have been integrated into critical systems, several methods to attack these systems have been developed. These adversarial attacks make imperceptible modifications to an image that fool DNN classifiers. We present an adaptive JPEG encoder which defends against many of these attacks. Experimentally, we show that our method produces images with high visual quality while greatly reducing the potency of state-of-the-art attacks. Our algorithm requires only a modest increase in encoding time, produces a compressed image which can be decompressed by an off-the-shelf JPEG decoder, and classified by an unmodified classifier
Semantic Perceptual Image Compression using Deep Convolution Networks
Mar 29, 2017
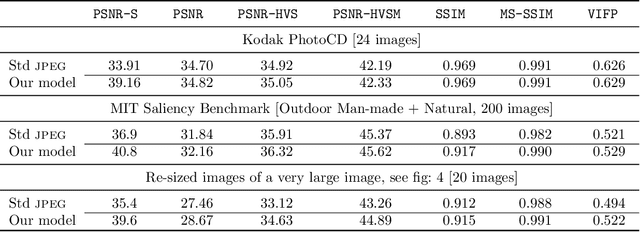


Abstract:It has long been considered a significant problem to improve the visual quality of lossy image and video compression. Recent advances in computing power together with the availability of large training data sets has increased interest in the application of deep learning cnns to address image recognition and image processing tasks. Here, we present a powerful cnn tailored to the specific task of semantic image understanding to achieve higher visual quality in lossy compression. A modest increase in complexity is incorporated to the encoder which allows a standard, off-the-shelf jpeg decoder to be used. While jpeg encoding may be optimized for generic images, the process is ultimately unaware of the specific content of the image to be compressed. Our technique makes jpeg content-aware by designing and training a model to identify multiple semantic regions in a given image. Unlike object detection techniques, our model does not require labeling of object positions and is able to identify objects in a single pass. We present a new cnn architecture directed specifically to image compression, which generates a map that highlights semantically-salient regions so that they can be encoded at higher quality as compared to background regions. By adding a complete set of features for every class, and then taking a threshold over the sum of all feature activations, we generate a map that highlights semantically-salient regions so that they can be encoded at a better quality compared to background regions. Experiments are presented on the Kodak PhotoCD dataset and the MIT Saliency Benchmark dataset, in which our algorithm achieves higher visual quality for the same compressed size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge