James Ravenscroft
A Pipeline for Generating, Annotating and Employing Synthetic Data for Real World Question Answering
Nov 30, 2022



Abstract:Question Answering (QA) is a growing area of research, often used to facilitate the extraction of information from within documents. State-of-the-art QA models are usually pre-trained on domain-general corpora like Wikipedia and thus tend to struggle on out-of-domain documents without fine-tuning. We demonstrate that synthetic domain-specific datasets can be generated easily using domain-general models, while still providing significant improvements to QA performance. We present two new tools for this task: A flexible pipeline for validating the synthetic QA data and training downstream models on it, and an online interface to facilitate human annotation of this generated data. Using this interface, crowdworkers labelled 1117 synthetic QA pairs, which we then used to fine-tune downstream models and improve domain-specific QA performance by 8.75 F1.
CD2CR: Co-reference Resolution Across Documents and Domains
Jan 29, 2021



Abstract:Cross-document co-reference resolution (CDCR) is the task of identifying and linking mentions to entities and concepts across many text documents. Current state-of-the-art models for this task assume that all documents are of the same type (e.g. news articles) or fall under the same theme. However, it is also desirable to perform CDCR across different domains (type or theme). A particular use case we focus on in this paper is the resolution of entities mentioned across scientific work and newspaper articles that discuss them. Identifying the same entities and corresponding concepts in both scientific articles and news can help scientists understand how their work is represented in mainstream media. We propose a new task and English language dataset for cross-document cross-domain co-reference resolution (CD$^2$CR). The task aims to identify links between entities across heterogeneous document types. We show that in this cross-domain, cross-document setting, existing CDCR models do not perform well and we provide a baseline model that outperforms current state-of-the-art CDCR models on CD$^2$CR. Our data set, annotation tool and guidelines as well as our model for cross-document cross-domain co-reference are all supplied as open access open source resources.
Measuring prominence of scientific work in online news as a proxy for impact
Jul 28, 2020

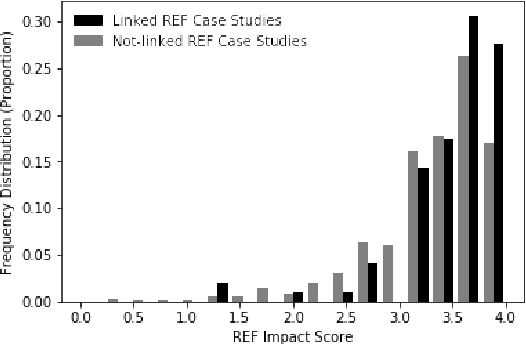

Abstract:The impact made by a scientific paper on the work of other academics has many established metrics, including metrics based on citation counts and social media commenting. However, determination of the impact of a scientific paper on the wider society is less well established. For example, is it important for scientific work to be newsworthy? Here we present a new corpus of newspaper articles linked to the scientific papers that they describe. We find that Impact Case studies submitted to the UK Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2014 that refer to scientific papers mentioned in newspaper articles were awarded a higher score in the REF assessment. The papers associated with these case studies also feature prominently in the newspaper articles. We hypothesise that such prominence can be a useful proxy for societal impact. We therefore provide a novel baseline approach for measuring the prominence of scientific papers mentioned within news articles. Our measurement of prominence is based on semantic similarity through a graph-based ranking algorithm. We find that scientific papers with an associated REF case study are more likely to have a stronger prominence score. This supports our hypothesis that linguistic prominence in news can be used to suggest the wider non-academic impact of scientific work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge