Jafar Majidpour
Video Forgery Detection for Surveillance Cameras: A Review
May 04, 2025Abstract:The widespread availability of video recording through smartphones and digital devices has made video-based evidence more accessible than ever. Surveillance footage plays a crucial role in security, law enforcement, and judicial processes. However, with the rise of advanced video editing tools, tampering with digital recordings has become increasingly easy, raising concerns about their authenticity. Ensuring the integrity of surveillance videos is essential, as manipulated footage can lead to misinformation and undermine judicial decisions. This paper provides a comprehensive review of existing forensic techniques used to detect video forgery, focusing on their effectiveness in verifying the authenticity of surveillance recordings. Various methods, including compression-based analysis, frame duplication detection, and machine learning-based approaches, are explored. The findings highlight the growing necessity for more robust forensic techniques to counteract evolving forgery methods. Strengthening video forensic capabilities will ensure that surveillance recordings remain credible and admissible as legal evidence.
Detection of Auditory Brainstem Response Peaks Using Image Processing Techniques in Infants with Normal Hearing Sensitivity
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:Introduction: The auditory brainstem response (ABR) is measured to find the brainstem-level peripheral auditory nerve system integrity in children having normal hearing. The Auditory Evoked Potential (AEP) is generated using acoustic stimuli. Interpreting these waves requires competence to avoid misdiagnosing hearing problems. Automating ABR test labeling with computer vision may reduce human error. Method: The ABR test results of 26 children aged 1 to 20 months with normal hearing in both ears were used. A new approach is suggested for automatically calculating the peaks of waves of different intensities (in decibels). The procedure entails acquiring wave images from an Audera device using the Color Thresholder method, segmenting each wave as a single wave image using the Image Region Analyzer application, converting all wave images into waves using Image Processing (IP) techniques, and finally calculating the latency of the peaks for each wave to be used by an audiologist for diagnosing the disease. Findings: Image processing techniques were able to detect 1, 3, and 5 waves in the diagnosis field with accuracy (0.82), (0.98), and (0.98), respectively, and its precision for waves 1, 3, and 5, were respectively (0.32), (0.97) and (0.87). This evaluation also worked well in the thresholding part and 82.7 % correctly detected the ABR waves. Conclusion: Our findings indicate that the audiology test battery suite can be made more accurate, quick, and error-free by using technology to automatically detect and label ABR waves.
Multi-Transfer Learning Techniques for Detecting Auditory Brainstem Response
Aug 29, 2023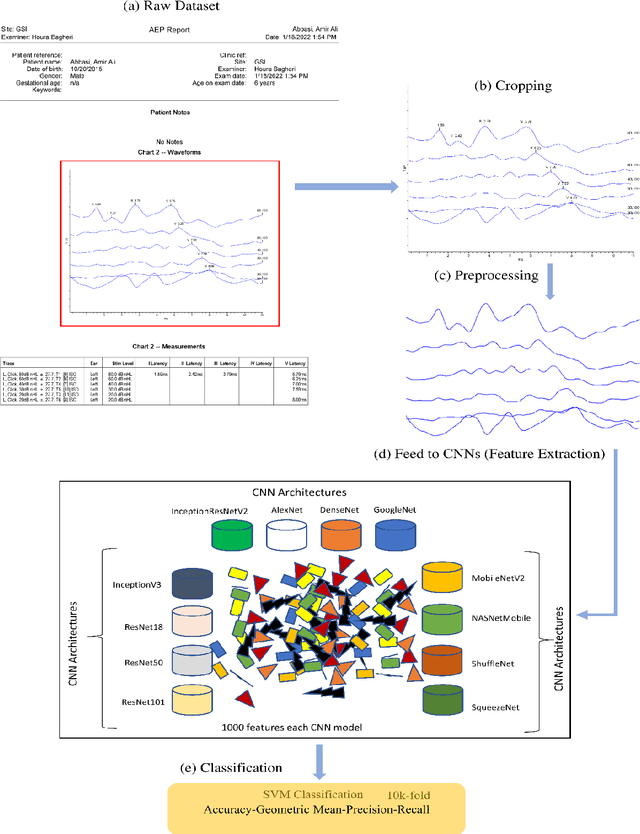
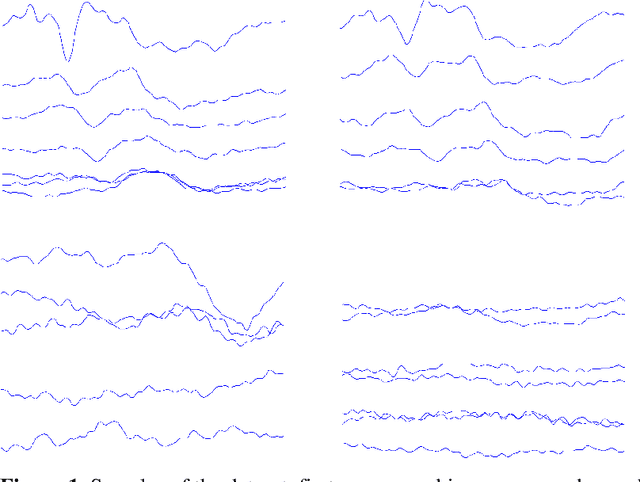
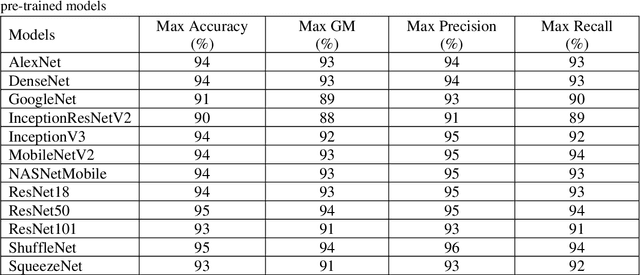
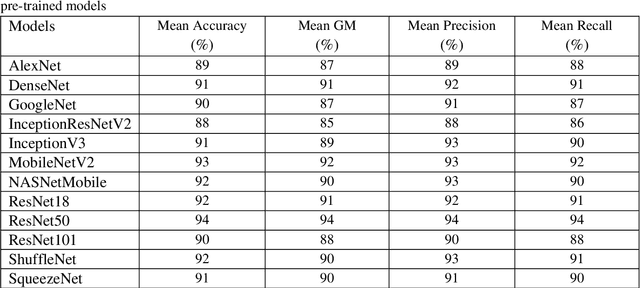
Abstract:The assessment of the well-being of the peripheral auditory nerve system in individuals experiencing hearing impairment is conducted through auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing. Audiologists assess and document the results of the ABR test. They interpret the findings and assign labels to them using reference-based markers like peak latency, waveform morphology, amplitude, and other relevant factors. Inaccurate assessment of ABR tests may lead to incorrect judgments regarding the integrity of the auditory nerve system; therefore, proper Hearing Loss (HL) diagnosis and analysis are essential. To identify and assess ABR automation while decreasing the possibility of human error, machine learning methods, notably deep learning, may be an appropriate option. To address these issues, this study proposed deep-learning models using the transfer-learning (TL) approach to extract features from ABR testing and diagnose HL using support vector machines (SVM). Pre-trained convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures like AlexNet, DenseNet, GoogleNet, InceptionResNetV2, InceptionV3, MobileNetV2, NASNetMobile, ResNet18, ResNet50, ResNet101, ShuffleNet, and SqueezeNet are used to extract features from the collected ABR reported images dataset in the proposed model. It has been decided to use six measures accuracy, precision, recall, geometric mean (GM), standard deviation (SD), and area under the ROC curve to measure the effectiveness of the proposed model. According to experimental findings, the ShuffleNet and ResNet50 models' TL is effective for ABR to diagnose HL using an SVM classifier, with a high accuracy rate of 95% when using the 5-fold cross-validation method.
* 19
Automatic image annotation base on Naive Bayes and Decision Tree classifiers using MPEG-7
Jan 27, 2021



Abstract:Recently it has become essential to search for and retrieve high-resolution and efficient images easily due to swift development of digital images, many present annotation algorithms facing a big challenge which is the variance for represent the image where high level represent image semantic and low level illustrate the features, this issue is known as semantic gab. This work has been used MPEG-7 standard to extract the features from the images, where the color feature was extracted by using Scalable Color Descriptor (SCD) and Color Layout Descriptor (CLD), whereas the texture feature was extracted by employing Edge Histogram Descriptor (EHD), the CLD produced high dimensionality feature vector therefore it is reduced by Principal Component Analysis (PCA). The features that have extracted by these three descriptors could be passing to the classifiers (Naive Bayes and Decision Tree) for training. Finally, they annotated the query image. In this study TUDarmstadt image bank had been used. The results of tests and comparative performance evaluation indicated better precision and executing time of Naive Bayes classification in comparison with Decision Tree classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge