JaeHo Chung
Active Learning for Finely-Categorized Image-Text Retrieval by Selecting Hard Negative Unpaired Samples
May 25, 2024

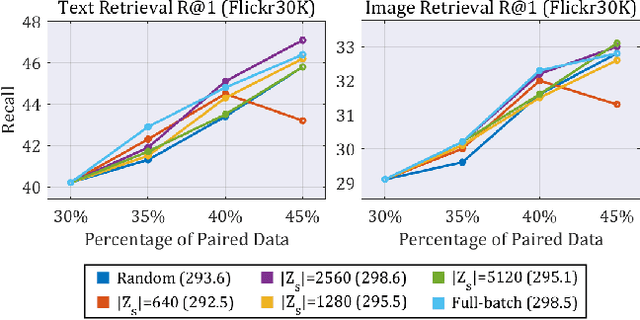
Abstract:Securing a sufficient amount of paired data is important to train an image-text retrieval (ITR) model, but collecting paired data is very expensive. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose an active learning algorithm for ITR that can collect paired data cost-efficiently. Previous studies assume that image-text pairs are given and their category labels are asked to the annotator. However, in the recent ITR studies, the importance of category label is decreased since a retrieval model can be trained with only image-text pairs. For this reason, we set up an active learning scenario where unpaired images (or texts) are given and the annotator provides corresponding texts (or images) to make paired data. The key idea of the proposed AL algorithm is to select unpaired images (or texts) that can be hard negative samples for existing texts (or images). To this end, we introduce a novel scoring function to choose hard negative samples. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method on Flickr30K and MS-COCO datasets.
Three Factors to Improve Out-of-Distribution Detection
Aug 02, 2023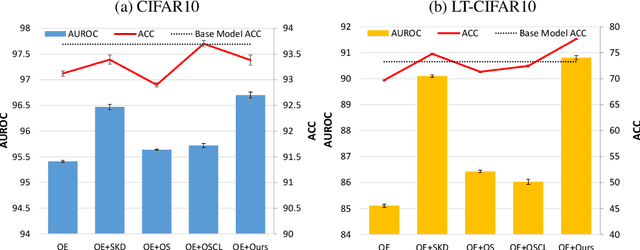
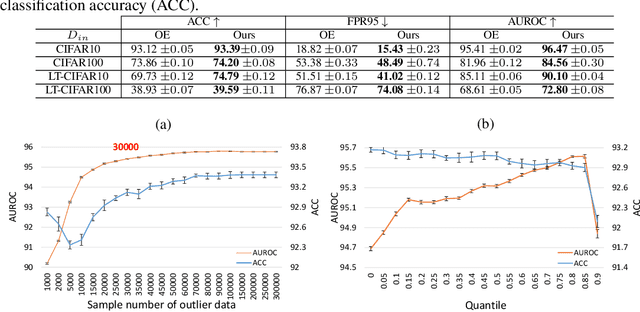
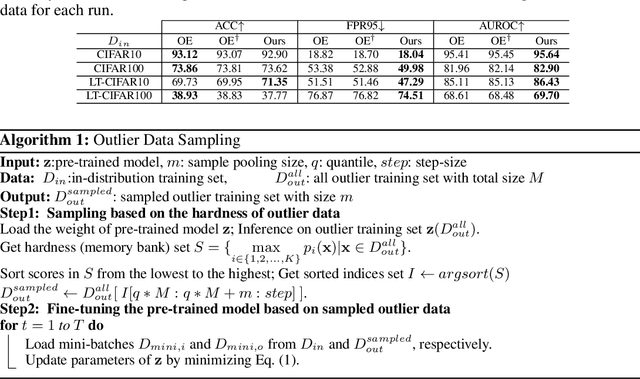
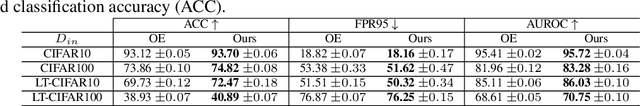
Abstract:In the problem of out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, the usage of auxiliary data as outlier data for fine-tuning has demonstrated encouraging performance. However, previous methods have suffered from a trade-off between classification accuracy (ACC) and OOD detection performance (AUROC, FPR, AUPR). To improve this trade-off, we make three contributions: (i) Incorporating a self-knowledge distillation loss can enhance the accuracy of the network; (ii) Sampling semi-hard outlier data for training can improve OOD detection performance with minimal impact on accuracy; (iii) The introduction of our novel supervised contrastive learning can simultaneously improve OOD detection performance and the accuracy of the network. By incorporating all three factors, our approach enhances both accuracy and OOD detection performance by addressing the trade-off between classification and OOD detection. Our method achieves improvements over previous approaches in both performance metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge