Jacques Felblinger
IADI, CIC-IT
Automatic Tongue Delineation from MRI Images with a Convolutional Neural Network Approach
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Tongue contour extraction from real-time magnetic resonance images is a nontrivial task due to the presence of artifacts manifesting in form of blurring or ghostly contours. In this work, we present results of automatic tongue delineation achieved by means of U-Net auto-encoder convolutional neural network. We present both intra- and inter-subject validation. We used real-time magnetic resonance images and manually annotated 1-pixel wide contours as inputs. Predicted probability maps were post-processed in order to obtain 1-pixel wide tongue contours. The results are very good and slightly outperform published results on automatic tongue segmentation.
Extraction of 3D trajectories of mandibular condyles from 2D real-time MRI
Jun 21, 2024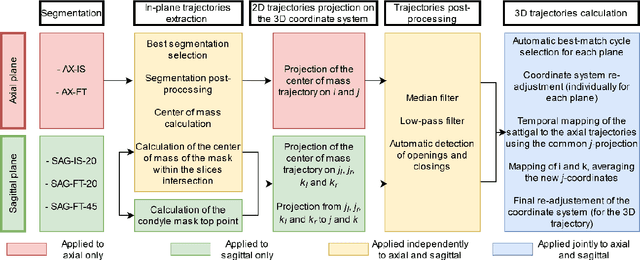
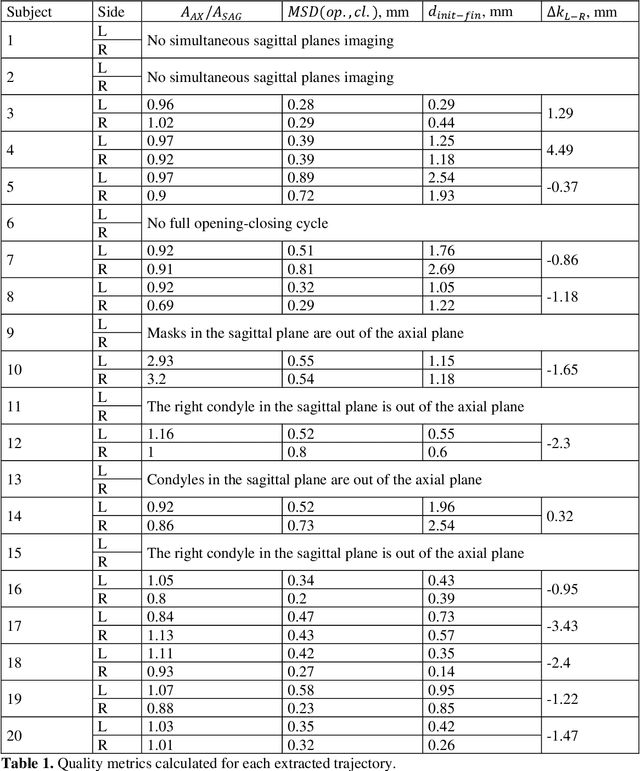
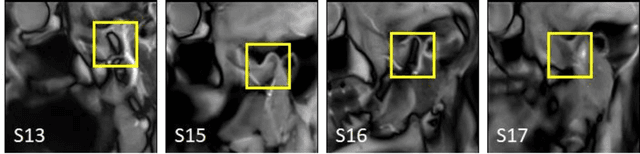
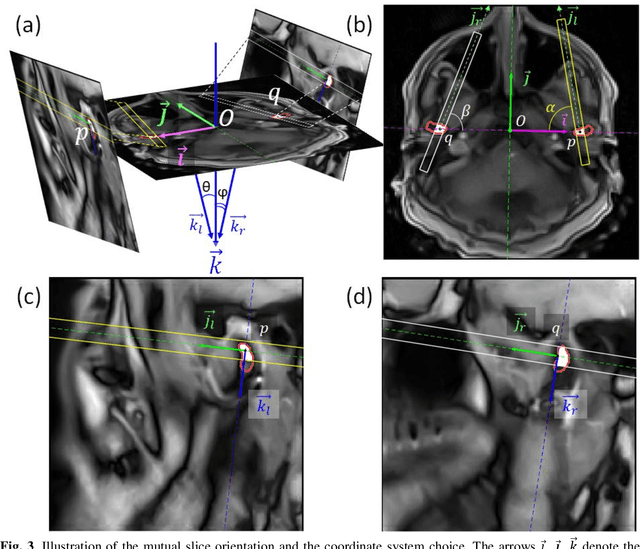
Abstract:Computing the trajectories of mandibular condyles directly from MRI could provide a comprehensive examination, allowing for the extraction of both anatomical and kinematic details. This study aimed to investigate the feasibility of extracting 3D condylar trajectories from 2D real-time MRI and to assess their precision.Twenty healthy subjects underwent real-time MRI while opening and closing their jaws. One axial and two sagittal slices were segmented using a U-Net-based algorithm. The centers of mass of the resulting masks were projected onto the coordinate system based on anatomical markers and temporally adjusted using a common projection. The quality of the computed trajectories was evaluated using metrics designed to estimate movement reproducibility, head motion, and slice placement symmetry.The segmentation of the axial slices demonstrated good-to-excellent quality; however, the segmentation of the sagittal slices required some fine-tuning. The movement reproducibility was acceptable for most cases; nevertheless, head motion displaced the trajectories by 1 mm on average. The difference in the superior-inferior coordinate of the condyles in the closed jaw position was 1.7 mm on average.Despite limitations in precision, real-time MRI enables the extraction of condylar trajectories with sufficient accuracy for evaluating clinically relevant parameters such as condyle displacement, trajectories aspect, and symmetry.
Motion Estimated-Compensated Reconstruction with Preserved-Features in Free-Breathing Cardiac MRI
Nov 15, 2016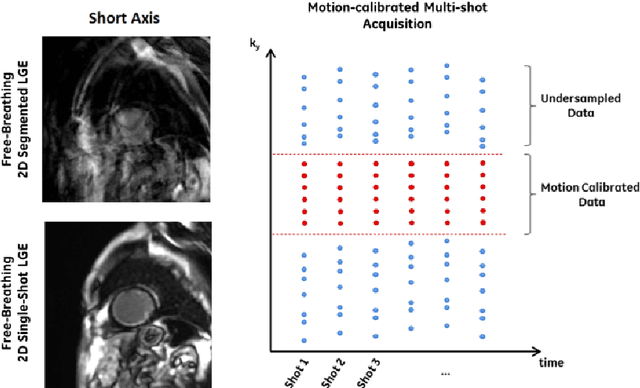
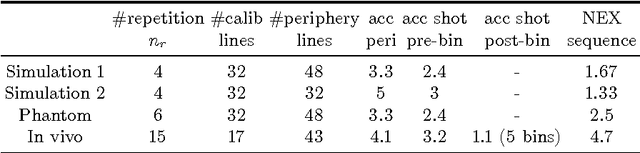
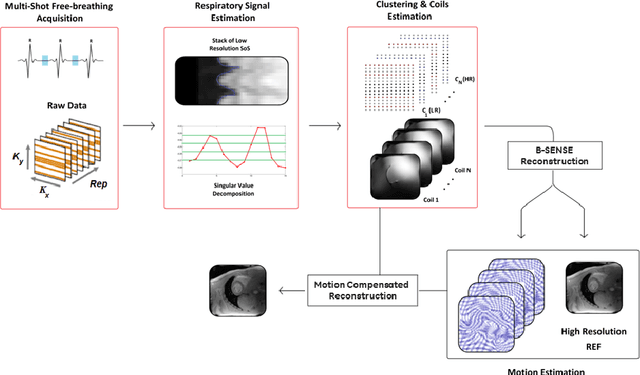
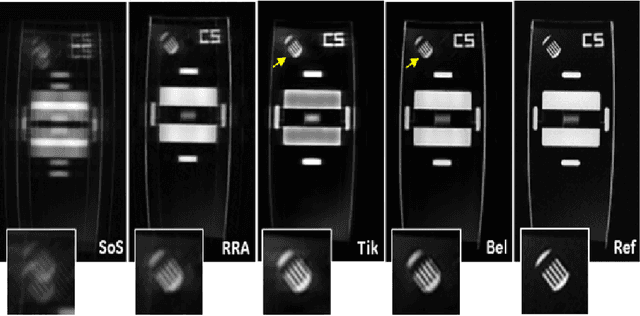
Abstract:To develop an efficient motion-compensated reconstruction technique for free-breathing cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that allows high-quality images to be reconstructed from multiple undersampled single-shot acquisitions. The proposed method is a joint image reconstruction and motion correction method consisting of several steps, including a non-rigid motion extraction and a motion-compensated reconstruction. The reconstruction includes a denoising with the Beltrami regularization, which offers an ideal compromise between feature preservation and staircasing reduction. Results were assessed in simulation, phantom and volunteer experiments. The proposed joint image reconstruction and motion correction method exhibits visible quality improvement over previous methods while reconstructing sharper edges. Moreover, when the acceleration factor increases, standard methods show blurry results while the proposed method preserves image quality. The method was applied to free-breathing single-shot cardiac MRI, successfully achieving high image quality and higher spatial resolution than conventional segmented methods, with the potential to offer high-quality delayed enhancement scans in challenging patients.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge