Pierre-André Vuissoz
IADI
Automatic Tongue Delineation from MRI Images with a Convolutional Neural Network Approach
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Tongue contour extraction from real-time magnetic resonance images is a nontrivial task due to the presence of artifacts manifesting in form of blurring or ghostly contours. In this work, we present results of automatic tongue delineation achieved by means of U-Net auto-encoder convolutional neural network. We present both intra- and inter-subject validation. We used real-time magnetic resonance images and manually annotated 1-pixel wide contours as inputs. Predicted probability maps were post-processed in order to obtain 1-pixel wide tongue contours. The results are very good and slightly outperform published results on automatic tongue segmentation.
Complete reconstruction of the tongue contour through acoustic to articulatory inversion using real-time MRI data
Nov 04, 2024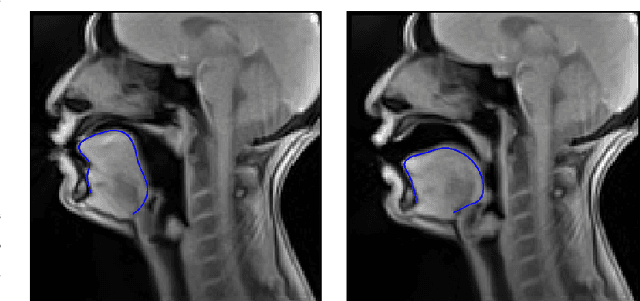
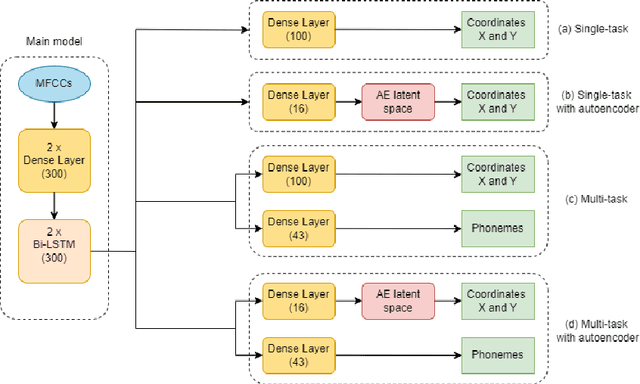
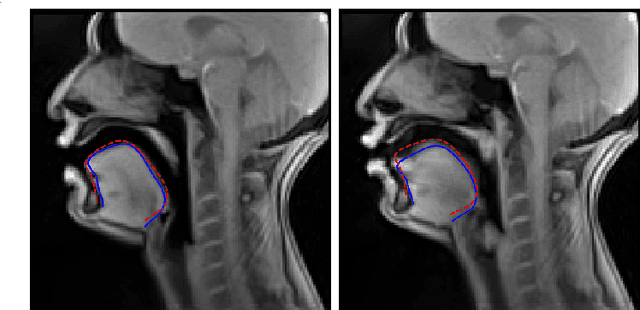
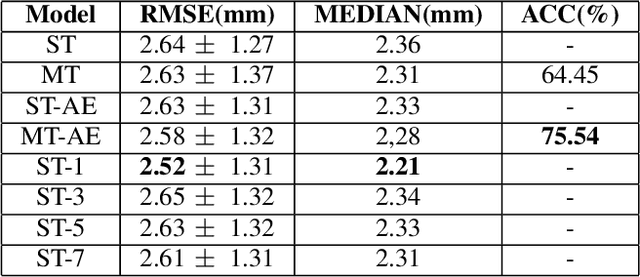
Abstract:Acoustic articulatory inversion is a major processing challenge, with a wide range of applications from speech synthesis to feedback systems for language learning and rehabilitation. In recent years, deep learning methods have been applied to the inversion of less than a dozen geometrical positions corresponding to sensors glued to easily accessible articulators. It is therefore impossible to know the shape of the whole tongue from root to tip. In this work, we use high-quality real-time MRI data to track the contour of the tongue. The data used to drive the inversion are therefore the unstructured speech signal and the tongue contours. Several architectures relying on a Bi-MSTM including or not an autoencoder to reduce the dimensionality of the latent space, using or not the phonetic segmentation have been explored. The results show that the tongue contour can be recovered with a median accuracy of 2.21 mm (or 1.37 pixel) taking a context of 1 MFCC frame (static, delta and double-delta cepstral features).
Extraction of 3D trajectories of mandibular condyles from 2D real-time MRI
Jun 21, 2024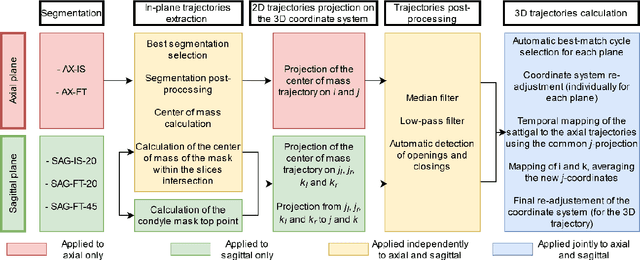
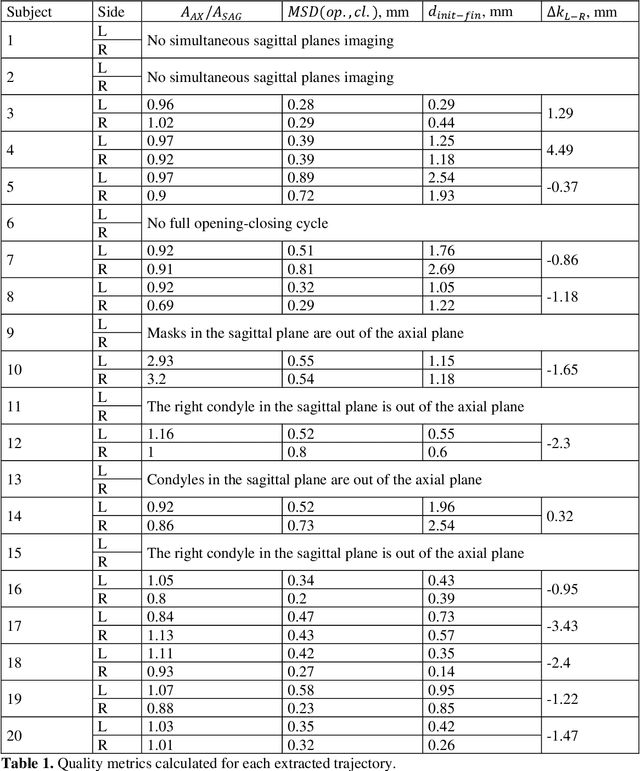
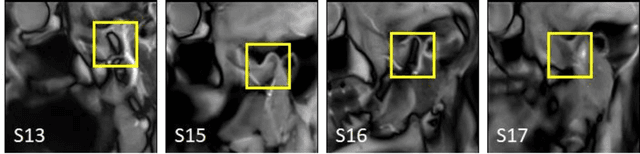
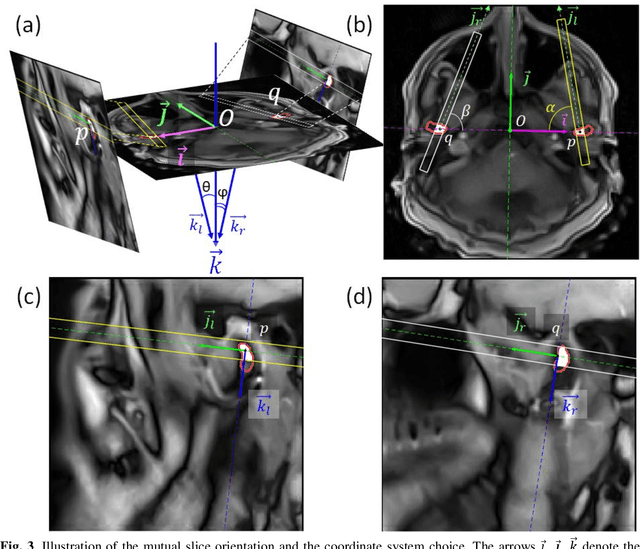
Abstract:Computing the trajectories of mandibular condyles directly from MRI could provide a comprehensive examination, allowing for the extraction of both anatomical and kinematic details. This study aimed to investigate the feasibility of extracting 3D condylar trajectories from 2D real-time MRI and to assess their precision.Twenty healthy subjects underwent real-time MRI while opening and closing their jaws. One axial and two sagittal slices were segmented using a U-Net-based algorithm. The centers of mass of the resulting masks were projected onto the coordinate system based on anatomical markers and temporally adjusted using a common projection. The quality of the computed trajectories was evaluated using metrics designed to estimate movement reproducibility, head motion, and slice placement symmetry.The segmentation of the axial slices demonstrated good-to-excellent quality; however, the segmentation of the sagittal slices required some fine-tuning. The movement reproducibility was acceptable for most cases; nevertheless, head motion displaced the trajectories by 1 mm on average. The difference in the superior-inferior coordinate of the condyles in the closed jaw position was 1.7 mm on average.Despite limitations in precision, real-time MRI enables the extraction of condylar trajectories with sufficient accuracy for evaluating clinically relevant parameters such as condyle displacement, trajectories aspect, and symmetry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge