Jacqueline Urakami
Qualitative Approaches to Voice UX
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:Voice is a natural mode of expression offered by modern computer-based systems. Qualitative perspectives on voice-based user experiences (voice UX) offer rich descriptions of complex interactions that numbers alone cannot fully represent. We conducted a systematic review of the literature on qualitative approaches to voice UX, capturing the nature of this body of work in a systematic map and offering a qualitative synthesis of findings. We highlight the benefits of qualitative methods for voice UX research, identify opportunities for increasing rigour in methods and outcomes, and distill patterns of experience across a diversity of devices and modes of qualitative praxis.
Nonverbal Cues in Human-Robot Interaction: A Communication Studies Perspective
Apr 22, 2023Abstract:Communication between people is characterized by a broad range of nonverbal cues. Transferring these cues into the design of robots and other artificial agents that interact with people may foster more natural, inviting, and accessible experiences. In this position paper, we offer a series of definitive nonverbal codes for human-robot interaction (HRI) that address the five human sensory systems (visual, auditory, haptic, olfactory, gustatory) drawn from the field of communication studies. We discuss how these codes can be translated into design patterns for HRI using a curated sample of the communication studies and HRI literatures. As nonverbal codes are an essential mode in human communication, we argue that integrating robotic nonverbal codes in HRI will afford robots a feeling of "aliveness" or "social agency" that would otherwise be missing. We end with suggestions for research directions to stimulate work on nonverbal communication within the field of HRI and improve communication between human and robots.
* 21 pages
Exoskeleton for the Mind: Exploring Strategies Against Misinformation with a Metacognitive Agent
Apr 18, 2023Abstract:Misinformation is a global problem in modern social media platforms with few solutions known to be effective. Social media platforms have offered tools to raise awareness of information, but these are closed systems that have not been empirically evaluated. Others have developed novel tools and strategies, but most have been studied out of context using static stimuli, researcher prompts, or low fidelity prototypes. We offer a new anti-misinformation agent grounded in theories of metacognition that was evaluated within Twitter. We report on a pilot study (n=17) and multi-part experimental study (n=57, n=49) where participants experienced three versions of the agent, each deploying a different strategy. We found that no single strategy was superior over the control. We also confirmed the necessity of transparency and clarity about the agent's underlying logic, as well as concerns about repeated exposure to misinformation and lack of user engagement.
* Pages 209-220
Trust in Human-AI Interaction: Scoping Out Models, Measures, and Methods
Apr 30, 2022
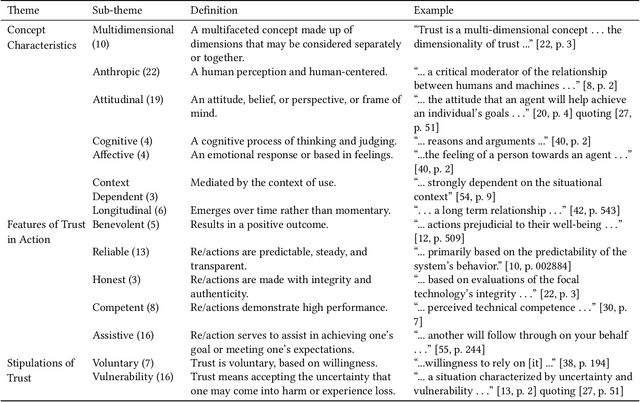
Abstract:Trust has emerged as a key factor in people's interactions with AI-infused systems. Yet, little is known about what models of trust have been used and for what systems: robots, virtual characters, smart vehicles, decision aids, or others. Moreover, there is yet no known standard approach to measuring trust in AI. This scoping review maps out the state of affairs on trust in human-AI interaction (HAII) from the perspectives of models, measures, and methods. Findings suggest that trust is an important and multi-faceted topic of study within HAII contexts. However, most work is under-theorized and under-reported, generally not using established trust models and missing details about methods, especially Wizard of Oz. We offer several targets for systematic review work as well as a research agenda for combining the strengths and addressing the weaknesses of the current literature.
* Accepted at CHI EA '22
Measuring Voice UX Quantitatively: A Rapid Review
Mar 12, 2021



Abstract:Computer voice is experiencing a renaissance through the growing popularity of voice-based interfaces, agents, and environments. Yet, how to measure the user experience (UX) of voice-based systems remains an open and urgent question, especially given that their form factors and interaction styles tend to be non-visual, intangible, and often considered disembodied or "body-less." As a first step, we surveyed the ACM and IEEE literatures to determine which quantitative measures and measurements have been deemed important for voice UX. Our findings show that there is little consensus, even with similar situations and systems, as well as an overreliance on lab work and unvalidated scales. In response, we offer two high-level descriptive frameworks for guiding future research, developing standardized instruments, and informing ongoing review work. Our work highlights the current strengths and weaknesses of voice UX research and charts a path towards measuring voice UX in a more comprehensive way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge