Jaclyn R. Lunger
Learning Ordering in Crystalline Materials with Symmetry-Aware Graph Neural Networks
Sep 20, 2024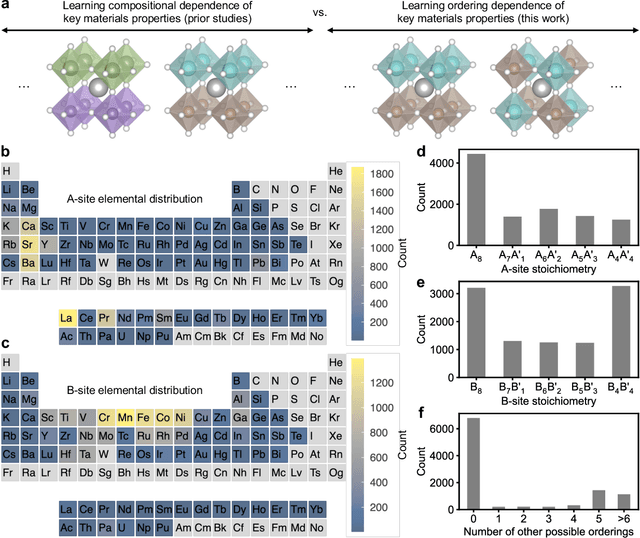
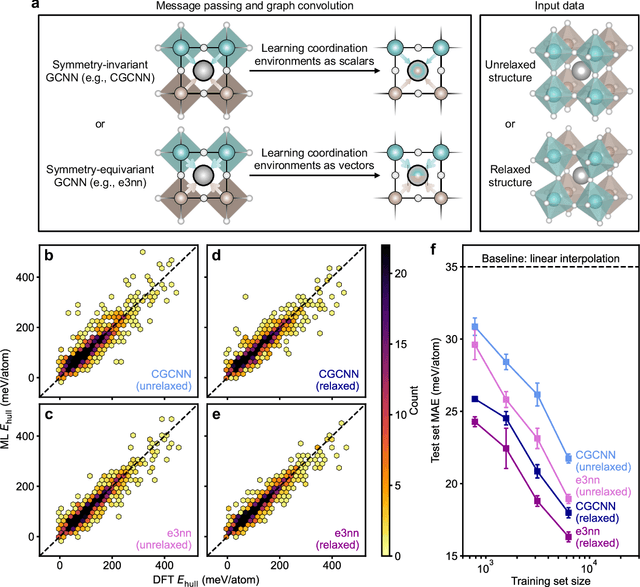
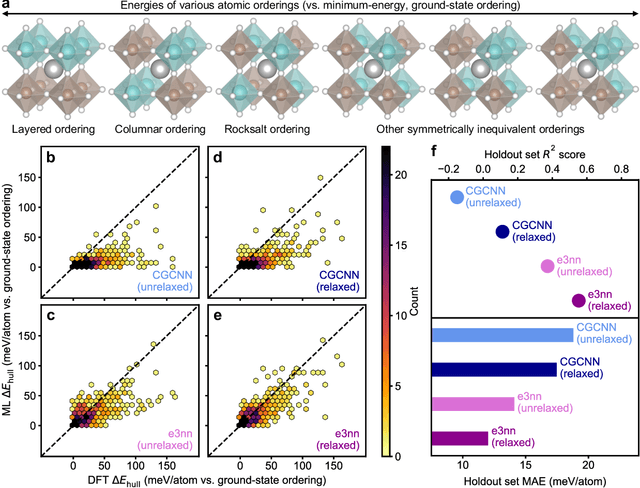
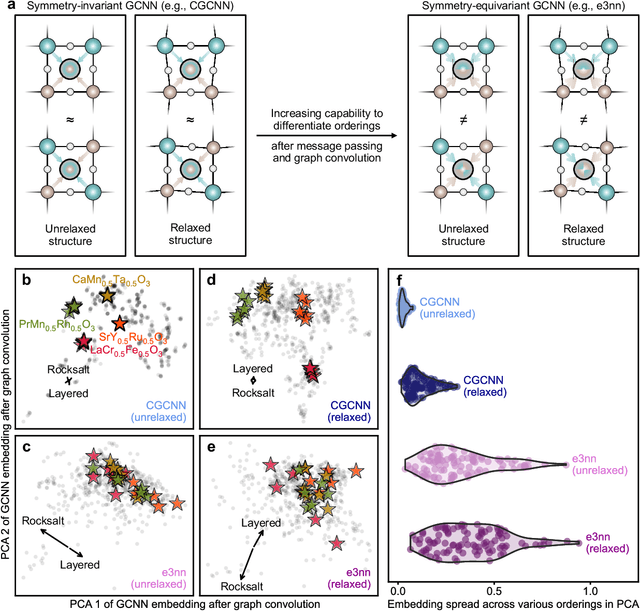
Abstract:Graph convolutional neural networks (GCNNs) have become a machine learning workhorse for screening the chemical space of crystalline materials in fields such as catalysis and energy storage, by predicting properties from structures. Multicomponent materials, however, present a unique challenge since they can exhibit chemical (dis)order, where a given lattice structure can encompass a variety of elemental arrangements ranging from highly ordered structures to fully disordered solid solutions. Critically, properties like stability, strength, and catalytic performance depend not only on structures but also on orderings. To enable rigorous materials design, it is thus critical to ensure GCNNs are capable of distinguishing among atomic orderings. However, the ordering-aware capability of GCNNs has been poorly understood. Here, we benchmark various neural network architectures for capturing the ordering-dependent energetics of multicomponent materials in a custom-made dataset generated with high-throughput atomistic simulations. Conventional symmetry-invariant GCNNs were found unable to discern the structural difference between the diverse symmetrically inequivalent atomic orderings of the same material, while symmetry-equivariant model architectures could inherently preserve and differentiate the distinct crystallographic symmetries of various orderings.
Machine-learning-accelerated simulations enable heuristic-free surface reconstruction
May 12, 2023Abstract:Understanding material surfaces and interfaces is vital in applications like catalysis or electronics. Ab initio simulations, combining energies from electronic structure with statistical mechanics, can, in principle, predict the structure of material surfaces as a function of thermodynamic variables. However, accurate energy simulations are prohibitive when coupled to the vast phase space that must be statistically sampled. Here, we present a bi-faceted computational loop to predict surface phase diagrams of multi-component materials that accelerates both the energy scoring and statistical sampling methods. Fast, scalable, and data-efficient machine learning interatomic potentials are trained on high-throughput density-functional theory calculations through closed-loop active learning. Markov-chain Monte Carlo sampling in the semi-grand canonical ensemble is enabled by using virtual surface sites. The predicted surfaces for GaN(0001) and SrTiO3(001) are in agreement with past work and suggest that the proposed strategy can model complex material surfaces and discover previously unreported surface terminations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge