J. P. Naiman
UniverseTBD
pathfinder: A Semantic Framework for Literature Review and Knowledge Discovery in Astronomy
Aug 02, 2024



Abstract:The exponential growth of astronomical literature poses significant challenges for researchers navigating and synthesizing general insights or even domain-specific knowledge. We present Pathfinder, a machine learning framework designed to enable literature review and knowledge discovery in astronomy, focusing on semantic searching with natural language instead of syntactic searches with keywords. Utilizing state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) and a corpus of 350,000 peer-reviewed papers from the Astrophysics Data System (ADS), Pathfinder offers an innovative approach to scientific inquiry and literature exploration. Our framework couples advanced retrieval techniques with LLM-based synthesis to search astronomical literature by semantic context as a complement to currently existing methods that use keywords or citation graphs. It addresses complexities of jargon, named entities, and temporal aspects through time-based and citation-based weighting schemes. We demonstrate the tool's versatility through case studies, showcasing its application in various research scenarios. The system's performance is evaluated using custom benchmarks, including single-paper and multi-paper tasks. Beyond literature review, Pathfinder offers unique capabilities for reformatting answers in ways that are accessible to various audiences (e.g. in a different language or as simplified text), visualizing research landscapes, and tracking the impact of observatories and methodologies. This tool represents a significant advancement in applying AI to astronomical research, aiding researchers at all career stages in navigating modern astronomy literature.
CloudFindr: A Deep Learning Cloud Artifact Masker for Satellite DEM Data
Oct 26, 2021


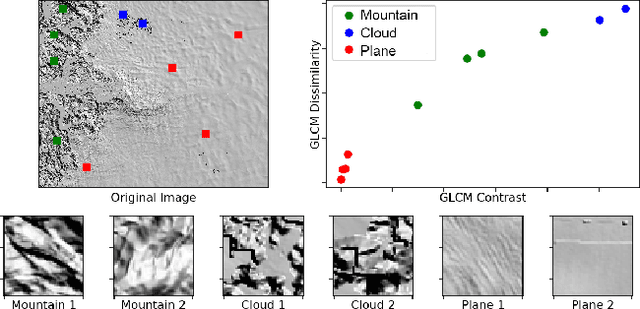
Abstract:Artifact removal is an integral component of cinematic scientific visualization, and is especially challenging with big datasets in which artifacts are difficult to define. In this paper, we describe a method for creating cloud artifact masks which can be used to remove artifacts from satellite imagery using a combination of traditional image processing together with deep learning based on U-Net. Compared to previous methods, our approach does not require multi-channel spectral imagery but performs successfully on single-channel Digital Elevation Models (DEMs). DEMs are a representation of the topography of the Earth and have a variety applications including planetary science, geology, flood modeling, and city planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge