Itai Cohen
$Γ$-VAE: Curvature regularized variational autoencoders for uncovering emergent low dimensional geometric structure in high dimensional data
Mar 02, 2024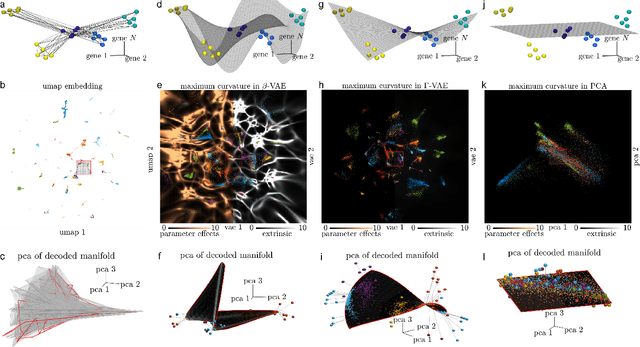
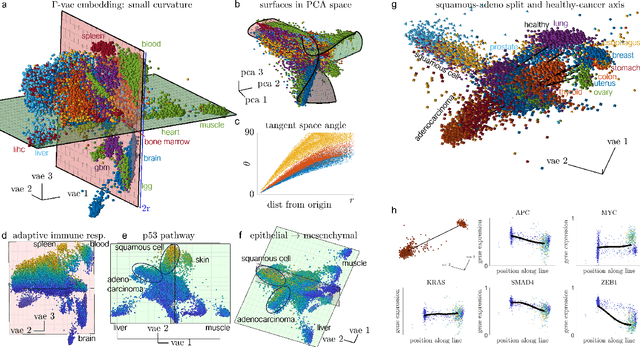
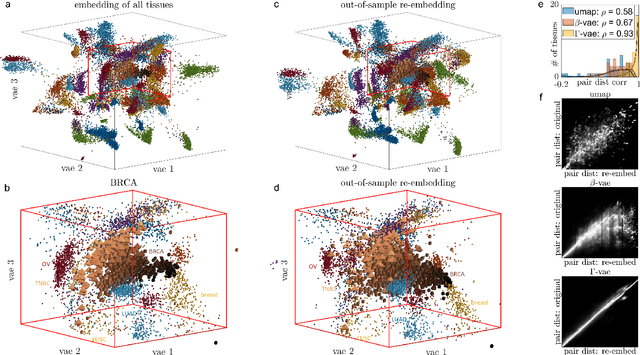

Abstract:Natural systems with emergent behaviors often organize along low-dimensional subsets of high-dimensional spaces. For example, despite the tens of thousands of genes in the human genome, the principled study of genomics is fruitful because biological processes rely on coordinated organization that results in lower dimensional phenotypes. To uncover this organization, many nonlinear dimensionality reduction techniques have successfully embedded high-dimensional data into low-dimensional spaces by preserving local similarities between data points. However, the nonlinearities in these methods allow for too much curvature to preserve general trends across multiple non-neighboring data clusters, thereby limiting their interpretability and generalizability to out-of-distribution data. Here, we address both of these limitations by regularizing the curvature of manifolds generated by variational autoencoders, a process we coin ``$\Gamma$-VAE''. We demonstrate its utility using two example data sets: bulk RNA-seq from the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Genotype Tissue Expression (GTEx); and single cell RNA-seq from a lineage tracing experiment in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation. We find that the resulting regularized manifolds identify mesoscale structure associated with different cancer cell types, and accurately re-embed tissues from completely unseen, out-of distribution cancers as if they were originally trained on them. Finally, we show that preserving long-range relationships to differentiated cells separates undifferentiated cells -- which have not yet specialized -- according to their eventual fate. Broadly, we anticipate that regularizing the curvature of generative models will enable more consistent, predictive, and generalizable models in any high-dimensional system with emergent low-dimensional behavior.
A watershed-based algorithm to segment and classify cells in fluorescence microscopy images
Jun 02, 2017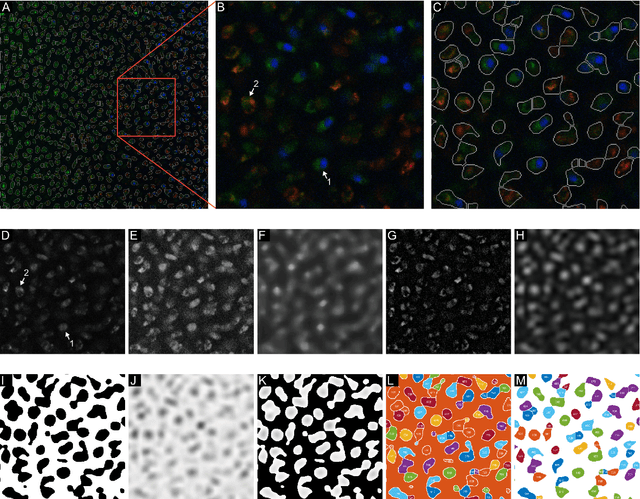
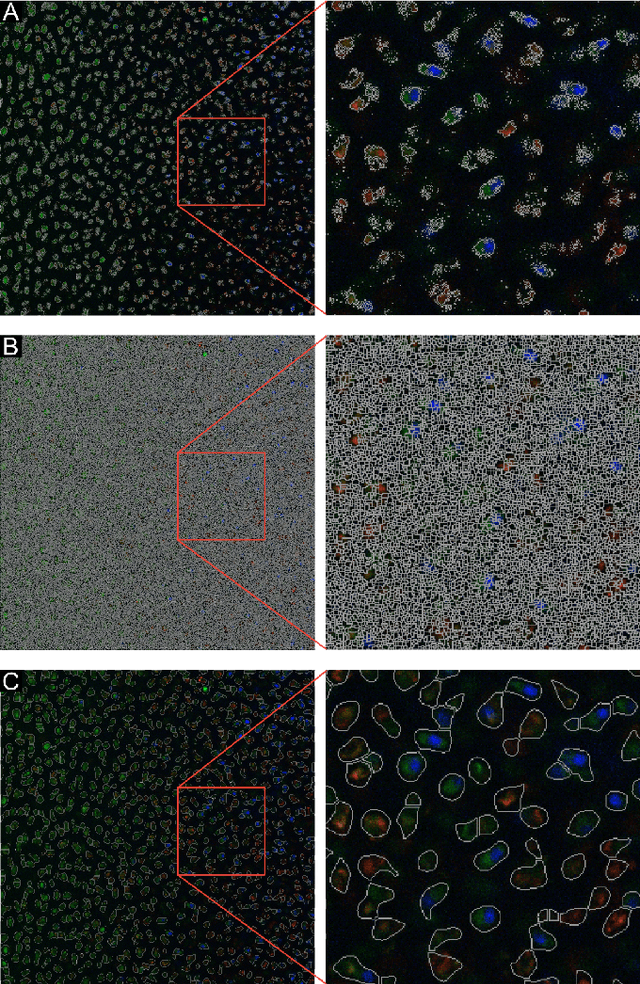
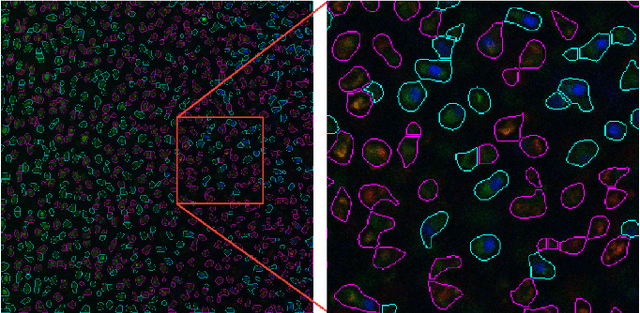
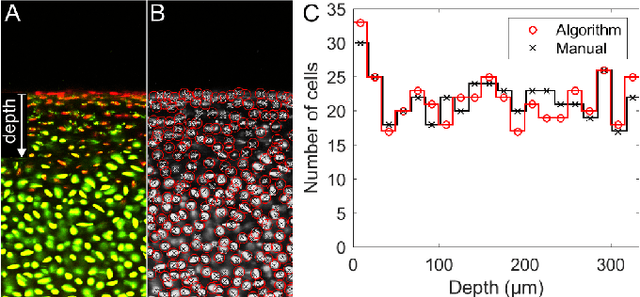
Abstract:Imaging assays of cellular function, especially those using fluorescent stains, are ubiquitous in the biological and medical sciences. Despite advances in computer vision, such images are often analyzed using only manual or rudimentary automated processes. Watershed-based segmentation is an effective technique for identifying objects in images; it outperforms commonly used image analysis methods, but requires familiarity with computer-vision techniques to be applied successfully. In this report, we present and implement a watershed-based image analysis and classification algorithm in a GUI, enabling a broad set of users to easily understand the algorithm and adjust the parameters to their specific needs. As an example, we implement this algorithm to find and classify cells in a complex imaging assay for mitochondrial function. In a second example, we demonstrate a workflow using manual comparisons and receiver operator characteristics to optimize the algorithm parameters for finding live and dead cells in a standard viability assay. Overall, this watershed-based algorithm is more advanced than traditional thresholding and can produce optimized, automated results. By incorporating associated pre-processing steps in the GUI, the algorithm is also easily adjusted, rendering it user-friendly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge