Irit Hochberg
Evaluation of a Bi-Directional Methodology for Automated Assessment of Compliance to Continuous Application of Clinical Guidelines, in the Type 2 Diabetes-Management Domain
Mar 16, 2021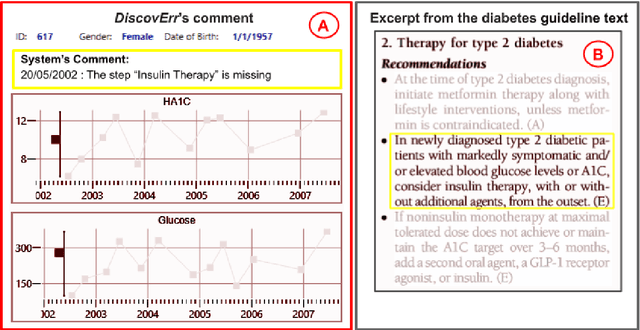
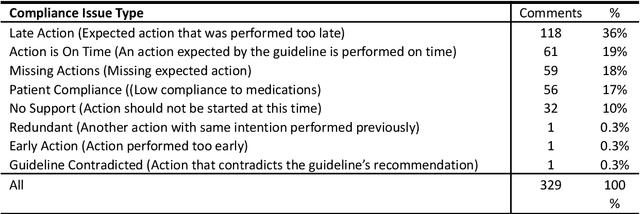
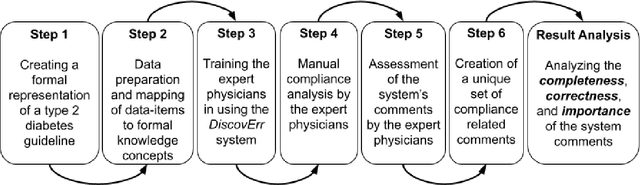
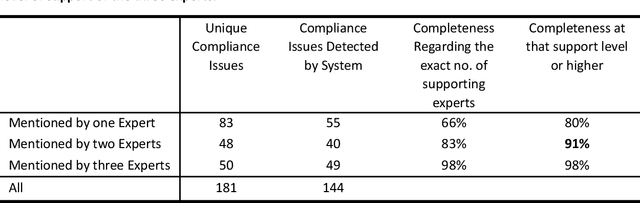
Abstract:We evaluated the DiscovErr system, in which we had previously implemented a new methodology for assessment of compliance to continuous application of evidence-based clinical guidelines, based on a bidirectional search from the guideline objectives to the patient's longitudinal data, and vice versa. We compared the system comments on 1584 transactions regarding the management, over a mean of 5.23 years, of 10 randomly selected Type 2 diabetes patients, to those of two diabetes experts and a senior family practitioner. After providing their own comments, the experts assessed both the correctness (precision) and the importance of each of the DiscovErr system comments. The completeness (recall or coverage) of the system was computed by comparing its comments to those made by the experts. The system made 279 comments. The experts made 181 unique comments. The completeness of the system was 91% compared to comments made by at least two experts, and 98% when compared to comments made by all three. 172 comments were evaluated by the experts for correctness and importance: All 114 medication-related comments, and a random 35% of the 165 monitoring-related comments. The system's correctness was 81% compared to comments judged as correct by both diabetes experts, and 91% compared to comments judged as correct by a diabetes expert and at least as partially correct by the other. 89% of the comments were judged as important by both diabetes experts, 8% were judged as important by one expert, 3% were judged as less important by both experts. The completeness scores of the three experts (compared to the comments of all experts plus the validated system comments) were 75%, 60%, and 55%; the experts' correctness scores (compared to their majority) were respectively 99%, 91%, and 88%. Conclusion: Systems such as DiscovErr can assess the quality of continuous guideline-based care.
A Reinforcement Learning System to Encourage Physical Activity in Diabetes Patients
May 13, 2016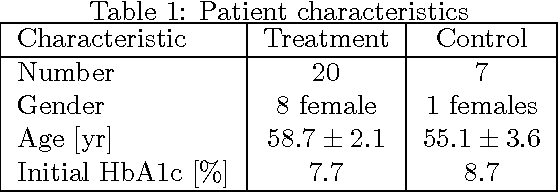
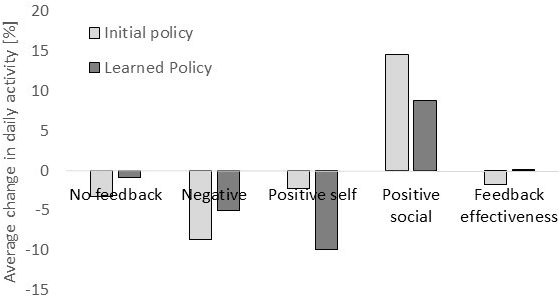
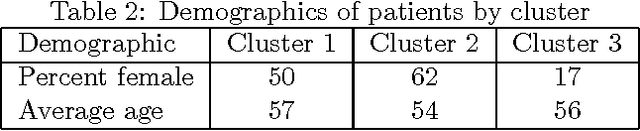
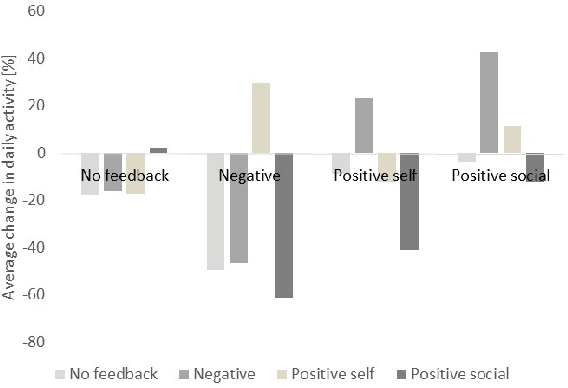
Abstract:Regular physical activity is known to be beneficial to people suffering from diabetes type 2. Nevertheless, most such people are sedentary. Smartphones create new possibilities for helping people to adhere to their physical activity goals, through continuous monitoring and communication, coupled with personalized feedback. We provided 27 sedentary diabetes type 2 patients with a smartphone-based pedometer and a personal plan for physical activity. Patients were sent SMS messages to encourage physical activity between once a day and once per week. Messages were personalized through a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm which optimized messages to improve each participant's compliance with the activity regimen. The RL algorithm was compared to a static policy for sending messages and to weekly reminders. Our results show that participants who received messages generated by the RL algorithm increased the amount of activity and pace of walking, while the control group patients did not. Patients assigned to the RL algorithm group experienced a superior reduction in blood glucose levels (HbA1c) compared to control policies, and longer participation caused greater reductions in blood glucose levels. The learning algorithm improved gradually in predicting which messages would lead participants to exercise. Our results suggest that a mobile phone application coupled with a learning algorithm can improve adherence to exercise in diabetic patients. As a learning algorithm is automated, and delivers personalized messages, it could be used in large populations of diabetic patients to improve health and glycemic control. Our results can be expanded to other areas where computer-led health coaching of humans may have a positive impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge