Irene Hou
"All Roads Lead to ChatGPT": How Generative AI is Eroding Social Interactions and Student Learning Communities
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:The widespread adoption of generative AI is already impacting learning and help-seeking. While the benefits of generative AI are well-understood, recent studies have also raised concerns about increased potential for cheating and negative impacts on students' metacognition and critical thinking. However, the potential impacts on social interactions, peer learning, and classroom dynamics are not yet well understood. To investigate these aspects, we conducted 17 semi-structured interviews with undergraduate computing students across seven R1 universities in North America. Our findings suggest that help-seeking requests are now often mediated by generative AI. For example, students often redirected questions from their peers to generative AI instead of providing assistance themselves, undermining peer interaction. Students also reported feeling increasingly isolated and demotivated as the social support systems they rely on begin to break down. These findings are concerning given the important role that social interactions play in students' learning and sense of belonging.
The Evolving Usage of GenAI by Computing Students
Dec 21, 2024

Abstract:Help-seeking is a critical aspect of learning and problem-solving for computing students. Recent research has shown that many students are aware of generative AI (GenAI) tools; however, there are gaps in the extent and effectiveness of how students use them. With over two years of widespread GenAI usage, it is crucial to understand whether students' help-seeking behaviors with these tools have evolved and how. This paper presents findings from a repeated cross-sectional survey conducted among computing students across North American universities (n=95). Our results indicate shifts in GenAI usage patterns. In 2023, 34.1% of students (n=47) reported never using ChatGPT for help, ranking it fourth after online searches, peer support, and class forums. By 2024, this figure dropped sharply to 6.3% (n=48), with ChatGPT nearly matching online search as the most commonly used help resource. Despite this growing prevalence, there has been a decline in students' hourly and daily usage of GenAI tools, which may be attributed to a common tendency to underestimate usage frequency. These findings offer new insights into the evolving role of GenAI in computing education, highlighting its increasing acceptance and solidifying its position as a key help resource.
Seeing the Forest and the Trees: Solving Visual Graph and Tree Based Data Structure Problems using Large Multimodal Models
Dec 15, 2024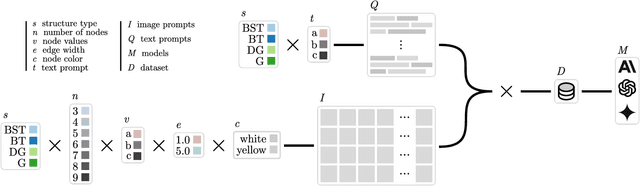

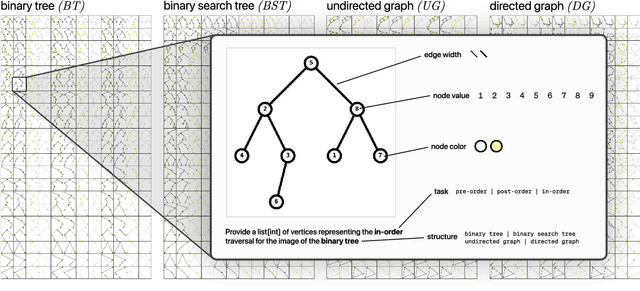

Abstract:Recent advancements in generative AI systems have raised concerns about academic integrity among educators. Beyond excelling at solving programming problems and text-based multiple-choice questions, recent research has also found that large multimodal models (LMMs) can solve Parsons problems based only on an image. However, such problems are still inherently text-based and rely on the capabilities of the models to convert the images of code blocks to their corresponding text. In this paper, we further investigate the capabilities of LMMs to solve graph and tree data structure problems based only on images. To achieve this, we computationally construct and evaluate a novel benchmark dataset comprising 9,072 samples of diverse graph and tree data structure tasks to assess the performance of the GPT-4o, GPT-4v, Gemini 1.5 Pro, Gemini 1.5 Flash, Gemini 1.0 Pro Vision, and Claude 3 model families. GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Flash performed best on trees and graphs respectively. GPT-4o achieved 87.6% accuracy on tree samples, while Gemini 1.5 Flash, achieved 56.2% accuracy on graph samples. Our findings highlight the influence of structural and visual variations on model performance. This research not only introduces an LMM benchmark to facilitate replication and further exploration but also underscores the potential of LMMs in solving complex computing problems, with important implications for pedagogy and assessment practices.
More Robots are Coming: Large Multimodal Models (ChatGPT) can Solve Visually Diverse Images of Parsons Problems
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:The advent of large language models is reshaping computing education. Recent research has demonstrated that these models can produce better explanations than students, answer multiple-choice questions at or above the class average, and generate code that can pass automated tests in introductory courses. These capabilities have prompted instructors to rapidly adapt their courses and assessment methods to accommodate changes in learning objectives and the potential for academic integrity violations. While some scholars have advocated for the integration of visual problems as a safeguard against the capabilities of language models, new multimodal language models now have vision and language capabilities that may allow them to analyze and solve visual problems. In this paper, we evaluate the performance of two large multimodal models on visual assignments, with a specific focus on Parsons problems presented across diverse visual representations. Our results show that GPT-4V solved 96.7\% of these visual problems, struggling minimally with a single Parsons problem. Conversely, Bard performed poorly by only solving 69.2\% of problems, struggling with common issues like hallucinations and refusals. These findings suggest that merely transitioning to visual programming problems might not be a panacea to issues of academic integrity in the generative AI era.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge