Ioannis Dadiotis
Dynamic object goal pushing with mobile manipulators through model-free constrained reinforcement learning
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:Non-prehensile pushing to move and reorient objects to a goal is a versatile loco-manipulation skill. In the real world, the object's physical properties and friction with the floor contain significant uncertainties, which makes the task challenging for a mobile manipulator. In this paper, we develop a learning-based controller for a mobile manipulator to move an unknown object to a desired position and yaw orientation through a sequence of pushing actions. The proposed controller for the robotic arm and the mobile base motion is trained using a constrained Reinforcement Learning (RL) formulation. We demonstrate its capability in experiments with a quadrupedal robot equipped with an arm. The learned policy achieves a success rate of 91.35% in simulation and at least 80% on hardware in challenging scenarios. Through our extensive hardware experiments, we show that the approach demonstrates high robustness against unknown objects of different masses, materials, sizes, and shapes. It reactively discovers the pushing location and direction, thus achieving contact-rich behavior while observing only the pose of the object. Additionally, we demonstrate the adaptive behavior of the learned policy towards preventing the object from toppling.
Whole-body MPC for highly redundant legged manipulators: experimental evaluation with a 37 DoF dual-arm quadruped
Oct 04, 2023



Abstract:Recent progress in legged locomotion has rendered quadruped manipulators a promising solution for performing tasks that require both mobility and manipulation (loco-manipulation). In the real world, task specifications and/or environment constraints may require the quadruped manipulator to be equipped with high redundancy as well as whole-body motion coordination capabilities. This work presents an experimental evaluation of a whole-body Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework achieving real-time performance on a dual-arm quadruped platform consisting of 37 actuated joints. To the best of our knowledge this is the legged manipulator with the highest number of joints to be controlled with real-time whole-body MPC so far. The computational efficiency of the MPC while considering the full robot kinematics and the centroidal dynamics model builds upon an open-source DDP-variant solver and a state-of-the-art optimal control problem formulation. Differently from previous works on quadruped manipulators, the MPC is directly interfaced with the low-level joint impedance controllers without the need of designing an instantaneous whole-body controller. The feasibility on the real hardware is showcased using the CENTAURO platform for the challenging task of picking a heavy object from the ground. Dynamic stepping (trotting) is also showcased for first time with this robot. The results highlight the potential of replanning with whole-body information in a predictive control loop.
Trajectory Optimization for Quadruped Mobile Manipulators that Carry Heavy Payload
Oct 13, 2022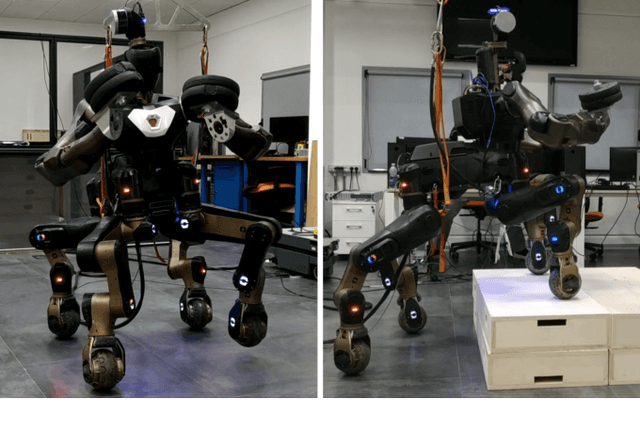



Abstract:This paper presents a simplified model-based trajectory optimization (TO) formulation for motion planning on quadruped mobile manipulators that carry heavy payload of known mass. The proposed payload-aware formulation simultaneously plans locomotion, payload manipulation and considers both robot and payload model dynamics while remaining computationally efficient. At the presence of heavy payload, the approach exhibits reduced leg outstretching (thus increased manipulability) in kinematically demanding motions due to the contribution of payload manipulation in the optimization. The framework's computational efficiency and performance is validated through a number of simulation and experimental studies with the bi-manual quadruped CENTAURO robot carrying on its arms a payload that exceeds 15 % of its mass and traversing non-flat terrain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge