Indraneel Borgohain
Towards a vision foundation model for comprehensive assessment of Cardiac MRI
Oct 02, 2024


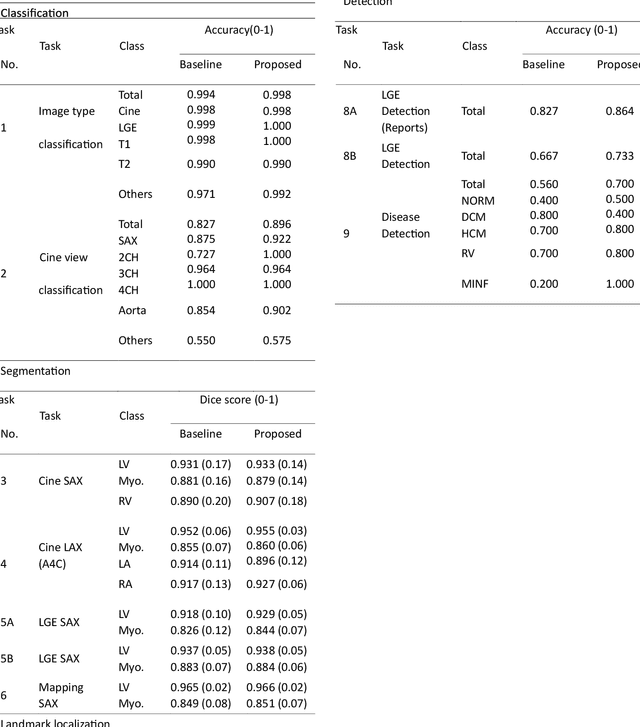
Abstract:Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR), considered the gold standard for noninvasive cardiac assessment, is a diverse and complex modality requiring a wide variety of image processing tasks for comprehensive assessment of cardiac morphology and function. Advances in deep learning have enabled the development of state-of-the-art (SoTA) models for these tasks. However, model training is challenging due to data and label scarcity, especially in the less common imaging sequences. Moreover, each model is often trained for a specific task, with no connection between related tasks. In this work, we introduce a vision foundation model trained for CMR assessment, that is trained in a self-supervised fashion on 36 million CMR images. We then finetune the model in supervised way for 9 clinical tasks typical to a CMR workflow, across classification, segmentation, landmark localization, and pathology detection. We demonstrate improved accuracy and robustness across all tasks, over a range of available labeled dataset sizes. We also demonstrate improved few-shot learning with fewer labeled samples, a common challenge in medical image analyses. We achieve an out-of-box performance comparable to SoTA for most clinical tasks. The proposed method thus presents a resource-efficient, unified framework for CMR assessment, with the potential to accelerate the development of deep learning-based solutions for image analysis tasks, even with few annotated data available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge