Imran Ahamad Sheikh
MULTISPEECH
Joint Beamforming and Speaker-Attributed ASR for Real Distant-Microphone Meeting Transcription
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Distant-microphone meeting transcription is a challenging task. State-of-the-art end-to-end speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (SA-ASR) architectures lack a multichannel noise and reverberation reduction front-end, which limits their performance. In this paper, we introduce a joint beamforming and SA-ASR approach for real meeting transcription. We first describe a data alignment and augmentation method to pretrain a neural beamformer on real meeting data. We then compare fixed, hybrid, and fully neural beamformers as front-ends to the SA-ASR model. Finally, we jointly optimize the fully neural beamformer and the SA-ASR model. Experiments on the real AMI corpus show that,while state-of-the-art multi-frame cross-channel attention based channel fusion fails to improve ASR performance, fine-tuning SA-ASR on the fixed beamformer's output and jointly fine-tuning SA-ASR with the neural beamformer reduce the word error rate by 8% and 9% relative, respectively.
Improving Speaker Assignment in Speaker-Attributed ASR for Real Meeting Applications
Mar 11, 2024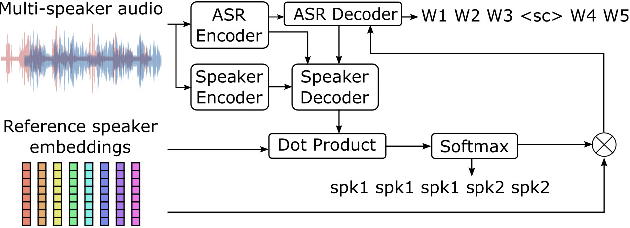
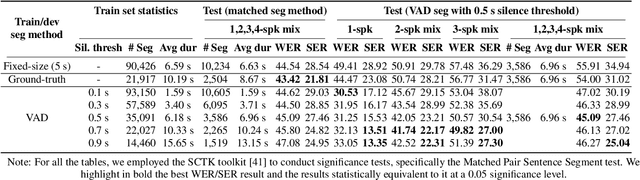
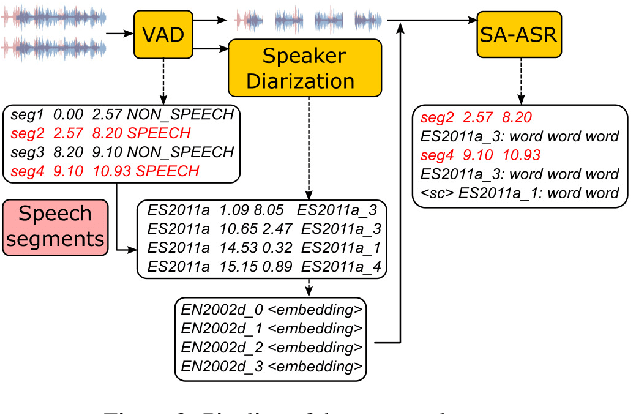
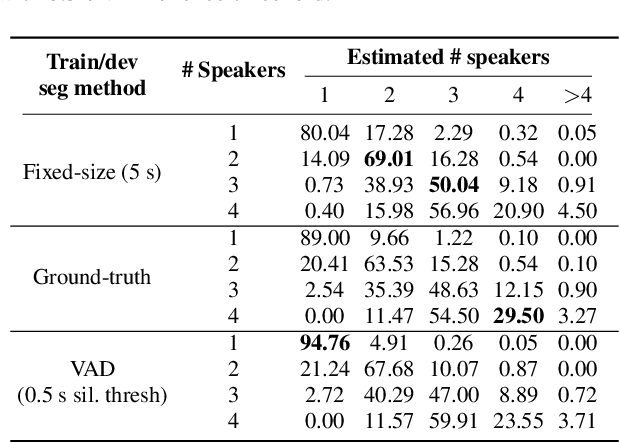
Abstract:Past studies on end-to-end meeting transcription have focused on model architecture and have mostly been evaluated on simulated meeting data. We present a novel study aiming to optimize the use of a Speaker-Attributed ASR (SA-ASR) system in real-life scenarios, such as the AMI meeting corpus, for improved speaker assignment of speech segments. First, we propose a pipeline tailored to real-life applications involving Voice Activity Detection (VAD), Speaker Diarization (SD), and SA-ASR. Second, we advocate using VAD output segments to fine-tune the SA-ASR model, considering that it is also applied to VAD segments during test, and show that this results in a relative reduction of Speaker Error Rate (SER) up to 28%. Finally, we explore strategies to enhance the extraction of the speaker embedding templates used as inputs by the SA-ASR system. We show that extracting them from SD output rather than annotated speaker segments results in a relative SER reduction up to 20%.
End-to-end Joint Rich and Normalized ASR with a limited amount of rich training data
Nov 29, 2023Abstract:Joint rich and normalized automatic speech recognition (ASR), that produces transcriptions both with and without punctuation and capitalization, remains a challenge. End-to-end (E2E) ASR models offer both convenience and the ability to perform such joint transcription of speech. Training such models requires paired speech and rich text data, which is not widely available. In this paper, we compare two different approaches to train a stateless Transducer-based E2E joint rich and normalized ASR system, ready for streaming applications, with a limited amount of rich labeled data. The first approach uses a language model to generate pseudo-rich transcriptions of normalized training data. The second approach uses a single decoder conditioned on the type of the output. The first approach leads to E2E rich ASR which perform better on out-of-domain data, with up to 9% relative reduction in errors. The second approach demonstrates the feasibility of an E2E joint rich and normalized ASR system using as low as 5% rich training data with moderate (2.42% absolute) increase in errors.
End-to-end Multichannel Speaker-Attributed ASR: Speaker Guided Decoder and Input Feature Analysis
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:We present an end-to-end multichannel speaker-attributed automatic speech recognition (MC-SA-ASR) system that combines a Conformer-based encoder with multi-frame crosschannel attention and a speaker-attributed Transformer-based decoder. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first model that efficiently integrates ASR and speaker identification modules in a multichannel setting. On simulated mixtures of LibriSpeech data, our system reduces the word error rate (WER) by up to 12% and 16% relative compared to previously proposed single-channel and multichannel approaches, respectively. Furthermore, we investigate the impact of different input features, including multichannel magnitude and phase information, on the ASR performance. Finally, our experiments on the AMI corpus confirm the effectiveness of our system for real-world multichannel meeting transcription.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge