Ilhoon Yoon
Enhancing Source-Free Domain Adaptive Object Detection with Low-confidence Pseudo Label Distillation
Jul 18, 2024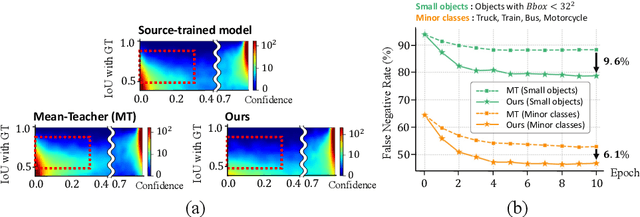
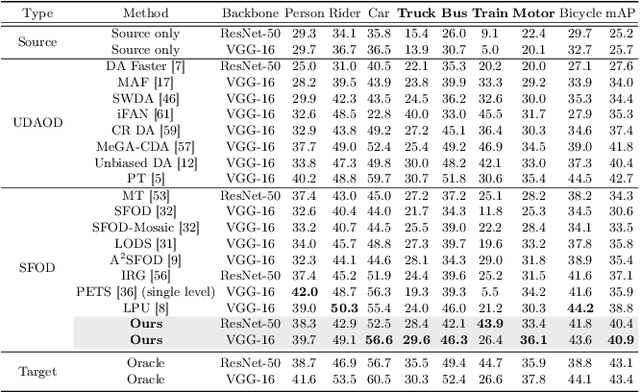
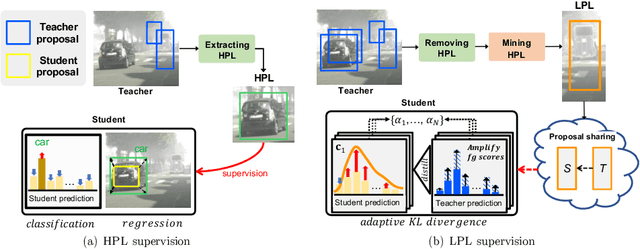
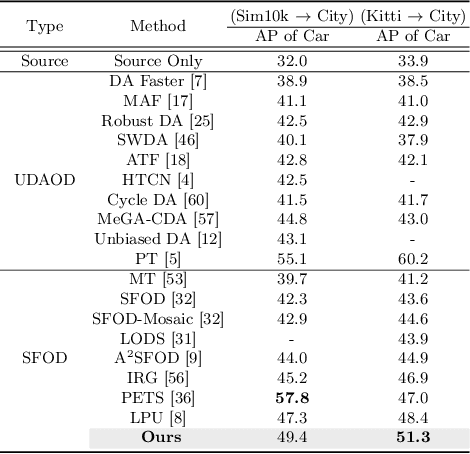
Abstract:Source-Free domain adaptive Object Detection (SFOD) is a promising strategy for deploying trained detectors to new, unlabeled domains without accessing source data, addressing significant concerns around data privacy and efficiency. Most SFOD methods leverage a Mean-Teacher (MT) self-training paradigm relying heavily on High-confidence Pseudo Labels (HPL). However, these HPL often overlook small instances that undergo significant appearance changes with domain shifts. Additionally, HPL ignore instances with low confidence due to the scarcity of training samples, resulting in biased adaptation toward familiar instances from the source domain. To address this limitation, we introduce the Low-confidence Pseudo Label Distillation (LPLD) loss within the Mean-Teacher based SFOD framework. This novel approach is designed to leverage the proposals from Region Proposal Network (RPN), which potentially encompasses hard-to-detect objects in unfamiliar domains. Initially, we extract HPL using a standard pseudo-labeling technique and mine a set of Low-confidence Pseudo Labels (LPL) from proposals generated by RPN, leaving those that do not overlap significantly with HPL. These LPL are further refined by leveraging class-relation information and reducing the effect of inherent noise for the LPLD loss calculation. Furthermore, we use feature distance to adaptively weight the LPLD loss to focus on LPL containing a larger foreground area. Our method outperforms previous SFOD methods on four cross-domain object detection benchmarks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LPLD loss leads to effective adaptation by reducing false negatives and facilitating the use of domain-invariant knowledge from the source model. Code is available at https://github.com/junia3/LPLD.
Layer-wise Auto-Weighting for Non-Stationary Test-Time Adaptation
Nov 26, 2023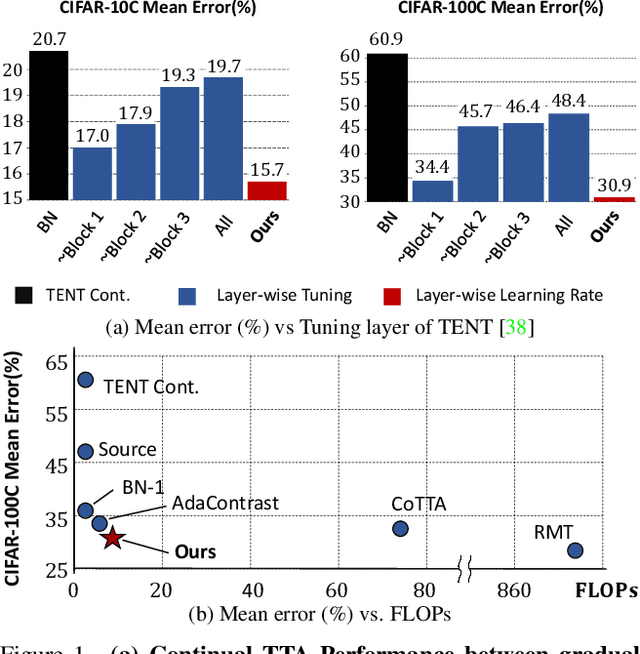
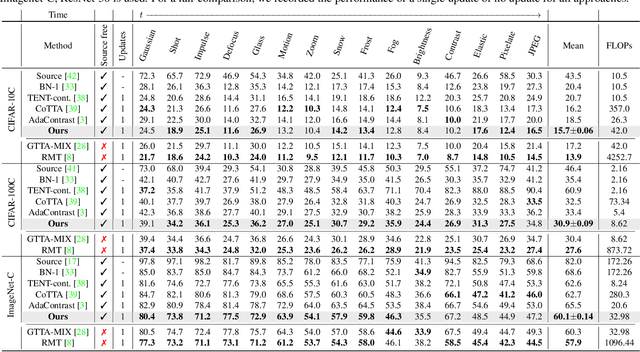
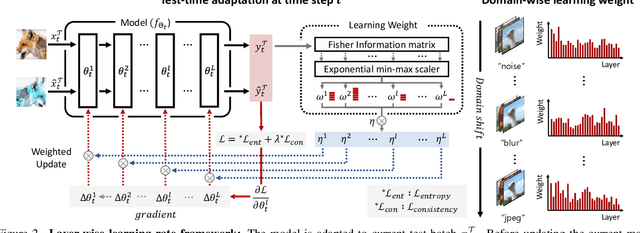
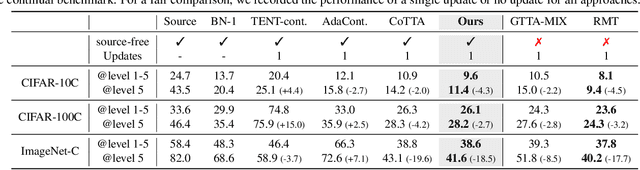
Abstract:Given the inevitability of domain shifts during inference in real-world applications, test-time adaptation (TTA) is essential for model adaptation after deployment. However, the real-world scenario of continuously changing target distributions presents challenges including catastrophic forgetting and error accumulation. Existing TTA methods for non-stationary domain shifts, while effective, incur excessive computational load, making them impractical for on-device settings. In this paper, we introduce a layer-wise auto-weighting algorithm for continual and gradual TTA that autonomously identifies layers for preservation or concentrated adaptation. By leveraging the Fisher Information Matrix (FIM), we first design the learning weight to selectively focus on layers associated with log-likelihood changes while preserving unrelated ones. Then, we further propose an exponential min-max scaler to make certain layers nearly frozen while mitigating outliers. This minimizes forgetting and error accumulation, leading to efficient adaptation to non-stationary target distribution. Experiments on CIFAR-10C, CIFAR-100C, and ImageNet-C show our method outperforms conventional continual and gradual TTA approaches while significantly reducing computational load, highlighting the importance of FIM-based learning weight in adapting to continuously or gradually shifting target domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge