Ibrahim Batuhan Akkaya
Enhancing Performance of Vision Transformers on Small Datasets through Local Inductive Bias Incorporation
May 15, 2023Abstract:Vision transformers (ViTs) achieve remarkable performance on large datasets, but tend to perform worse than convolutional neural networks (CNNs) when trained from scratch on smaller datasets, possibly due to a lack of local inductive bias in the architecture. Recent studies have therefore added locality to the architecture and demonstrated that it can help ViTs achieve performance comparable to CNNs in the small-size dataset regime. Existing methods, however, are architecture-specific or have higher computational and memory costs. Thus, we propose a module called Local InFormation Enhancer (LIFE) that extracts patch-level local information and incorporates it into the embeddings used in the self-attention block of ViTs. Our proposed module is memory and computation efficient, as well as flexible enough to process auxiliary tokens such as the classification and distillation tokens. Empirical results show that the addition of the LIFE module improves the performance of ViTs on small image classification datasets. We further demonstrate how the effect can be extended to downstream tasks, such as object detection and semantic segmentation. In addition, we introduce a new visualization method, Dense Attention Roll-Out, specifically designed for dense prediction tasks, allowing the generation of class-specific attention maps utilizing the attention maps of all tokens.
Self-training via Metric Learning for Source-Free Domain Adaptation of Semantic Segmentation
Dec 08, 2022Abstract:Unsupervised source-free domain adaptation methods aim to train a model to be used in the target domain utilizing the pretrained source-domain model and unlabeled target-domain data, where the source data may not be accessible due to intellectual property or privacy issues. These methods frequently utilize self-training with pseudo-labeling thresholded by prediction confidence. In a source-free scenario, only supervision comes from target data, and thresholding limits the contribution of the self-training. In this study, we utilize self-training with a mean-teacher approach. The student network is trained with all predictions of the teacher network. Instead of thresholding the predictions, the gradients calculated from the pseudo-labels are weighted based on the reliability of the teacher's predictions. We propose a novel method that uses proxy-based metric learning to estimate reliability. We train a metric network on the encoder features of the teacher network. Since the teacher is updated with the moving average, the encoder feature space is slowly changing. Therefore, the metric network can be updated in training time, which enables end-to-end training. We also propose a metric-based online ClassMix method to augment the input of the student network where the patches to be mixed are decided based on the metric reliability. We evaluated our method in synthetic-to-real and cross-city scenarios. The benchmarks show that our method significantly outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods.
Self-training Guided Adversarial Domain Adaptation For Thermal Imagery
Jun 14, 2021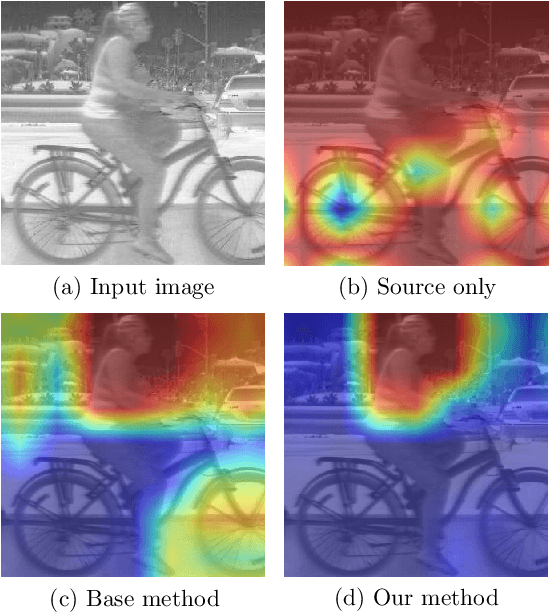
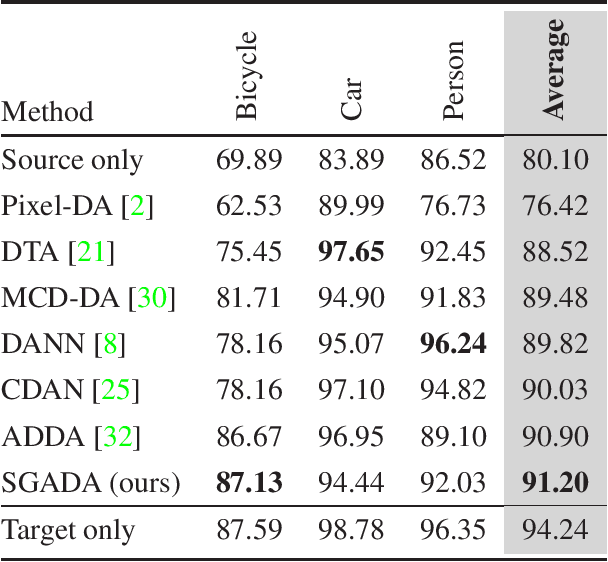
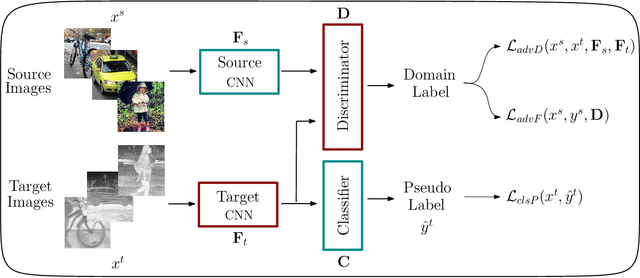
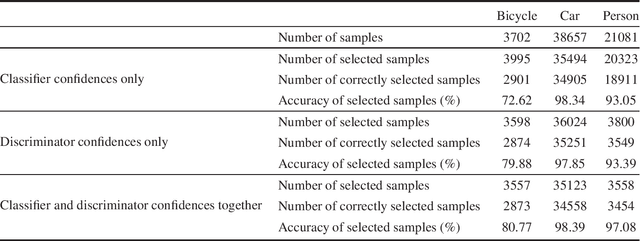
Abstract:Deep models trained on large-scale RGB image datasets have shown tremendous success. It is important to apply such deep models to real-world problems. However, these models suffer from a performance bottleneck under illumination changes. Thermal IR cameras are more robust against such changes, and thus can be very useful for the real-world problems. In order to investigate efficacy of combining feature-rich visible spectrum and thermal image modalities, we propose an unsupervised domain adaptation method which does not require RGB-to-thermal image pairs. We employ large-scale RGB dataset MS-COCO as source domain and thermal dataset FLIR ADAS as target domain to demonstrate results of our method. Although adversarial domain adaptation methods aim to align the distributions of source and target domains, simply aligning the distributions cannot guarantee perfect generalization to the target domain. To this end, we propose a self-training guided adversarial domain adaptation method to promote generalization capabilities of adversarial domain adaptation methods. To perform self-training, pseudo labels are assigned to the samples on the target thermal domain to learn more generalized representations for the target domain. Extensive experimental analyses show that our proposed method achieves better results than the state-of-the-art adversarial domain adaptation methods. The code and models are publicly available.
GAIT: Gradient Adjusted Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
Sep 02, 2020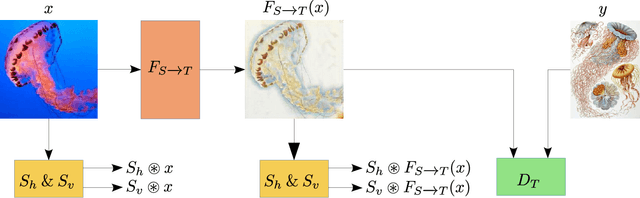
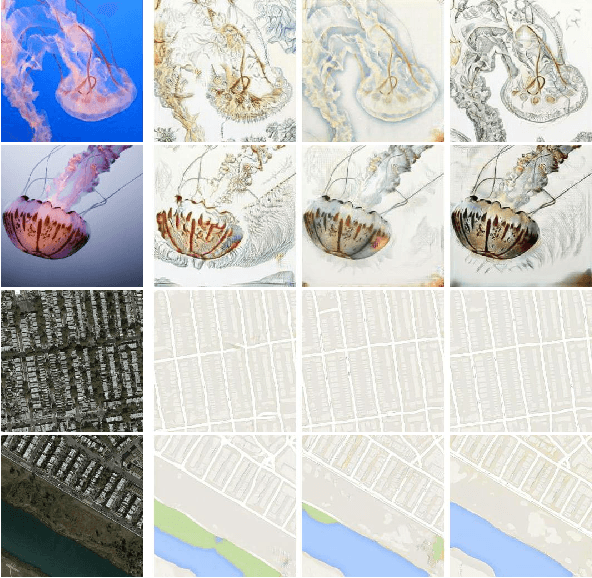
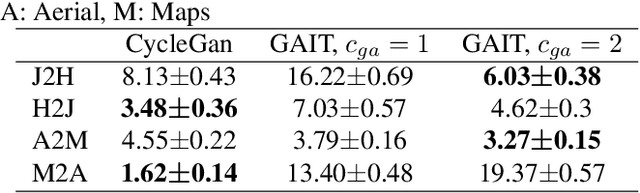
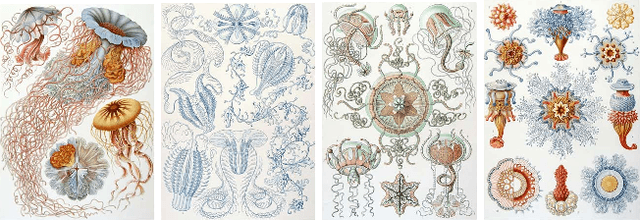

Abstract:Image-to-image translation (IIT) has made much progress recently with the development of adversarial learning. In most of the recent work, an adversarial loss is utilized to match the distributions of the translated and target image sets. However, this may create artifacts if two domains have different marginal distributions, for example, in uniform areas. In this work, we propose an unsupervised IIT method that preserves the uniform regions after the translation. The gradient adjustment loss, which is the L2 norm between the Sobel response of the target image and the adjusted Sobel response of the source images, is utilized. The proposed method is validated on the jellyfish-to-Haeckel dataset, which is prepared to demonstrate the mentioned problem, which contains images with different background distributions. We demonstrate that our method obtained a performance gain compared to the baseline method qualitatively and quantitatively, showing the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge