Hyeonmok Ko
MeKi: Memory-based Expert Knowledge Injection for Efficient LLM Scaling
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Scaling Large Language Models (LLMs) typically relies on increasing the number of parameters or test-time computations to boost performance. However, these strategies are impractical for edge device deployment due to limited RAM and NPU resources. Despite hardware constraints, deploying performant LLM on edge devices such as smartphone remains crucial for user experience. To address this, we propose MeKi (Memory-based Expert Knowledge Injection), a novel system that scales LLM capacity via storage space rather than FLOPs. MeKi equips each Transformer layer with token-level memory experts that injects pre-stored semantic knowledge into the generation process. To bridge the gap between training capacity and inference efficiency, we employ a re-parameterization strategy to fold parameter matrices used during training into a compact static lookup table. By offloading the knowledge to ROM, MeKi decouples model capacity from computational cost, introducing zero inference latency overhead. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MeKi significantly outperforms dense LLM baselines with identical inference speed, validating the effectiveness of memory-based scaling paradigm for on-device LLMs. Project homepage is at https://github.com/ningding-o/MeKi.
Data-driven Clustering and Merging of Adapters for On-device Large Language Models
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:On-device large language models commonly employ task-specific adapters (e.g., LoRAs) to deliver strong performance on downstream tasks. While storing all available adapters is impractical due to memory constraints, mobile devices typically have sufficient capacity to store a limited number of these parameters. This raises a critical challenge: how to select representative adapters that generalize well across multiple tasks - a problem that remains unexplored in existing literature. We propose a novel method D2C for adapter clustering that leverages minimal task-specific examples (e.g., 10 per task) and employs an iterative optimization process to refine cluster assignments. The adapters within each cluster are merged, creating multi-task adapters deployable on resource-constrained devices. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively boosts performance for considered storage budgets.
HydraOpt: Navigating the Efficiency-Performance Trade-off of Adapter Merging
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often leverage adapters, such as low-rank-based adapters, to achieve strong performance on downstream tasks. However, storing a separate adapter for each task significantly increases memory requirements, posing a challenge for resource-constrained environments such as mobile devices. Although model merging techniques can reduce storage costs, they typically result in substantial performance degradation. In this work, we introduce HydraOpt, a new model merging technique that capitalizes on the inherent similarities between the matrices of low-rank adapters. Unlike existing methods that produce a fixed trade-off between storage size and performance, HydraOpt allows us to navigate this spectrum of efficiency and performance. Our experiments show that HydraOpt significantly reduces storage size (48% reduction) compared to storing all adapters, while achieving competitive performance (0.2-1.8% drop). Furthermore, it outperforms existing merging techniques in terms of performance at the same or slightly worse storage efficiency.
BRIDO: Bringing Democratic Order to Abstractive Summarization
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Hallucination refers to the inaccurate, irrelevant, and inconsistent text generated from large language models (LLMs). While the LLMs have shown great promise in a variety of tasks, the issue of hallucination still remains a major challenge for many practical uses. In this paper, we tackle the issue of hallucination in abstract text summarization by mitigating exposure bias. Existing models targeted for exposure bias mitigation, namely BRIO, aim for better summarization quality in the ROUGE score. We propose a model that uses a similar exposure bias mitigation strategy but with a goal that is aligned with less hallucination. We conjecture that among a group of candidate outputs, ones with hallucinations will comprise the minority of the whole group. That is, candidates with less similarity with others will have a higher chance of containing hallucinated content. Our method uses this aspect and utilizes contrastive learning, incentivizing candidates with high inter-candidate ROUGE scores. We performed experiments on the XSum and CNN/DM summarization datasets, and our method showed 6.25% and 3.82% improvement, respectively, on the consistency G-Eval score over BRIO.
Hansel: Output Length Controlling Framework for Large Language Models
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Despite the great success of large language models (LLMs), efficiently controlling the length of the output sequence still remains a challenge. In this paper, we propose Hansel, an efficient framework for length control in LLMs without affecting its generation ability. Hansel utilizes periodically outputted hidden special tokens to keep track of the remaining target length of the output sequence. Together with techniques to avoid abrupt termination of the output, this seemingly simple method proved to be efficient and versatile, while not harming the coherency and fluency of the generated text. The framework can be applied to any pre-trained LLMs during the finetuning stage of the model, regardless of its original positional encoding method. We demonstrate this by finetuning four different LLMs with Hansel and show that the mean absolute error of the output sequence decreases significantly in every model and dataset compared to the prompt-based length control finetuning. Moreover, the framework showed a substantially improved ability to extrapolate to target lengths unseen during finetuning, such as long dialog responses or extremely short summaries. This indicates that the model learns the general means of length control, rather than learning to match output lengths to those seen during training.
KILDST: Effective Knowledge-Integrated Learning for Dialogue State Tracking using Gazetteer and Speaker Information
Jan 18, 2023
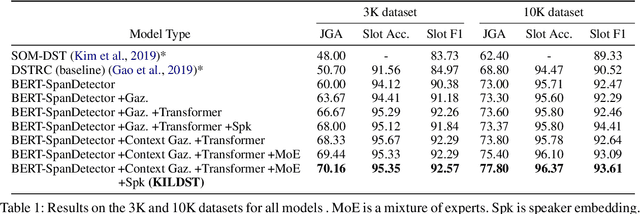
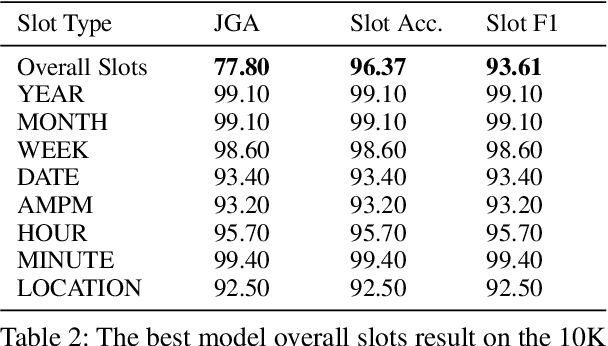
Abstract:Dialogue State Tracking (DST) is core research in dialogue systems and has received much attention. In addition, it is necessary to define a new problem that can deal with dialogue between users as a step toward the conversational AI that extracts and recommends information from the dialogue between users. So, we introduce a new task - DST from dialogue between users about scheduling an event (DST-USERS). The DST-USERS task is much more challenging since it requires the model to understand and track dialogue states in the dialogue between users and to understand who suggested the schedule and who agreed to the proposed schedule. To facilitate DST-USERS research, we develop dialogue datasets between users that plan a schedule. The annotated slot values which need to be extracted in the dialogue are date, time, and location. Previous approaches, such as Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) and traditional DST techniques, have not achieved good results in our extensive evaluations. By adopting the knowledge-integrated learning method, we achieve exceptional results. The proposed model architecture combines gazetteer features and speaker information efficiently. Our evaluations of the dialogue datasets between users that plan a schedule show that our model outperforms the baseline model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge