Huw Lloyd
A Generic Performance Model for Deep Learning in a Distributed Environment
May 19, 2023Abstract:Performance modelling of a deep learning application is essential to improve and quantify the efficiency of the model framework. However, existing performance models are mostly case-specific, with limited capability for the new deep learning frameworks/applications. In this paper, we propose a generic performance model of an application in a distributed environment with a generic expression of the application execution time that considers the influence of both intrinsic factors/operations (e.g. algorithmic parameters/internal operations) and extrinsic scaling factors (e.g. the number of processors, data chunks and batch size). We formulate it as a global optimization problem and solve it using regularization on a cost function and differential evolution algorithm to find the best-fit values of the constants in the generic expression to match the experimentally determined computation time. We have evaluated the proposed model on three deep learning frameworks (i.e., TensorFlow, MXnet, and Pytorch). The experimental results show that the proposed model can provide accurate performance predictions and interpretability. In addition, the proposed work can be applied to any distributed deep neural network without instrumenting the code and provides insight into the factors affecting performance and scalability.
Layer-Wise Partitioning and Merging for Efficient and Scalable Deep Learning
Jul 22, 2022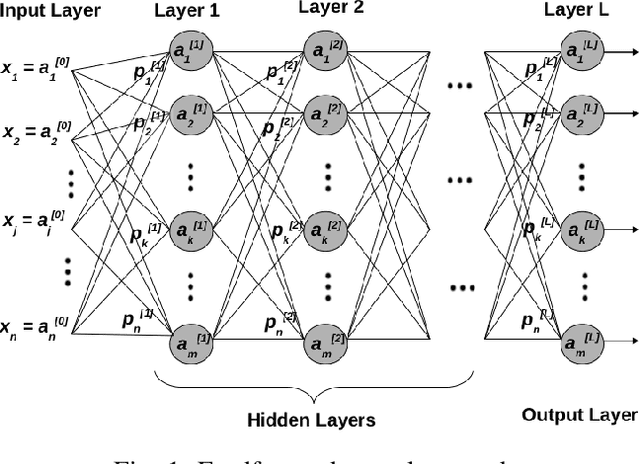
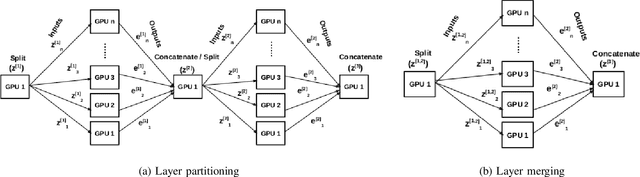

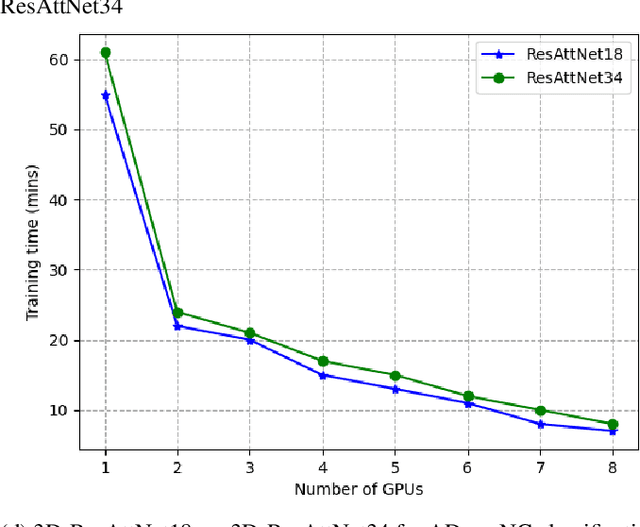
Abstract:Deep Neural Network (DNN) models are usually trained sequentially from one layer to another, which causes forward, backward and update locking's problems, leading to poor performance in terms of training time. The existing parallel strategies to mitigate these problems provide suboptimal runtime performance. In this work, we have proposed a novel layer-wise partitioning and merging, forward and backward pass parallel framework to provide better training performance. The novelty of the proposed work consists of 1) a layer-wise partition and merging model which can minimise communication overhead between devices without the memory cost of existing strategies during the training process; 2) a forward pass and backward pass parallelisation and optimisation to address the update locking problem and minimise the total training cost. The experimental evaluation on real use cases shows that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches in terms of training speed; and achieves almost linear speedup without compromising the accuracy performance of the non-parallel approach.
Solving Sudoku with Ant Colony Optimisation
May 09, 2018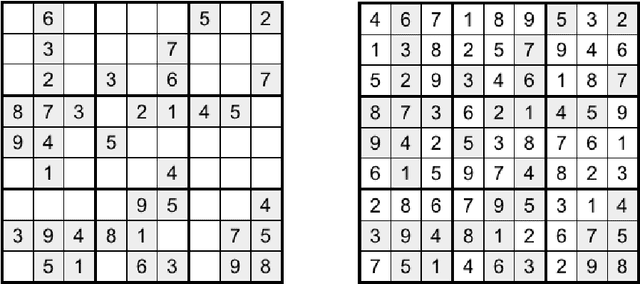
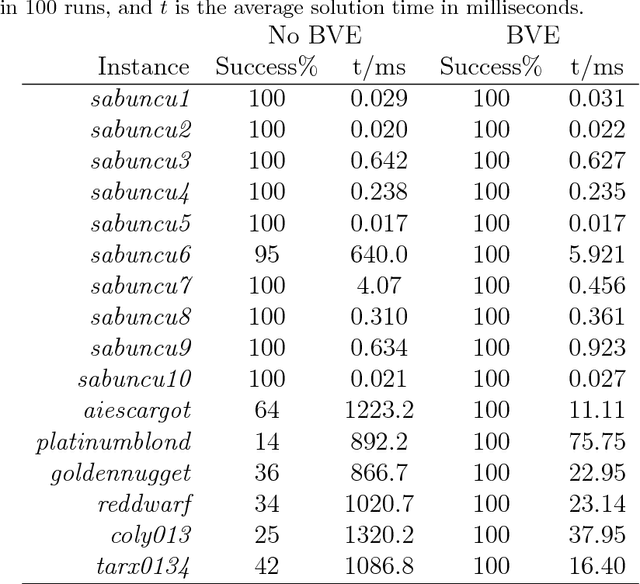
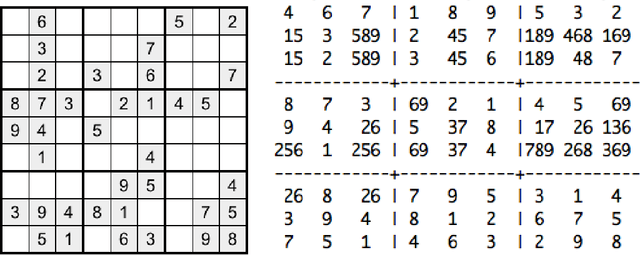
Abstract:In this paper we present a new Ant Colony Optimisation-based algorithm for Sudoku, which out-performs existing methods on large instances. Our method includes a novel anti-stagnation operator, which we call Best Value Evaporation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge