Hunor Csala
Autoregressive long-horizon prediction of plasma edge dynamics
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Accurate modeling of scrape-off layer (SOL) and divertor-edge dynamics is vital for designing plasma-facing components in fusion devices. High-fidelity edge fluid/neutral codes such as SOLPS-ITER capture SOL physics with high accuracy, but their computational cost limits broad parameter scans and long transient studies. We present transformer-based, autoregressive surrogates for efficient prediction of 2D, time-dependent plasma edge state fields. Trained on SOLPS-ITER spatiotemporal data, the surrogates forecast electron temperature, electron density, and radiated power over extended horizons. We evaluate model variants trained with increasing autoregressive horizons (1-100 steps) on short- and long-horizon prediction tasks. Longer-horizon training systematically improves rollout stability and mitigates error accumulation, enabling stable predictions over hundreds to thousands of steps and reproducing key dynamical features such as the motion of high-radiation regions. Measured end-to-end wall-clock times show the surrogate is orders of magnitude faster than SOLPS-ITER, enabling rapid parameter exploration. Prediction accuracy degrades when the surrogate enters physical regimes not represented in the training dataset, motivating future work on data enrichment and physics-informed constraints. Overall, this approach provides a fast, accurate surrogate for computationally intensive plasma edge simulations, supporting rapid scenario exploration, control-oriented studies, and progress toward real-time applications in fusion devices.
Physics-constrained coupled neural differential equations for one dimensional blood flow modeling
Nov 08, 2024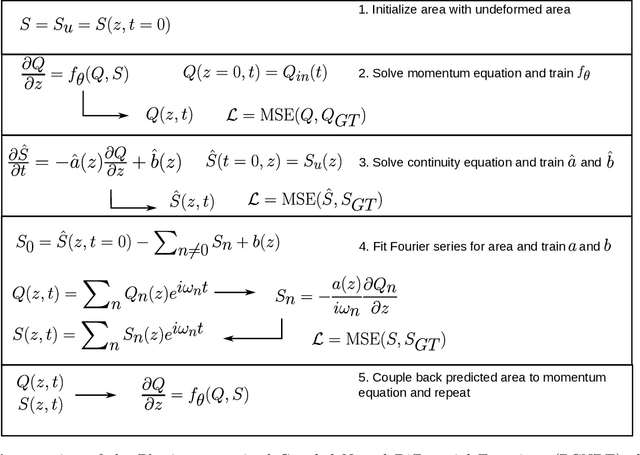
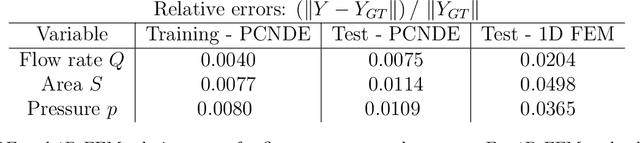
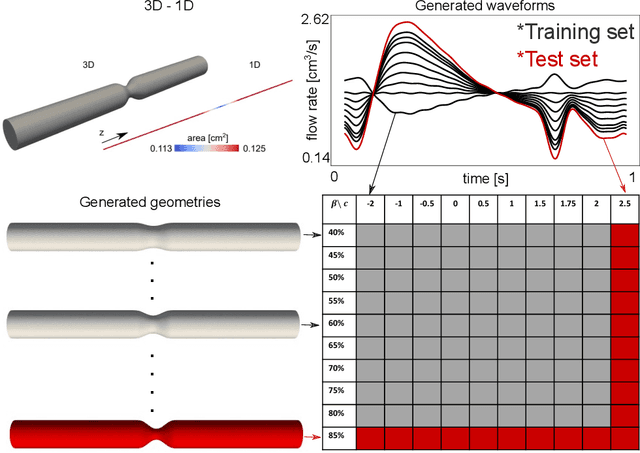
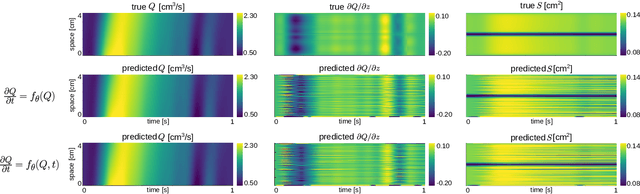
Abstract:Computational cardiovascular flow modeling plays a crucial role in understanding blood flow dynamics. While 3D models provide acute details, they are computationally expensive, especially with fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulations. 1D models offer a computationally efficient alternative, by simplifying the 3D Navier-Stokes equations through axisymmetric flow assumption and cross-sectional averaging. However, traditional 1D models based on finite element methods (FEM) often lack accuracy compared to 3D averaged solutions. This study introduces a novel physics-constrained machine learning technique that enhances the accuracy of 1D blood flow models while maintaining computational efficiency. Our approach, utilizing a physics-constrained coupled neural differential equation (PCNDE) framework, demonstrates superior performance compared to conventional FEM-based 1D models across a wide range of inlet boundary condition waveforms and stenosis blockage ratios. A key innovation lies in the spatial formulation of the momentum conservation equation, departing from the traditional temporal approach and capitalizing on the inherent temporal periodicity of blood flow. This spatial neural differential equation formulation switches space and time and overcomes issues related to coupling stability and smoothness, while simplifying boundary condition implementation. The model accurately captures flow rate, area, and pressure variations for unseen waveforms and geometries. We evaluate the model's robustness to input noise and explore the loss landscapes associated with the inclusion of different physics terms. This advanced 1D modeling technique offers promising potential for rapid cardiovascular simulations, achieving computational efficiency and accuracy. By combining the strengths of physics-based and data-driven modeling, this approach enables fast and accurate cardiovascular simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge