Hongtian Chen
MotionGS : Compact Gaussian Splatting SLAM by Motion Filter
May 18, 2024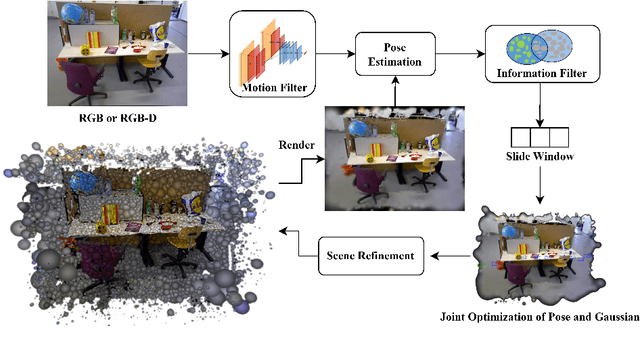
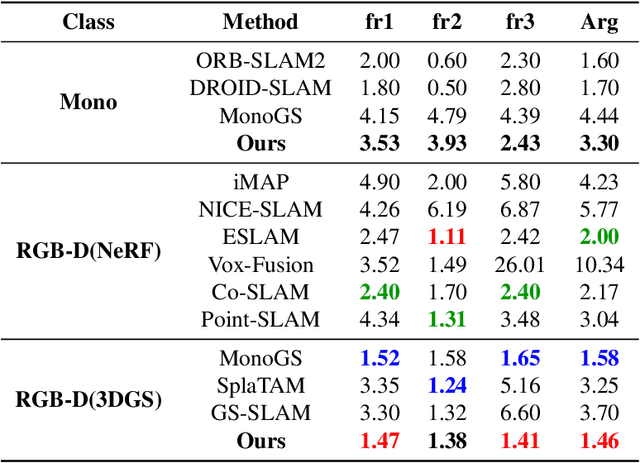
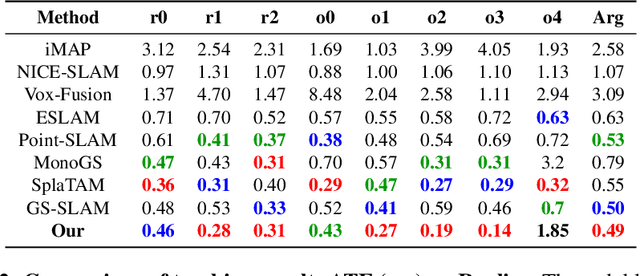
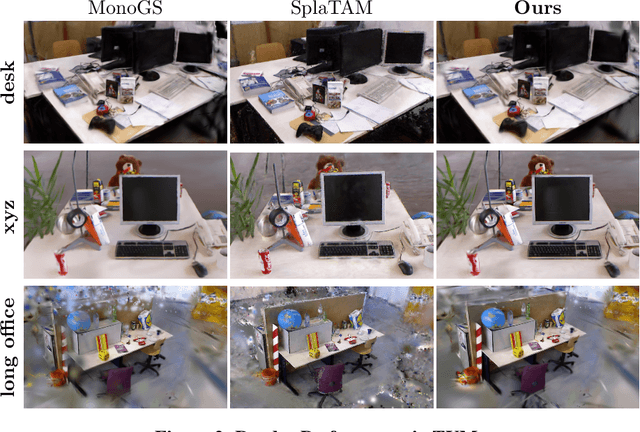
Abstract:With their high-fidelity scene representation capability, the attention of SLAM field is deeply attracted by the Neural Radiation Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Recently, there has been a Surge in NeRF-based SLAM, while 3DGS-based SLAM is sparse. A novel 3DGS-based SLAM approach with a fusion of deep visual feature, dual keyframe selection and 3DGS is presented in this paper. Compared with the existing methods, the proposed selectively tracking is achieved by feature extraction and motion filter on each frame. The joint optimization of pose and 3D Gaussian runs through the entire mapping process. Additionally, the coarse-to-fine pose estimation and compact Gaussian scene representation are implemented by dual keyfeature selection and novel loss functions. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm not only outperforms the existing methods in tracking and mapping, but also has less memory usage.
Generation of Uncorrelated Residual Variables for Chemical Process Fault Diagnosis via Transfer Learning-based Input-Output Decoupled Network
Apr 29, 2024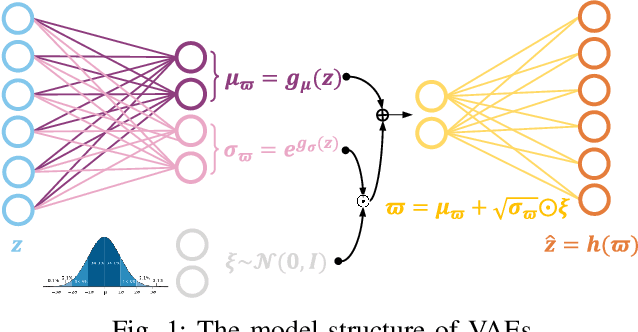
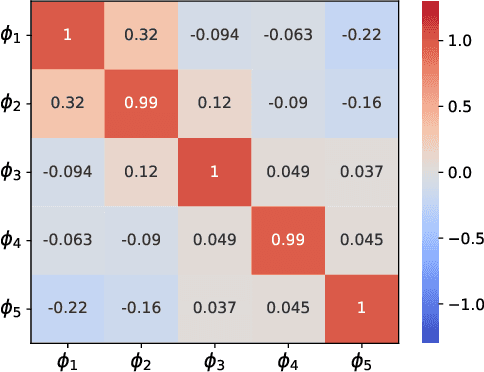
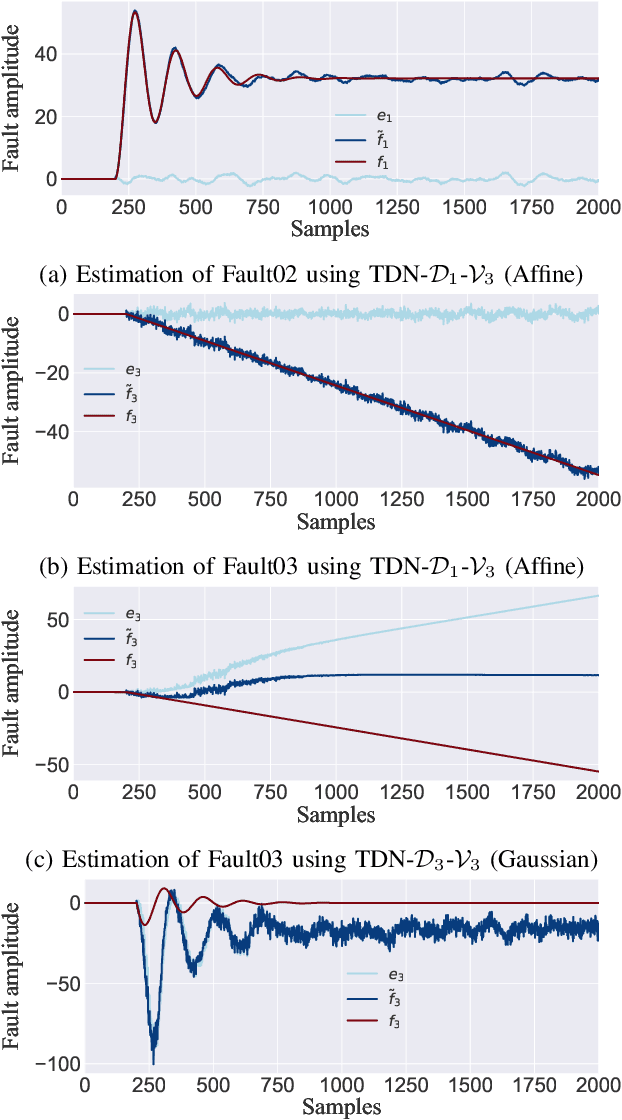
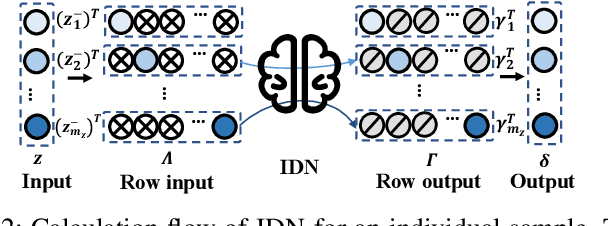
Abstract:Structural decoupling has played an essential role in model-based fault isolation and estimation in past decades, which facilitates accurate fault localization and reconstruction thanks to the diagonal transfer matrix design. However, traditional methods exhibit limited effectiveness in modeling high-dimensional nonlinearity and big data, and the decoupling idea has not been well-valued in data-driven frameworks. Known for big data and complex feature extraction capabilities, deep learning has recently been used to develop residual generation models. Nevertheless, it lacks decoupling-related diagnostic designs. To this end, this paper proposes a transfer learning-based input-output decoupled network (TDN) for diagnostic purposes, which consists of an input-output decoupled network (IDN) and a pre-trained variational autocoder (VAE). In IDN, uncorrelated residual variables are generated by diagonalization and parallel computing operations. During the transfer learning phase, knowledge of normal status is provided according to VAE's loss and maximum mean discrepancy loss to guide the training of IDN. After training, IDN learns the mapping from faulty to normal, thereby serving as the fault detection index and the estimated fault signal simultaneously. At last, the effectiveness of the developed TDN is verified by a numerical example and a chemical simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge