Hoang M. Ngo
Q-ShiftDP: A Differentially Private Parameter-Shift Rule for Quantum Machine Learning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Quantum Machine Learning (QML) promises significant computational advantages, but preserving training data privacy remains challenging. Classical approaches like differentially private stochastic gradient descent (DP-SGD) add noise to gradients but fail to exploit the unique properties of quantum gradient estimation. In this work, we introduce the Differentially Private Parameter-Shift Rule (Q-ShiftDP), the first privacy mechanism tailored to QML. By leveraging the inherent boundedness and stochasticity of quantum gradients computed via the parameter-shift rule, Q-ShiftDP enables tighter sensitivity analysis and reduces noise requirements. We combine carefully calibrated Gaussian noise with intrinsic quantum noise to provide formal privacy and utility guarantees, and show that harnessing quantum noise further improves the privacy-utility trade-off. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that Q-ShiftDP consistently outperforms classical DP methods in QML.
QUPID: A Partitioned Quantum Neural Network for Anomaly Detection in Smart Grid
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Smart grid infrastructures have revolutionized energy distribution, but their day-to-day operations require robust anomaly detection methods to counter risks associated with cyber-physical threats and system faults potentially caused by natural disasters, equipment malfunctions, and cyber attacks. Conventional machine learning (ML) models are effective in several domains, yet they struggle to represent the complexities observed in smart grid systems. Furthermore, traditional ML models are highly susceptible to adversarial manipulations, making them increasingly unreliable for real-world deployment. Quantum ML (QML) provides a unique advantage, utilizing quantum-enhanced feature representations to model the intricacies of the high-dimensional nature of smart grid systems while demonstrating greater resilience to adversarial manipulation. In this work, we propose QUPID, a partitioned quantum neural network (PQNN) that outperforms traditional state-of-the-art ML models in anomaly detection. We extend our model to R-QUPID that even maintains its performance when including differential privacy (DP) for enhanced robustness. Moreover, our partitioning framework addresses a significant scalability problem in QML by efficiently distributing computational workloads, making quantum-enhanced anomaly detection practical in large-scale smart grid environments. Our experimental results across various scenarios exemplifies the efficacy of QUPID and R-QUPID to significantly improve anomaly detection capabilities and robustness compared to traditional ML approaches.
Leveraging Soft Prompts for Privacy Attacks in Federated Prompt Tuning
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Membership inference attack (MIA) poses a significant privacy threat in federated learning (FL) as it allows adversaries to determine whether a client's private dataset contains a specific data sample. While defenses against membership inference attacks in standard FL have been well studied, the recent shift toward federated fine-tuning has introduced new, largely unexplored attack surfaces. To highlight this vulnerability in the emerging FL paradigm, we demonstrate that federated prompt-tuning, which adapts pre-trained models with small input prefixes to improve efficiency, also exposes a new vector for privacy attacks. We propose PromptMIA, a membership inference attack tailored to federated prompt-tuning, in which a malicious server can insert adversarially crafted prompts and monitors their updates during collaborative training to accurately determine whether a target data point is in a client's private dataset. We formalize this threat as a security game and empirically show that PromptMIA consistently attains high advantage in this game across diverse benchmark datasets. Our theoretical analysis further establishes a lower bound on the attack's advantage which explains and supports the consistently high advantage observed in our empirical results. We also investigate the effectiveness of standard membership inference defenses originally developed for gradient or output based attacks and analyze their interaction with the distinct threat landscape posed by PromptMIA. The results highlight non-trivial challenges for current defenses and offer insights into their limitations, underscoring the need for defense strategies that are specifically tailored to prompt-tuning in federated settings.
CHARME: A chain-based reinforcement learning approach for the minor embedding problem
Jun 11, 2024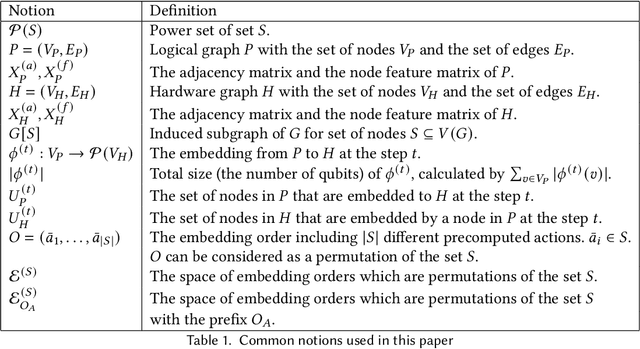
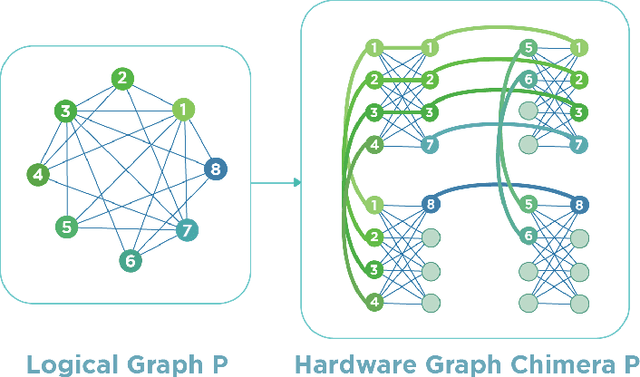
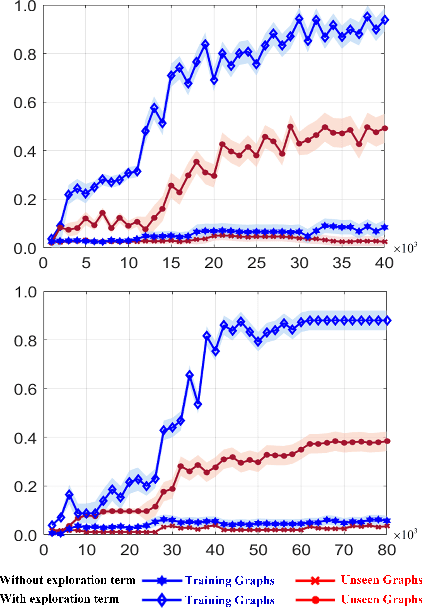
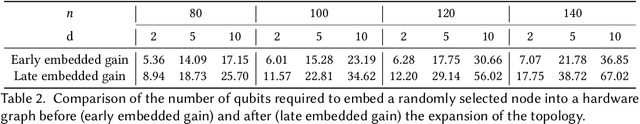
Abstract:Quantum Annealing (QA) holds great potential for solving combinatorial optimization problems efficiently. However, the effectiveness of QA algorithms heavily relies on the embedding of problem instances, represented as logical graphs, into the quantum unit processing (QPU) whose topology is in form of a limited connectivity graph, known as the minor embedding Problem. Existing methods for the minor embedding problem suffer from scalability issues when confronted with larger problem sizes. In this paper, we propose a novel approach utilizing Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques to address the minor embedding problem, named CHARME. CHARME includes three key components: a Graph Neural Network (GNN) architecture for policy modeling, a state transition algorithm ensuring solution validity, and an order exploration strategy for effective training. Through comprehensive experiments on synthetic and real-world instances, we demonstrate that the efficiency of our proposed order exploration strategy as well as our proposed RL framework, CHARME. In details, CHARME yields superior solutions compared to fast embedding methods such as Minorminer and ATOM. Moreover, our method surpasses the OCT-based approach, known for its slower runtime but high-quality solutions, in several cases. In addition, our proposed exploration enhances the efficiency of the training of the CHARME framework by providing better solutions compared to the greedy strategy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge