Hisashi Uematsu
DOA Estimation by DNN-based Denoising and Dereverberation from Sound Intensity Vector
Oct 10, 2019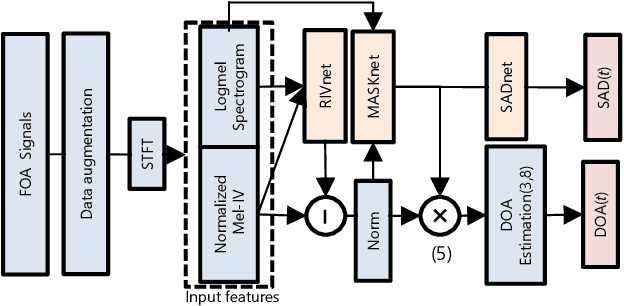
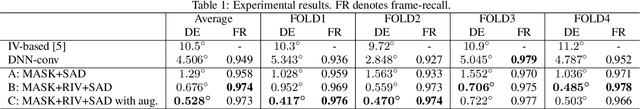
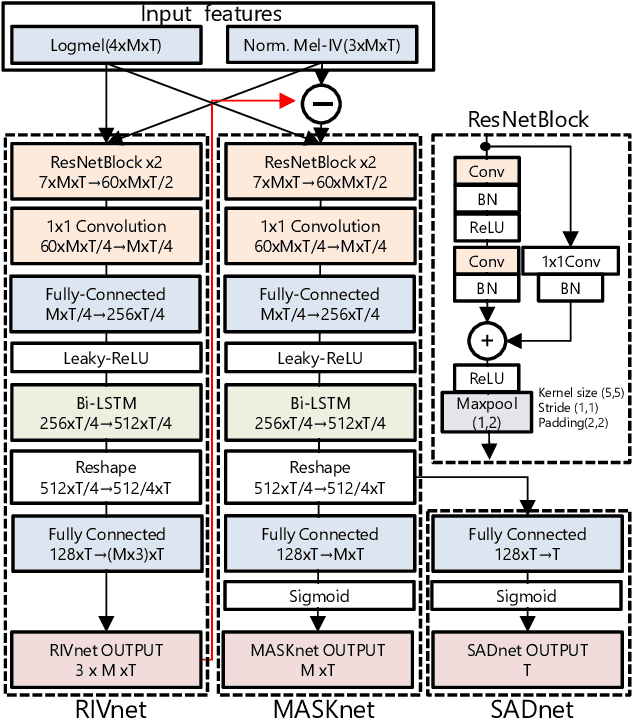
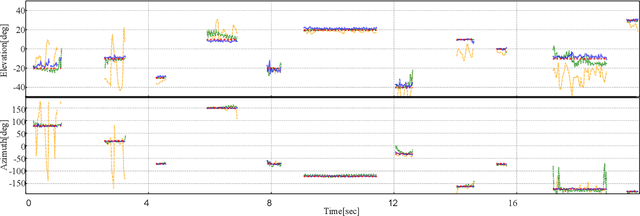
Abstract:We propose a direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method that combines sound-intensity vector (IV)-based DOA estimation and DNN-based denoising and dereverberation. Since the accuracy of IV-based DOA estimation degrades due to environmental noise and reverberation, two DNNs are used to remove such effects from the observed IVs. DOA is then estimated from the refined IVs based on the physics of wave propagation. Experiments on an open dataset showed that the average DOA error of the proposed method was 0.528 degrees, and it outperformed a conventional IV-based and DNN-based DOA estimation method.
ToyADMOS: A Dataset of Miniature-Machine Operating Sounds for Anomalous Sound Detection
Aug 09, 2019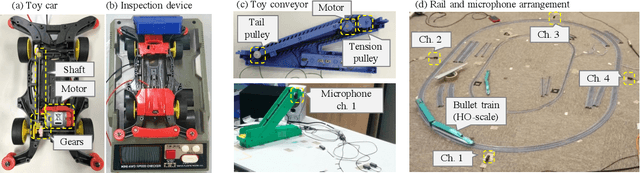
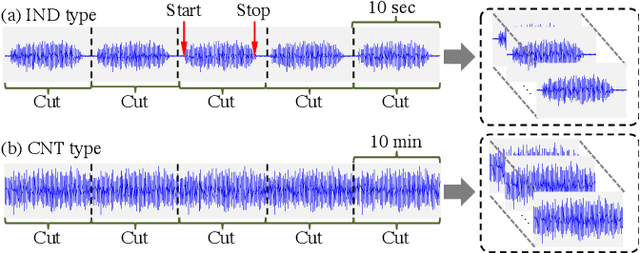
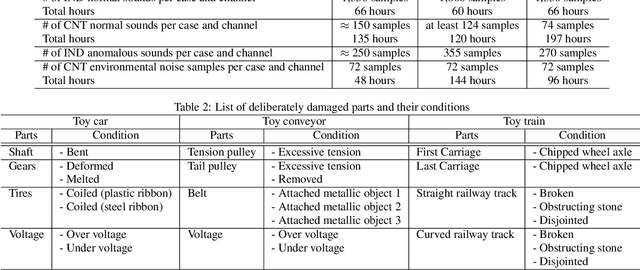
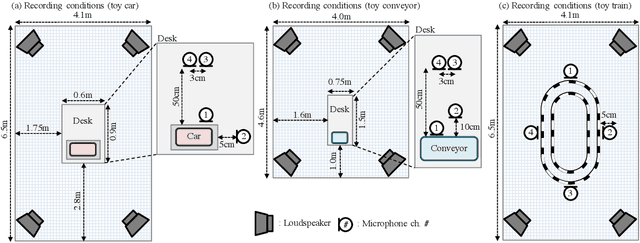
Abstract:This paper introduces a new dataset called "ToyADMOS" designed for anomaly detection in machine operating sounds (ADMOS). To the best our knowledge, no large-scale datasets are available for ADMOS, although large-scale datasets have contributed to recent advancements in acoustic signal processing. This is because anomalous sound data are difficult to collect. To build a large-scale dataset for ADMOS, we collected anomalous operating sounds of miniature machines (toys) by deliberately damaging them. The released dataset consists of three sub-datasets for machine-condition inspection, fault diagnosis of machines with geometrically fixed tasks, and fault diagnosis of machines with moving tasks. Each sub-dataset includes over 180 hours of normal machine-operating sounds and over 4,000 samples of anomalous sounds collected with four microphones at a 48-kHz sampling rate. The dataset is freely available for download at https://github.com/YumaKoizumi/ToyADMOS-dataset
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge