HeuiSeok Lim
Domain Adaptive Training BERT for Response Selection
Aug 13, 2019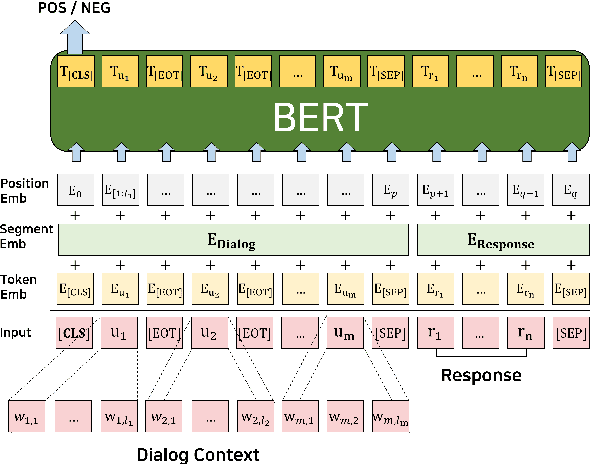
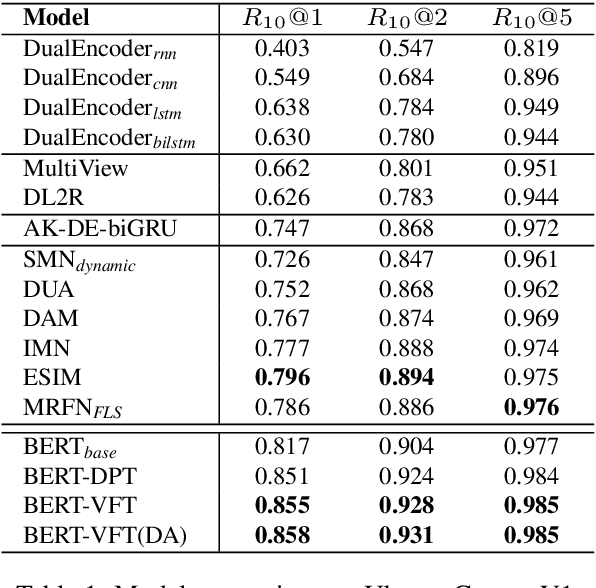
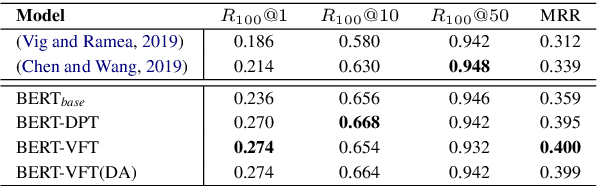
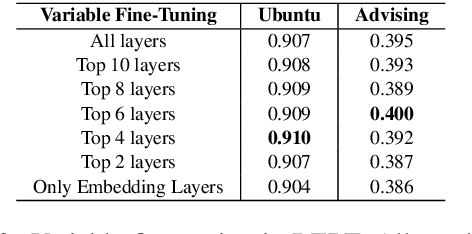
Abstract:We focus on multi-turn response selection in a retrieval-based dialog system. In this paper, we utilize the powerful pre-trained language model Bi-directional Encoder Representations from Transformer (BERT) for a multi-turn dialog system and propose a highly effective post-training method on domain-specific corpus. Although BERT is easily adopted to various NLP tasks and outperforms previous baselines of each task, it still has limitations if a task corpus is too focused on a certain domain. Post-training on domain-specific corpus (e.g., Ubuntu Corpus) helps the model to train contextualized representations and words that do not appear in general corpus (e.g.,English Wikipedia). Experiment results show that our approach achieves new state-of-the-art on two response selection benchmark datasets (i.e.,Ubuntu Corpus V1, Advising Corpus) performance improvement by 5.9% and 6% on Recall@1.
Character-Level Feature Extraction with Densely Connected Networks
Jul 26, 2018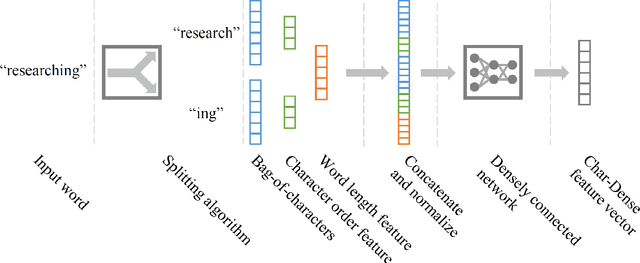

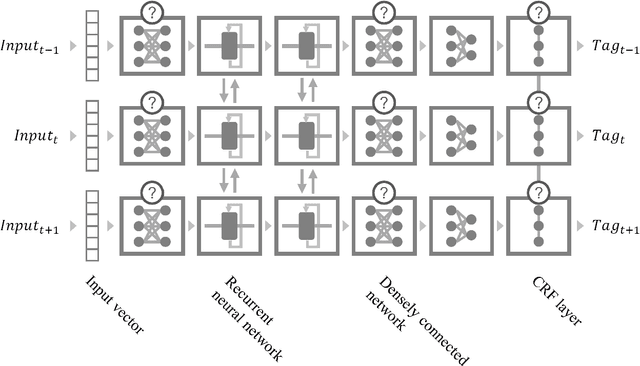
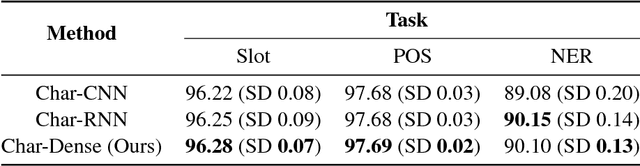
Abstract:Generating character-level features is an important step for achieving good results in various natural language processing tasks. To alleviate the need for human labor in generating hand-crafted features, methods that utilize neural architectures such as Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) or Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) to automatically extract such features have been proposed and have shown great results. However, CNN generates position-independent features, and RNN is slow since it needs to process the characters sequentially. In this paper, we propose a novel method of using a densely connected network to automatically extract character-level features. The proposed method does not require any language or task specific assumptions, and shows robustness and effectiveness while being faster than CNN- or RNN-based methods. Evaluating this method on three sequence labeling tasks - slot tagging, Part-of-Speech (POS) tagging, and Named-Entity Recognition (NER) - we obtain state-of-the-art performance with a 96.62 F1-score and 97.73% accuracy on slot tagging and POS tagging, respectively, and comparable performance to the state-of-the-art 91.13 F1-score on NER.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge